Dental bodies corporate (DBC) are corporations entitled to practice dentistry in the UK using the structure of a limited company. [1]
Dental bodies corporate (DBC) are corporations entitled to practice dentistry in the UK using the structure of a limited company. [1]
DBCs have practised dentistry in the UK for over a hundred years. [2] The Dentists Act 1878 established a register for qualified dentists in order to combat an increase in unregistered practice by dental companies. [3] In its 1946 report, The Teviot Committee [4] recommended the inclusion of a comprehensive dental service as part of a national health service. As a result, The General Dental Council (GDC) was established to make dentistry a self-governing profession. [5]
The 1955 Dentists Bill [6] prohibited DBCs from dentistry unless they were open and practising on 21 July 1955, as well as registered with the GDC. When the Bill received Royal assent on 15 March 1956, [7] there were 74 DBCs listed. [8] This number fell to 27 in 2002 [9] when DBCs became the subject of a government consultation. [10]
Although DBCs were originally limited in number by the Dentists Act 1984, [11] their status changed following a 2005 Amendment to the Act [12] which removed key restrictions. Although a DBC does not require GDC approval to set itself up, it must satisfy the requirements of Sections 40 and 43 of the Dentists Act 1984. [13] The GDC was also required to maintain a list of DBCs.
DBCs have since expanded to the extent that in 2015, they held over 40% of NHS contracts in England worth over £1.3 billion. [14]

Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist.
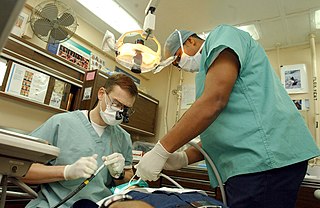
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.

The British Dental Association (BDA) is a registered trade union for dentists in the United Kingdom.
A number of professional degrees in dentistry are offered by dental schools in various countries around the world.
An oral medicine or stomatology doctor/dentist has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities including oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders and facial pain, taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region.
The General Dental Council (GDC) is an organisation which regulates dental professionals in the United Kingdom. It keeps an up-to-date register of all qualified dentists and other dental care professionals such as: dental hygienists, dental therapists, dental nurses, dental technicians and clinical dental technicians. It was established in 1956 to set and maintain standards in UK dentistry, with the aims of protecting the general public from unqualified dental professionals.

The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow is an institute of physicians and surgeons in Glasgow, Scotland.
The Dental Professionals Association, previously known as the Dental Practitioners Association and the General Dental Practitioners Association, is a trade union for professionals involved in primary dental care in the United Kingdom. It is based in Harley Street in London.

The Dental Council of India was incorporated under The Dentists Act, 1948 to regulate dental education and the profession throughout India. It is financed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and through the local state dental councils.
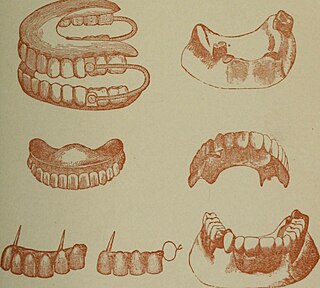
A denturist in the United States and Canada, clinical dental technologist in the United Kingdom and Ireland, dental prosthetist in Australia, or a clinical dental technician in New Zealand is a member of the oral health care team and role as primary oral health care provider who provides an oral health examination, planning treatment, takes impressions of the surrounding oral tissues, constructs and delivers removable oral prosthesis treatment directly to the patient.

Ian Anthony Hamilton-Smith, 3rd Baron Colwyn, commonly known as Anthony Hamilton-Smith, is a British peer and former politician. He was one of 90 hereditary peers elected to remain in the House of Lords after the House of Lords Act 1999, sitting as a Conservative. He retired from the House of Lords on 21 July 2022.
The Faculty of Dental Surgery of the Royal College of Surgeons of England is an independent UK professional body committed to enabling dental specialists to provide patients with the highest possible standards of practice and care. The faculty is an integral part of the Royal College of Surgeons of England and is located at the College's headquarters in Lincoln's Inn Fields in London.

Dentistry throughout the world is practiced differently, and training in dentistry varies as well.

Hal Alan Huggins was an American alternative dentistry advocate and campaigner against the use of dental amalgam fillings and other dental therapies that he believed to be unsafe. Huggins began to promote his ideas in the 1970s and played a major role in generating controversy over the use of amalgam. Huggins's license to practice dentistry was revoked in 1996 after a panel found him guilty of gross negligence. Since then, he continued to publish on the topic of mercury and human health and believed that dental amalgam and other dental practices were responsible for a range of serious diseases. Many of Huggins' health claims have been criticized as pseudoscientific and quackery.

The Dentists Act 1984 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom regulating dentistry. In particular the function of the General Dental Council, dental bodies corporate etc.
Computers and software have been used in dental medicine since the 1960s. Since then, computers and information technology have spread progressively in dental practice. According to one study, in 2000, 85.1% of all dentists in the United States were using computers.

Lilian Lindsay, CBE, FSA was a dentist, dental historian, librarian and author who became the first qualified female dentist in Britain and the first female president of the British Dental Association.
Dentistry provided by the National Health Service in the United Kingdom is supposed to ensure that dental treatment is available to the whole population. Most dentistry is provided by private practitioners, most of whom also provide, on a commercial basis, services which the NHS does not provide, largely cosmetic. Most adult patients have to pay some NHS charges, although these are often significantly cheaper than the cost of private dentistry. The majority of people choose NHS dental care rather than private care: as of 2005, the national average proportion of people opting for private care was 23%. NHS dentistry is not always available and is not managed in the way that other NHS services are managed.
Dentists in the UK may undertake work under the National Health Service or privately. They may opt for either of these alternatives, or both. A small number of dentists are employed by the NHS but the vast majority are in private practice. UK dentists are regulated by the General Dental Council and the Care Quality Commission.

Stanley Gelbier is emeritus professor of dental public health and honorary professor of the history of dentistry at King's College London. He is a past president of the History of Medicine Society, and the former curator of the British Dental Association's museum.