Related Research Articles

Energy in Thailand refers to the production, storage, import and export, and use of energy in the Southeast Asian nation of Thailand. Thailand's energy resources are modest and being depleted. The nation imports most of its oil and significant quantities of natural gas and coal. Its energy consumption has grown at an average rate of 3.3% from 2007 to 2017. Energy from renewables has only recently begun to contribute significant energy.

The Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT) is a state enterprise, managed by the Ministry of Energy, responsible for electric power generation and transmission as well as bulk electric energy sales in Thailand. EGAT, established on 1 May 1969, is the largest power producer in Thailand, owning and operating power plants at 45 sites across the country with a total installed capacity of 15,548 MW.

India is world's 3rd largest consumer of electricity and world's 3rd largest renewable energy producer with 40% of energy capacity installed in the year 2022 coming from renewable sources. Ernst & Young's (EY) 2021 Renewable Energy Country Attractiveness Index (RECAI) ranked India 3rd behind USA and China. In FY2023-24, India is planning to issue 50 GW tenders for wind, solar and hybrid projects. India has committed for a goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030. In line with this commitment, India's installed renewable energy capacity has been experiencing a steady upward trend. From 94.4 GW in 2021, the capacity has gone up to 119.1 GW in 2023 as of Q4.
Energy in Ethiopia is energy and electricity production, consumption, transport, exportation, and importation in Ethiopia.
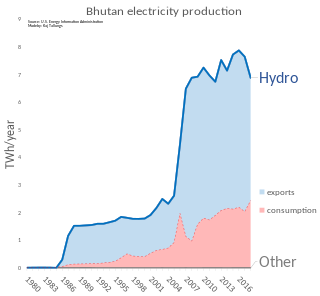
Energy in Bhutan has been a primary focus of development in the kingdom under its Five-Year Plans. In cooperation with India, Bhutan has undertaken several hydroelectric projects whose output is traded between the countries. Though Bhutan's many hydroelectric plants provide energy far in excess of its needs in the summer, dry winters and increased fuel demand makes the kingdom a marginal net importer of energy from India.

The Ministry of Energy of the Kingdom of Thailand is a cabinet ministry in the Government of Thailand. Its budget for fiscal year 2019 is 2,319 million baht.

Solar power in Thailand is targeted to reach 6,000 MW by 2036. In 2013 installed photovoltaic capacity nearly doubled and reached 704 MW by the end of the year. At the end of 2015, with a total capacity of 2,500-2,800 MW, Thailand has more solar power capacity than all the rest of Southeast Asia combined.

Renewable energy in Nepal is a sector that is rapidly developing in Nepal. While Nepal mainly relies on burning biomass for its energy needs, solar and wind power is being seen as an important supplement to solve its energy crisis. The most common form of renewable energy in Nepal is hydroelectricity.

Most of Kenya's electricity is generated by renewable energy sources. Access to reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy is one of the 17 main goals of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Development of the energy sector is also critical to help Kenya achieve the goals in Kenya Vision 2030 to become a newly industrializing, middle-income country. With an installed power capacity of 2,819 MW, Kenya currently generates 826 MW hydroelectric power, 828 geothermal power, 749 MW thermal power, 331 MW wind power, and the rest from solar and biomass sources. Kenya is the largest geothermal energy producer in Africa and also has the largest wind farm on the continent. In March 2011, Kenya opened Africa's first carbon exchange to promote investments in renewable energy projects. Kenya has also been selected as a pilot country under the Scaling-Up Renewable Energy Programmes in Low Income Countries Programme to increase deployment of renewable energy solutions in low-income countries. Despite significant strides in renewable energy development, about a quarter of the Kenyan population still lacks access to electricity, necessitating policy changes to diversify the energy generation mix and promote public-private partnerships for financing renewable energy projects.

Renewable energy in Afghanistan includes biomass, geothermal, hydropower, solar, and wind power. Afghanistan is a landlocked country surrounded by five other countries. With a population of less than 35 million people, it is one of the lowest energy consuming countries in relation to a global standing. It holds a spot as one of the countries with a smaller ecological footprint. Hydropower is currently the main source of renewable energy due to Afghanistan's geographical location. Its large mountainous environment facilitates the siting of hydroelectric dams and other facets of hydro energy.
Renewable energy in Bhutan is the use of renewable energy for electricity generation in Bhutan. The renewable energy sources include hydropower.

Wind power in Thailand amounted to an installed production capacity of 224.5 MW as of the end of 2014. Installed capacity was 112 MW at the end of 2012, with 111 MW added in 2013, and a minor amount added in 2014. This ranked Thailand 46th in the world by installed capacity as of 2015.
Thailand has set targets and policies for the development of its energy sector for 2035, with priority being given to indigenous renewable energy resources, including hydropower.

