Related Research Articles

Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat closing due to swelling that can obstruct or stop breathing; severe tongue swelling that can also interfere with or stop breathing; shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, low blood pressure, and medical shock. These symptoms typically start in minutes to hours and then increase very rapidly to life-threatening levels. Urgent medical treatment is required to prevent serious harm and death, even if the patient has used an epipen or has taken other medications in response, and even if symptoms appear to be improving.
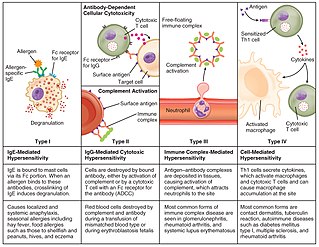
Hypersensitivity is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes immune diseases including allergies and autoimmunity. It is caused by many types of particles and substances from the external environment or from within the body that are recognized by the immune cells as antigens. The immune reactions are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and they are often damaging and uncomfortable.
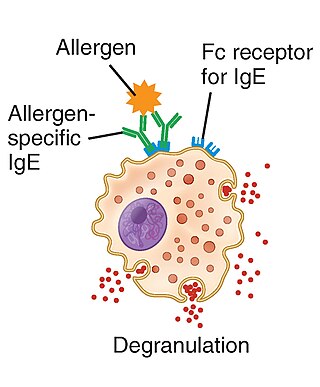
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis, and Fasciola hepatica. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms.
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. This typically occurs within minutes to several hours of exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis. A food intolerance and food poisoning are separate conditions, not due to an immune response.
Type I hypersensitivity, in the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions, is an allergic reaction provoked by re-exposure to a specific type of antigen referred to as an allergen. Type I is distinct from type II, type III and type IV hypersensitivities. The relevance of the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions has been questioned in the modern-day understanding of allergy, and it has limited utility in clinical practice.

Allergen immunotherapy, also known as desensitization or hypo-sensitization, is a medical treatment for environmental allergies and asthma. Immunotherapy involves exposing people to larger and larger amounts of allergens in an attempt to change the immune system's response.

Peanut allergy is a type of food allergy to peanuts. It is different from tree nut allergies, because peanuts are legumes and not true nuts. Physical symptoms of allergic reaction can include itchiness, hives, swelling, eczema, sneezing, asthma attack, abdominal pain, drop in blood pressure, diarrhea, and cardiac arrest. Anaphylaxis may occur. Those with a history of asthma are more likely to be severely affected.

Milk allergy is an adverse immune reaction to one or more proteins in cow's milk. Symptoms may take hours to days to manifest, with symptoms including atopic dermatitis, inflammation of the esophagus, enteropathy involving the small intestine and proctocolitis involving the rectum and colon. However, rapid anaphylaxis is possible, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires treatment with epinephrine, among other measures.

Egg allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in chicken eggs, and possibly goose, duck, or turkey eggs. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus.
Enzyme potentiated desensitization (EPD), is a treatment for allergies developed in the 1960s by Dr. Leonard M. McEwen in the United Kingdom. EPD uses much lower doses of antigens than conventional desensitization treatment paired with the enzyme β-glucuronidase. EPD is approved in the United Kingdom for the treatment of hay fever, food allergy and intolerance and environmental allergies.
A drug allergy is an allergy to a drug, most commonly a medication, and is a form of adverse drug reaction. Medical attention should be sought immediately if an allergic reaction is suspected.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to immunology:
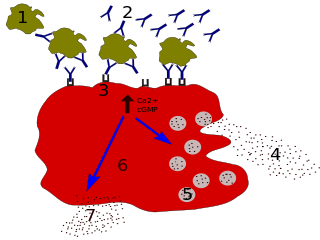
Pseudoallergy, sometimes known as nonallergic hypersensitivity, is a type of hypersensitivity reaction mostly described in the context of drug allergy. The mechanism is somewhat similar to the type 1 hypersensitivity in the Gell and Coombs classification in that the effector cell is also mast cell. In pseudoallergic reaction, the mast cell is directly activated, rather than through the mediation of Immunoglobulin E (IgE). Therefore, it is also known as direct mast cell activation.
Kounis syndrome is defined as acute coronary syndrome caused by an allergic reaction or a strong immune reaction to a drug or other substance. It is a rare syndrome with authentic cases reported in 130 males and 45 females, as reviewed in 2017; however, the disorder is suspected of being commonly overlooked and therefore much more prevalent. Mast cell activation and release of inflammatory cytokines as well as other inflammatory agents from the reaction leads to spasm of the arteries leading to the heart muscle or a plaque breaking free and blocking one or more of those arteries.
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), also known as alpha-gal allergy or mammalian meat allergy (MMA), is a type of acquired allergy characterized by a delayed onset of symptoms after ingesting mammalian meat. The condition results from past exposure to certain tick bites and was first reported in 2002. Symptoms of the allergy vary greatly between individuals and include rash, hives, nausea or vomiting, difficulty breathing, drop in blood pressure, dizziness or faintness, diarrhea, severe stomach pain, and possible anaphylaxis.

Fish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in fish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Fish is one of the eight common food allergens which are responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.

A food allergy to sesame seeds has prevalence estimates in the range of 0.1–0.2% of the general population, and are higher in the Middle East and other countries where sesame seeds are used in traditional foods. Reporting of sesame seed allergy has increased in the 21st century, either due to a true increase from exposure to more sesame foods or due to an increase in awareness. Increasing sesame allergy rates have induced more countries to regulate food labels to identify sesame ingredients in products and the potential for allergy. In the United States, sesame became the ninth food allergen with mandatory labeling, effective 1 January 2023.
Anti-allergic agents are medications used to treat allergic reactions. Anti-allergic agents have existed since 3000 B.C in countries such as China and Egypt. It was not until 1933 when antihistamines, the first type of anti-allergic agents, were developed. Common allergic diseases include allergic rhinitis, allergic asthma and atopic dermatitis with varying symptoms, including runny nose, watery eyes, itchiness, coughing, and shortness of breath. More than one-third of the world's population is currently being affected by one or more allergic conditions.
References
- ↑ Castells, Mariana C., ed. (2011). Anaphylaxis and hypersensitivity reactions. New York: Humana Press : Springer. pp. 60–62. ISBN 978-1-60327-950-5. OCLC 701718637.
- ↑ Nowak-Węgrzyn A, Sampson HA (March 2011). "Future therapies for food allergies". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 127 (3): 558–73, quiz 574–5. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.12.1098. PMC 3066474 . PMID 21277625.