Related Research Articles
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia.

Leptin, also known as obese protein, is a protein hormone predominantly made by adipocytes. Its primary role is likely to regulate long-term energy balance.

Adipose tissue is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body.

5' AMP-activated protein kinase or AMPK or 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase is an enzyme that plays a role in cellular energy homeostasis, largely to activate glucose and fatty acid uptake and oxidation when cellular energy is low. It belongs to a highly conserved eukaryotic protein family and its orthologues are SNF1 in yeast, and SnRK1 in plants. It consists of three proteins (subunits) that together make a functional enzyme, conserved from yeast to humans. It is expressed in a number of tissues, including the liver, brain, and skeletal muscle. In response to binding AMP and ADP, the net effect of AMPK activation is stimulation of hepatic fatty acid oxidation, ketogenesis, stimulation of skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake, inhibition of cholesterol synthesis, lipogenesis, and triglyceride synthesis, inhibition of adipocyte lipogenesis, inhibition of adipocyte lipolysis, and modulation of insulin secretion by pancreatic β-cells.
Adiponectin is a protein hormone and adipokine, which is involved in regulating glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown. In humans, it is encoded by the ADIPOQ gene and is produced primarily in adipose tissue, but also in muscle and even in the brain.

Mitochondrial myopathies are types of myopathies associated with mitochondrial disease. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the chemical used to provide energy for the cell, cannot be produced sufficiently by oxidative phosphorylation when the mitochondrion is either damaged or missing necessary enzymes or transport proteins. With ATP production deficient in mitochondria, there is an over-reliance on anaerobic glycolysis which leads to lactic acidosis either at rest or exercise-induced.

The Cahill cycle, also known as the alanine cycle or glucose-alanine cycle, is the series of reactions in which amino groups and carbons from muscle are transported to the liver. It is quite similar to the Cori cycle in the cycling of nutrients between skeletal muscle and the liver. When muscles degrade amino acids for energy needs, the resulting nitrogen is transaminated to pyruvate to form alanine. This is performed by the enzyme alanine transaminase (ALT), which converts L-glutamate and pyruvate into α-ketoglutarate and L-alanine. The resulting L-alanine is shuttled to the liver where the nitrogen enters the urea cycle and the pyruvate is used to make glucose.
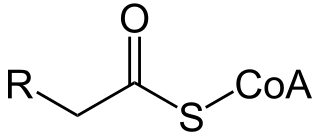
Acyl-CoA is a group of CoA-based coenzymes that metabolize carboxylic acids. Fatty acyl-CoA's are susceptible to beta oxidation, forming, ultimately, acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, eventually forming several equivalents of ATP. In this way, fats are converted to ATP, the common biochemical energy carrier.

Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) also known as carnitine acyltransferase I, CPTI, CAT1, CoA:carnitine acyl transferase (CCAT), or palmitoylCoA transferase I, is a mitochondrial enzyme responsible for the formation of acyl carnitines by catalyzing the transfer of the acyl group of a long-chain fatty acyl-CoA from coenzyme A to l-carnitine. The product is often palmitoylcarnitine, but other fatty acids may also be substrates. It is part of a family of enzymes called carnitine acyltransferases. This "preparation" allows for subsequent movement of the acyl carnitine from the cytosol into the intermembrane space of mitochondria.

Stearoyl-CoA desaturase is an endoplasmic reticulum enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the formation of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), specifically oleate and palmitoleate from stearoyl-CoA and palmitoyl-CoA. Oleate and palmitoleate are major components of membrane phospholipids, cholesterol esters and alkyl-diacylglycerol. In humans, the enzyme is present in two isoforms, encoded respectively by the SCD1 and SCD5 genes.

Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UCP3 gene. The gene is located in chromosome (11q13.4) with an exon count of 7 and is expressed on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Uncoupling proteins transfer anions from the inner mitochondrial membrane to the outer mitochondrial membrane, thereby separating oxidative phosphorylation from synthesis of ATP, and dissipating energy stored in the mitochondrial membrane potential as heat. Uncoupling proteins also reduce generation of reactive oxygen species.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 4, mitochondrial (PDK4) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDK4 gene. It codes for an isozyme of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.

Brain mitochondrial carrier protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A14 gene.

3-Aminoisobutyric acid is a product formed by the catabolism of thymine.

