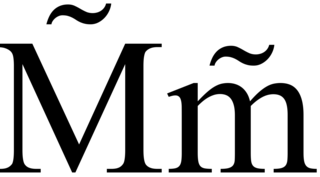The biological family Canidae is a lineage of carnivorans that includes domestic dogs, wolves, coyotes, foxes, jackals, dingoes, and many other extant and extinct dog-like mammals. A member of this family is called a canid.

Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, not all of which are closely related. Most of the 60 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—2 in North America, 9 in Central and South America, and 3 in Australia.
A genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, as well as viruses, in biology. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.
Binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name. The first part of the name – the generic name – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, while the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – identifies the species within the genus. For example, humans belong to the genus Homo and within this genus to the species Homo sapiens. Tyrannosaurus rex is probably the most widely known binomial. The formal introduction of this system of naming species is credited to Carl Linnaeus, effectively beginning with his work Species Plantarum in 1753. But Gaspard Bauhin, in as early as 1622, had introduced in his book Pinax theatri botanici many names of genera that were later adopted by Linnaeus.

Anseriformes is an order of birds that comprise about 180 living species in three families: Anhimidae, Anseranatidae, and Anatidae, the largest family, which includes over 170 species of waterfowl, among them the ducks, geese, and swans. Most modern species in the order are highly adapted for an aquatic existence at the water surface. With the exception of screamers, all have phalli, a trait that has been lost in the Neoaves. Due to their aquatic nature, most species are web-footed.

In zoological nomenclature, a type species is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups called a type genus.

Pasco is a region in central Peru. Its capital is Cerro de Pasco.

Chanchamayo or Chanchamayu is a province in northern Junín Region, in central Peru.

Tube-dwelling anemones or ceriantharians look very similar to sea anemones but belong to an entirely different subclass of anthozoans. They are solitary, living buried in soft sediments. Tube anemones live inside and can withdraw into tubes, which are composed of a fibrous material made from secreted mucus and threads of nematocyst-like organelles known as ptychocysts. Ceriantharians were formerly classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia along with the black corals but have since been moved to their own subclass, Ceriantharia.
P̃ is a Latin P with a diacritical tilde. It is or was used as a grapheme in some languages of Vanuatu, such as North Efate, South Efate and Namakura, to represent a. It is also used in the Yanesha language.

The Communal Reservation Yanesha or Yanesha Community Reserve is a communal reserve in the Palcazu District of Peru. It covers an area of 34,744 km2 (13,415 sq mi) in the Palcazu River basin. The reserve was creating by law on April 28, 1988 to protect both wild fauna and indigenous peoples. The Yanesha' people live in the reserve.
Amuesha, Amoesha, and Yanesha' may refer to two things:

The Oxapampa Province is the largest of three provinces that make up the Pasco Region in Peru. The capital of the Oxapampa province is the city of Oxapampa.
Yanesha', also called Amuesha or Amoesha is a language spoken by the Amuesha people of Peru in central and eastern Pasco Region.

The Yanesha' or Amuesha people are an ethnic group of the Peruvian Amazon rainforest. Presently, the most recent census count puts their population at over 7,000 distributed among 48 communities located in Puerto Inca Province (Huánuco), Chanchamayo Province (Junín) and Oxapampa Province (Pasco). They are a relatively small group, making up barely 2.91% of indigenous inhabitants located in the Peruvian Amazon. Their communities are situated in altitudes ranging from 200 to 1600 meters above sea level and can also be found along the shores of various rivers including the Pichis, Palcazu, Pachitea, Huancabamba, Cacazú, Chorobamba, and the Yurinaqui Rivers.
Under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme, there are 125 biosphere reserves recognized as part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in Latin America and the Caribbean. These are distributed across 21 countries in the region.

Play'd: A Hip Hop Story is 2002 television drama film starring Rashaan Nall, Faizon Love, Toni Braxton and Merlin Santana. The film was directed by Oz Scott
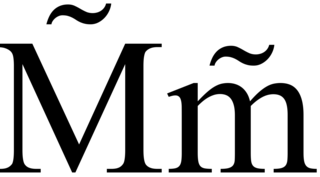
M̃ is a Latin M with a diacritical tilde. It is or was used as a grapheme in some languages of Vanuatu, such as North Efate, South Efate and Namakura, to represent a. It is also used in the Yanesha and Lithuanian languages. It is also used in the transliteration of the Lycian script. In Italian, the abbreviation Ssm̃o or SSm̃o may be used for Santissimo, "most holy".