Related Research Articles
Department is an organizational term used by the U.S. Army, mostly prior to World War I, to describe named geographical districts created for control and administration of installations and units. In 1920, most of the named departments were redesignated as numbered Corps Areas. However, the Hawaiian, Panama Canal, and Philippine Departments retained their old names. In 1939, the Puerto Rican Department was created and in May 1941 the Panama Canal and Puerto Rican Departments were combined as the Caribbean Defense Command, although each was still referred to as a department.
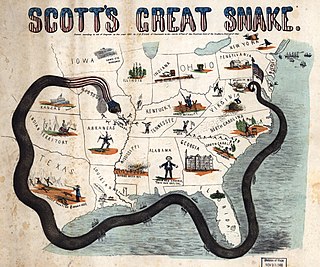
The Anaconda Plan was a strategy outlined by the Union Army for suppressing the Confederacy at the beginning of the American Civil War. Proposed by Union General-in-Chief Winfield Scott, the plan emphasized a Union blockade of the Southern ports and called for an advance down the Mississippi River to cut the South in two. Because the blockade would be rather passive, it was widely derided by a vociferous faction of Union generals who wanted a more vigorous prosecution of the war and likened it to the coils of an anaconda suffocating its victim. The snake image caught on, giving the proposal its popular name.

The lower seaboard theater of the American Civil War encompassed major military and naval operations that occurred near the coastal areas of the Southeastern United States: in Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, Texas, Port Hudson, Louisiana, and points south of it.

Christopher Columbus Augur was an American military officer, most noted for his role in the American Civil War. Although less well known than many other army contemporaries, he was considered an able battlefield commander.

Florida participated in the American Civil War as a member of the Confederate States of America. It had been admitted to the United States as a slave state in 1845. In January 1861, Florida became the third Southern state to secede from the Union after the November 1860 presidential election victory of Abraham Lincoln. It was one of the initial seven slave states which formed the Confederacy on February 8, 1861, in advance of the American Civil War.

The Department of the Gulf was a command of the United States Army in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries and of the Confederate States Army during the Civil War.
USS Samuel Rotan was a schooner acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was outfitted by the Union Navy as a gunboat to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries. Prior to the war, the US Navy had mostly large, deep-draft, oceangoing vessels. The establishment of the Union blockade required small, fast, shallow-draft vessels like the Samuel Rotan for littoral operations.
USS Maria A. Wood was a schooner acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Wyandotte, originally USS Western Port, was a steamer acquired by the Navy as a gunboat for the Paraguay expedition in 1858. When the crisis of the American Civil War occurred, she operated in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

The state of Rhode Island during the American Civil War remained loyal to the Union, as did the other states of New England. Rhode Island furnished 25,236 fighting men to the Union Army, of which 1,685 died. The state used its industrial capacity to supply the Union Army with the materials needed to win the war. Rhode Island's continued growth and modernization led to the creation of an urban mass transit system and improved health and sanitation programs.
District of Arizona was a subordinate district of the Department of New Mexico territory created on August 30, 1862 and transferred to the Department of the Pacific in March 1865.
The Department of the East was a military administrative district established by the U.S. Army several times in its history. The first was from 1853 to 1861, the second Department of the East, from 1863 to 1873, and the last from 1877 to 1913.

1st Regiment Indiana Heavy Artillery was a heavy artillery regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was nicknamed the "Jackass Regiment". Before being converted into an artillery unit in 1863, it served as the 21st Regiment, Indiana Volunteer Infantry.

William Henry Chase was a Florida militia colonel during the events in early 1861 that led to the American Civil War. On January 15, 1861, on behalf of the State and Governor of Florida, Colonel Chase demanded the surrender of Fort Pickens at Pensacola, Florida and of its U.S. Army garrison. Chase had designed and constructed the fort while he was a captain in the United States Army Corps of Engineers. Lieutenant Adam J. Slemmer, commander of the fort, refused the surrender demand. An informal truce between the administration of President James Buchanan and Florida officials, including their still sitting U.S. Senators, avoided military action at Pensacola until after the Battle of Fort Sumter in April 1861.
During the American Civil War, a department was a geographical command within the Union's military organization, usually reporting directly to the War Department. Many of the Union's departments were named after rivers or other bodies of water, such as the Department of the Potomac and the Department of the Tennessee. The geographical boundaries of such departments changed frequently, as did their names. As the armies became larger Departments began to be subordinated to Military Divisions, and the Departments were often sub divided into Districts and from 1862 Subdistricts. Much information on Civil War departments can be found in Eicher & Eicher, Civil War High Commands.
Department of Washington, was a department of the Union Army constituted on April 9, 1861. It consisted of the District of Columbia to its original boundaries, and the State of Maryland as far as Bladensburg. It was merged into the Military Division of the Potomac on July 25, 1861. Later it was recreated on February 2, 1863 as the consolidated Department of Washington and XXII Corps. It was again made the Department of Washington in 1865 and that command remained until 1869 when it was disbanded.
District of the Kanawha, was a Union Army district during the American Civil War.
The Department of New England was a Union Army Department created on October 1, 1861, consisting of the six New England States. The department was discontinued on February 20, 1862.
Department of Key West, was a military department of the Union Army created in February 1862 from the Department of Florida. It had command over the posts that were newly captured by “Expeditionary Corps” combined of Army and Navy units under Brigadier General Thomas W. Sherman and Flag Officer Samuel Francis Du Pont. These were posts at Fernandina, St. Augustine and the forces investing Fort Pulaski and blockading the Savannah River on Tybee Island at the mouth of the river.
The Department of the South was a military department of the United States Army that existed in several iterations in the 19th century during and after the American Civil War.
References
- Eicher, John H., & Eicher, David J., Civil War High Commands, Stanford University Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8047-3641-3.
- National Archives, Guide to Federal Records; Records of United States Army Continental Commands, 1821-1920 (Record Group 393), 1817-1940 (bulk 1817-1920)