Renewable energy in Costa Rica supplied about 98.1% of the electrical energy output for the entire nation in 2016. Fossil fuel energy consumption in Costa Rica was 49.48 as of 2014, with demand for oil increasing in recent years. In 2014, 99% of its electrical energy was derived from renewable energy sources, about 80% of which from hydroelectric power. For the first 75 days of 2015, 100% of its electrical energy was derived from renewable energy sources and in mid 2016 that feat was accomplished for 110 consecutive days despite suboptimal weather conditions.
Myanmar had a total primary energy supply (TPES) of 16.57 Mtoe in 2013. Electricity consumption was 8.71 TWh. 65% of the primary energy supply consists of biomass energy, used almost exclusively (97%) in the residential sector. Myanmar’s energy consumption per capita is one of the lowest in Southeast Asia due to the low electrification rate and a widespread poverty. An estimated 65% of the population is not connected to the national grid. Energy consumption is growing rapidly, however, with an average annual growth rate of 3.3% from 2000 to 2007.
There is enormous potential for renewable energy in Kazakhstan, particularly from wind and small hydropower plants. The Republic of Kazakhstan has the potential to generate 10 times as much power as it currently needs from wind energy alone. But renewable energy accounts for just 0.6 percent of all power installations. Of that, 95 percent comes from small hydropower projects. The main barriers to investment in renewable energy are relatively high financing costs and an absence of uniform feed-in tariffs for electricity from renewable sources. The amount and duration of renewable energy feed-in tariffs are separately evaluated for each project, based on feasibility studies and project-specific generation costs. Power from wind, solar, biomass and water up to 35 MW, plus geothermal sources, are eligible for the tariff and transmission companies are required to purchase the energy of renewable energy producers. An amendment that introduces and clarifies technology-specific tariffs is now being prepared. It is expected to be adopted by Parliament by the end of 2014. In addition, the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business indicator shows the country to be relatively investor-friendly, ranking it in 10th position for investor protection.
Vietnam utilizes four main sources of renewable energy: hydroelectricity, wind power, solar power and biomass. By the end of 2018, hydropower was the largest source of renewable energy, contributing about 40% to the total national electricity capacity. In 2020, wind and solar had a combined share of 10% of the country's electrical generation, already meeting the government's 2030 goal, suggesting future displacement of growth of coal capacity. By the end of 2020, the total installed capacity of solar and wind power had reached over 17 GW. Over 25% of total power capacity is from variable renewable energy sources. The commercial biomass electricity generation is currently slow and limited to valorizing bagasse only, but the stream of forest products, agricultural and municipal waste is increasing. The government is studying a renewable portfolio standard that could promote this energy source.
Renewable energy sources are important for Azerbaijan. However, except for hydropower, few renewable energy sources are utilized. One of the alternative sources of energy is wind energy. It is also more profitable due to the cost, ecological cleanness, and its renewable properties compared to other alternative energy sources.

In Ukraine, the share of renewables within the total energy mix is less than 5%. In 2020 10% of electricity was generated from renewables; made up of 5% hydro, 4% wind, and 1% solar. Biomass provides renewable heat.

By the end of 2016 Austria already fulfilled their EU Renewables Directive goal for the year 2020. By 2016 renewable energies accounted to 33.5% of the final energy consumption in all sectors. The renewable energy sector is also accountable for hosting 41,591 jobs and creating a revenue of 7,219 million euros in 2016.
References
- 1 2 "Annual Report 2015" (Latest available annual report). Department of Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency (DEDE). Retrieved 25 April 2019.
- ↑ "BUDGET IN BRIEF FISCAL YEAR 2019 (Revised Edition)". Bureau of the Budget. p. 87. Retrieved 2019-04-24.
- ↑ "Vision / Mission / Duties". Department of Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency (DEDE). Retrieved 2019-04-25.
- ↑ "แผน EEP2015 และ แผน AEDP2015". Department of Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency (DEDE) (in Thai). 2016-07-28. Retrieved 2019-04-26.
- ↑ Chaichaloempreecha, Achiraya (October 2017). "Assessment of renewable energy and energy efficiency plans in Thailand's industrial sector". Energy Procedia. 138: 841–846. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.10.105 .
- ↑ Achawangkul, Yaowateera (2017-03-02). "Thailand's Alternative Energy Development Plan" (PDF). UNESCAP . Retrieved 25 April 2019.
- ↑ "Energy Ministry aims to boost alternative sources of power". The Nation. 2018-09-12. Retrieved 2019-04-26.
- ↑ Munkkunk, Pongphat. "Unlocking Energy Efficiency Potential: Thailand's Policies Perspective" (PDF). Singapore International Energy Week (SIEW) 2017. Department of Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency (DEDE). Retrieved 2019-04-26.
- ↑ "แผนอนุรักษ์พลังงาน พ.ศ.2558–2579 (Energy Efficiency Plan; EEP 2015)" (PDF). Energy Conservation Promotion Fund Thailand (in Thai). Department of Alternative Energy Development and Efficiency (DEDE). Retrieved 2019-04-26.