Related Research Articles

The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is a United States government corporation supplying deposit insurance to depositors in American commercial banks and savings banks. The FDIC was created by the Banking Act of 1933, enacted during the Great Depression to restore trust in the American banking system. More than one-third of banks failed in the years before the FDIC's creation, and bank runs were common. The insurance limit was initially US$2,500 per ownership category, and this has been increased several times over the years. Since the enactment of the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act in 2010, the FDIC insures deposits in member banks up to $250,000 per ownership category. FDIC insurance is backed by the full faith and credit of the government of the United States, and according to the FDIC, "since its start in 1933 no depositor has ever lost a penny of FDIC-insured funds".

Fractional-reserve banking is the system of banking in all countries worldwide, under which banks that take deposits from the public keep only part of their deposit liabilities in liquid assets as a reserve, typically lending the remainder to borrowers. Bank reserves are held as cash in the bank or as balances in the bank's account at the central bank. Fractional-reserve banking differs from the hypothetical alternative model, full-reserve banking, in which banks would keep all depositor funds on hand as reserves.
The Philadelphia Savings Fund Society (PSFS), originally called the Philadelphia Saving Fund Society, was a savings bank headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. PSFS was founded in December 1816, the first savings bank to organize and do business in the United States. The bank would develop as one of the largest savings banks in the United States and became a Philadelphia institution. Generations of Philadelphians first opened accounts as children and became lifelong depositors.

A certificate of deposit (CD) is a time deposit sold by banks, thrift institutions, and credit unions in the United States. CDs typically differ from savings accounts because the CD has a specific, fixed term before money can be withdrawn without penalty and generally higher interest rates. The bank expects the CDs to be held until maturity, at which time they can be withdrawn and interest paid.

A bank run or run on the bank occurs when many clients withdraw their money from a bank, because they believe the bank may fail in the near future. In other words, it is when, in a fractional-reserve banking system, numerous customers withdraw cash from deposit accounts with a financial institution at the same time because they believe that the financial institution is, or might become, insolvent. When they transfer funds to another institution, it may be characterized as a capital flight. As a bank run progresses, it may become a self-fulfilling prophecy: as more people withdraw cash, the likelihood of default increases, triggering further withdrawals. This can destabilize the bank to the point where it runs out of cash and thus faces sudden bankruptcy. To combat a bank run, a bank may acquire more cash from other banks or from the central bank, or limit the amount of cash customers may withdraw, either by imposing a hard limit or by scheduling quick deliveries of cash, encouraging high-return term deposits to reduce on-demand withdrawals or suspending withdrawals altogether.

A savings and loan association (S&L), or thrift institution, is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and making mortgage and other loans. The terms "S&L" and "thrift" are mainly used in the United States; similar institutions in the United Kingdom, Ireland and some Commonwealth countries include building societies and trustee savings banks. They are often mutually held, meaning that the depositors and borrowers are members with voting rights, and have the ability to direct the financial and managerial goals of the organization like the members of a credit union or the policyholders of a mutual insurance company. While it is possible for an S&L to be a joint-stock company, and even publicly traded, in such instances it is no longer truly a mutual association, and depositors and borrowers no longer have membership rights and managerial control. By law, thrifts can have no more than 20 percent of their lending in commercial loans—their focus on mortgage and consumer loans makes them particularly vulnerable to housing downturns such as the deep one the U.S. experienced in 2007.

The savings and loan crisis of the 1980s and 1990s was the failure of 32% of savings and loan associations (S&Ls) in the United States from 1986 to 1995. An S&L or "thrift" is a financial institution that accepts savings deposits and makes mortgage, car and other personal loans to individual members.
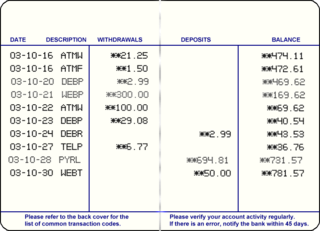
A savings account is a bank account at a retail bank. Common features include a limited number of withdrawals, a lack of cheque and linked debit card facilities, limited transfer options and the inability to be overdrawn. Traditionally, transactions on savings accounts were widely recorded in a passbook, and were sometimes called passbook savings accounts, and bank statements were not provided; however, currently such transactions are commonly recorded electronically and accessible online.

