Related Research Articles

The United States secretary of defense (SecDef) is the head of the United States Department of Defense, the executive department of the U.S. Armed Forces, and is a high ranking member of the federal cabinet. The secretary of defense's position of command and authority over the military is second only to that of the president of the United States, who is the commander-in-chief. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a defense minister in many other countries. The secretary of defense is appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate, and is by custom a member of the Cabinet and by law a member of the National Security Council.

The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is a standards organization that oversees global IP address allocation, autonomous system number allocation, root zone management in the Domain Name System (DNS), media types, and other Internet Protocol-related symbols and Internet numbers.

The Mitre Corporation is an American not-for-profit organization with dual headquarters in Bedford, Massachusetts, and McLean, Virginia. It manages federally funded research and development centers (FFRDCs) supporting various U.S. government agencies in the aviation, defense, healthcare, homeland security, and cybersecurity fields, among others.
A national identification number, national identity number, or national insurance number is used by the governments of many countries as a means of tracking their citizens, permanent residents, and temporary residents for the purposes of work, taxation, government benefits, health care, and other governmentally-related functions.
The Employer Identification Number (EIN), also known as the Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or the Federal Tax Identification Number, is a unique nine-digit number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to business entities operating in the United States for the purposes of identification. When the number is used for identification rather than employment tax reporting, it is usually referred to as a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). When used for the purposes of reporting employment taxes, it is usually referred to as an EIN. These numbers are used for tax administration and must not be used for any other purpose. For example, an EIN should not be used in tax lien auction or sales, lotteries, or for any other purposes not related to tax administration.
Personal data, also known as personal information or personally identifiable information (PII), is any information related to an identifiable person.
Identity documents in the United States are typically the regional state-issued driver's license or identity card, while also the Social Security card and the United States Passport Card may serve as national identification. The United States passport itself also may serve as identification. There is, however, no official "national identity card" in the United States, in the sense that there is no federal agency with nationwide jurisdiction that directly issues an identity document to all US citizens for mandatory regular use.
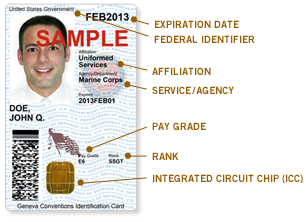
The Common Access Card, also commonly referred to as the CAC is a smart card about the size of a credit card. It is the standard identification for Active Duty United States Defense personnel, to include the Selected Reserve and National Guard, United States Department of Defense (DoD) civilian employees, United States Coast Guard (USCG) civilian employees and eligible DoD and USCG contractor personnel. It is also the principal card used to enable physical access to buildings and controlled spaces, and it provides access to defense computer networks and systems. It also serves as an identification card under the Geneva Conventions. In combination with a personal identification number, a CAC satisfies the requirement for two-factor authentication: something the user knows combined with something the user has. The CAC also satisfies the requirements for digital signature and data encryption technologies: authentication, integrity and non-repudiation.
The Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) is the principal set of rules regarding Government procurement in the United States, and is codified at Chapter 1 of Title 48 of the Code of Federal Regulations, 48 CFR 1. It covers many of the contracts issued by the US military and NASA, as well as US civilian federal agencies.
A Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is an identifying number used for tax purposes in the United States and in other countries under the Common Reporting Standard. In the United States it is also known as a Tax Identification Number or Federal Taxpayer Identification Number. A TIN may be assigned by the Social Security Administration or by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
The Trading Partner Identification Number is a confidential number assigned to organizations which are or intend to be contractors to the Federal Government of the United States. It is issued by the Central Contractor Registration (CCR) of the Department of Defense. Contractors are consistently advised by CCR to treat the TPIN as if it were a password, and not to reveal it to others not directly involved in their business operations.
The Data Universal Numbering System, abbreviated as DUNS or D-U-N-S, is a proprietary system developed and managed by Dun & Bradstreet (D&B) that assigns a unique numeric identifier, referred to as a "DUNS number" to a single business entity. It was introduced in 1963 to support D&B's credit reporting practice. It is standard worldwide. DUNS users include the European Commission, the United Nations, the United States government, and Apple. More than 50 global industry and trade associations recognize, recommend, or require DUNS. The DUNS database contains over 300 million entries for businesses throughout the world.
The United States government classification system is established under Executive Order 13526, the latest in a long series of executive orders on the topic. Issued by President Barack Obama in 2009, Executive Order 13526 replaced earlier executive orders on the topic and modified the regulations codified to 32 C.F.R. 2001. It lays out the system of classification, declassification, and handling of national security information generated by the U.S. government and its employees and contractors, as well as information received from other governments.

The United States Department of Defense is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national security and the United States Armed Forces. The DOD is the largest employer in the world, with over 1.4 million active-duty service members as of 2021. More employees include over 826,000 National Guard and reservists from the armed forces, and over 732,000 civilians bringing the total to over 2.8 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the DoD's stated mission is to provide "the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security".
"Right to know" empowers "people by allowing them to participate in an informed way in decisions that affect them, while also holding governments and others accountable". It pursues universal access to information as essential foundations of inclusive knowledge societies.
MIL-STD-130, "Identification Marking of U.S. Military Property," is a specification that describes markings required on items sold to the Department of Defense (DoD), including the addition, in about 2005, of UII Data Matrix machine-readable information (MRI) requirements. MIL-STD-130 describes the materials allowed, minimum text size and fonts, format, syntax and rules for identifying marks on a part, where to locate this marking plus exceptions and unique situations, such as vehicle identification numbers, cell phone IDs, etc. Other non-identifying markings—such as "this end up"—are covered under MIL-STD-129.
Unique Identification Marking, UID marking, Item Unique Identification or IUID, is a part of the compliance process mandated by the United States Department of Defense. It is a permanent marking method used to give equipment a unique ID. Marking is essential for all equipment with an acquisition cost of over $5,000, equipment which is mission essential, controlled inventory, or serially-controlled. UID-marking is a set of data for assets that is globally unique and unambiguous. The technology used to mark an item is 2D Data Matrix ECC 200 Symbol. UID marking can be used to ensure data integrity and data quality throughout an item's lifecycle; it also supports multi-faceted business applications.

A whistleblower is a person who exposes any kind of information or activity that is deemed illegal, unethical, or not correct within an organization that is either private or public. The Whistleblower Protection Act was made into federal law in the United States in 1989.
The Commercial and Government Entity Code, or CAGE Code, is a unique identifier assigned to suppliers to various government or defense agencies, as well as to government agencies themselves and various organizations. CAGE codes provide a standardized method of identifying a given facility at a specific location.

IDEMIA is a multinational technology company headquartered in Courbevoie, France. It provides identity-related security services, and sells facial recognition and other biometric identification products and software to private companies and governments.
References
- ↑ "The Department of Defense Activity Address Directory (DoDAAD)". Archived from the original on 2016-02-15. Retrieved 2020-06-22.
- ↑ "Defense Logistics Manuals". Archived from the original on 2016-05-13. Retrieved 2020-06-21.