Metabolic myopathies are myopathies that result from defects in biochemical metabolism that primarily affect muscle. They are generally genetic defects that interfere with the ability to create energy, causing a low ATP reservoir within the muscle cell.
Pyruvate cycling commonly refers to an intracellular loop of spatial movements and chemical transformations involving pyruvate. Spatial movements occur between mitochondria and cytosol and chemical transformations create various Krebs cycle intermediates. In all variants, pyruvate is imported into the mitochondrion for processing through part of the Krebs cycle. In addition to pyruvate, alpha-ketoglutarate may also be imported. At various points, the intermediate product is exported to the cytosol for additional transformations and then re-imported. Three specific pyruvate cycles are generally considered, each named for the principal molecule exported from the mitochondrion: malate, citrate, and isocitrate. Other variants may exist, such as dissipative or "futile" pyruvate cycles.
Lipid droplets, also referred to as lipid bodies, oil bodies or adiposomes, are lipid-rich cellular organelles that regulate the storage and hydrolysis of neutral lipids and are found largely in the adipose tissue. They also serve as a reservoir for cholesterol and acyl-glycerols for membrane formation and maintenance. Lipid droplets are found in all eukaryotic organisms and store a large portion of lipids in mammalian adipocytes. Initially, these lipid droplets were considered to merely serve as fat depots, but since the discovery in the 1990s of proteins in the lipid droplet coat that regulate lipid droplet dynamics and lipid metabolism, lipid droplets are seen as highly dynamic organelles that play a very important role in the regulation of intracellular lipid storage and lipid metabolism. The role of lipid droplets outside of lipid and cholesterol storage has recently begun to be elucidated and includes a close association to inflammatory responses through the synthesis and metabolism of eicosanoids and to metabolic disorders such as obesity, cancer, and atherosclerosis. In non-adipocytes, lipid droplets are known to play a role in protection from lipotoxicity by storage of fatty acids in the form of neutral triacylglycerol, which consists of three fatty acids bound to glycerol. Alternatively, fatty acids can be converted to lipid intermediates like diacylglycerol (DAG), ceramides and fatty acyl-CoAs. These lipid intermediates can impair insulin signaling, which is referred to as lipid-induced insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Lipid droplets also serve as platforms for protein binding and degradation. Finally, lipid droplets are known to be exploited by pathogens such as the hepatitis C virus, the dengue virus and Chlamydia trachomatis among others.

Lipotoxicity is a metabolic syndrome that results from the accumulation of lipid intermediates in non-adipose tissue, leading to cellular dysfunction and death. The tissues normally affected include the kidneys, liver, heart and skeletal muscle. Lipotoxicity is believed to have a role in heart failure, obesity, and diabetes, and is estimated to affect approximately 25% of the adult American population.
Sleep is important in regulating metabolism. Mammalian sleep can be sub-divided into two distinct phases - REM and non-REM (NREM) sleep. In humans and cats, NREM sleep has four stages, where the third and fourth stages are considered slow-wave sleep (SWS). SWS is considered deep sleep, when metabolism is least active.
Hepatokines are proteins produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) that are secreted into the circulation and function as hormones across the organism. Research is mostly focused on hepatokines that play a role in the regulation of metabolic diseases such as diabetes and fatty liver and include: Adropin, ANGPTL4, Fetuin-A, Fetuin-B, FGF-21, Hepassocin, LECT2, RBP4,Selenoprotein P, Sex hormone-binding globulin.
References
- 1 2 "Our alumni: Deborah M. Muoio". publichealth.buffalo.edu. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- 1 2 "Deborah Marie Muoio | Scholars@Duke profile". scholars.duke.edu. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ↑ "Deborah M Muoio Phd | Diabetes Research Centers". diabetescenters.org. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ↑ Muoio, Deborah M; Dohn, G Lynis; Fiedorek, Frederick T; Tapscott, Edward B; Coleman, Rosalind A (1 August 1997). "Leptin Directly Alters Lipid Partitioning in Skeletal Muscle". Diabetes. 46 (8): 1360–1363. doi: 10.2337/diab.46.8.1360 . ISSN 0012-1797. PMID 9231663.
- ↑ Muoio, Deborah M.; Seefeld, Kimberly; Witters, Lee A.; Coleman, Rosalind A. (15 March 1999). "AMP-activated kinase reciprocally regulates triacylglycerol synthesis and fatty acid oxidation in liver and muscle: evidence that sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase is a novel target". Biochemical Journal. 338 (3): 783–791. doi:10.1042/bj3380783. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1220117 . PMID 10051453.
- ↑ Muoio, Deborah M. (2014). "Metabolic Inflexibility: When Mitochondrial Indecision Leads to Metabolic Gridlock". Cell. 159 (6): 1253–1262. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.034. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 4765362 . PMID 25480291.
- ↑ Faherty, Sheena. "How Overeating May Contribute to a Metabolic "Traffic Jam"". Scientific American Blog Network. Retrieved 10 October 2023.