A time deposit or term deposit is a deposit in a financial institution with a specific maturity date or a period to maturity, commonly referred to as its "term". Time deposits differ from at call deposits, such as savings or checking accounts, which can be withdrawn at any time, without any notice or penalty. Deposits that require notice of withdrawal to be given are effectively time deposits, though they do not have a fixed maturity date.
Deposit insurance or deposit protection is a measure implemented in many countries to protect bank depositors, in full or in part, from losses caused by a bank's inability to pay its debts when due. Deposit insurance systems are one component of a financial system safety net that promotes financial stability.
The Continental Illinois National Bank and Trust Company was at one time the seventh-largest commercial bank in the United States as measured by deposits, with approximately $40 billion in assets. In 1984, Continental Illinois became the largest ever bank failure in U.S. history, when a run on the bank led to its seizure by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). Continental Illinois retained this dubious distinction until the failure of Washington Mutual in 2008 during the financial crisis of 2008, which ended up being over seven times larger than the failure of Continental Illinois.
The Expedited Funds Availability Act was enacted in 1987 by the United States Congress for the purpose of standardizing hold periods on deposits made to commercial banks and to regulate institutions' use of deposit holds. It is also referred to as Regulation CC or Reg CC, after the Federal Reserve regulation that implements the act. The law is codified in Title 12, Chapter 41 of the US Code and Title 12, Part 229 of the Code of Federal Regulations.
A sweep account is an account set up at a bank or other financial institution where the funds are automatically managed between a primary cash account and secondary investment accounts.
IndyMac, a contraction of Independent National Mortgage Corporation, was an American bank based in California that failed in 2008 and was seized by the United States Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).

The Korea Deposit Insurance Corporation (KDIC) is a South Korean deposit insurance corporation, established in 1996 to protect depositors and maintain the stability of the financial system. The main functions of KDIC are insurance management, risk surveillance, resolution, recovery, and investigation.

A bank failure occurs when a bank is unable to meet its obligations to its depositors or other creditors because it has become insolvent or too illiquid to meet its liabilities. A bank usually fails economically when the market value of its assets declines to a value that is less than the market value of its liabilities. The insolvent bank either borrows from other solvent banks or sells its assets at a lower price than its market value to generate liquid money to pay its depositors on demand. The inability of the solvent banks to lend liquid money to the insolvent bank creates a bank panic among the depositors as more depositors try to take out cash deposits from the bank. As such, the bank is unable to fulfill the demands of all of its depositors on time. A bank may be taken over by the regulating government agency if its shareholders' equity are below the regulatory minimum.
Bank regulation in the United States is highly fragmented compared with other G10 countries, where most countries have only one bank regulator. In the U.S., banking is regulated at both the federal and state level. Depending on the type of charter a banking organization has and on its organizational structure, it may be subject to numerous federal and state banking regulations. Apart from the bank regulatory agencies the U.S. maintains separate securities, commodities, and insurance regulatory agencies at the federal and state level, unlike Japan and the United Kingdom. Bank examiners are generally employed to supervise banks and to ensure compliance with regulations.

A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
The government interventions during the subprime mortgage crisis were a response to the 2007–2009 subprime mortgage crisis and resulted in a variety of government bailouts that were implemented to stabilize the financial system during late 2007 and early 2008.
The Certificate of Deposit Account Registry Service (CDARS), was a US for-profit service that broke up large deposits and placed them across a network of more than 3000 banks and savings associations around the United States. This allowed depositors to deal with a single bank that participates in CDARS but avoid having funds above the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) deposit insurance limits in any one bank.
References
- ↑ "Bank Data & Statistics". Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. March 31, 2023.
- ↑ "US banks report $872B YOY drop in deposits". S&P Global. September 25, 2023.