
Pressure measurement is the analysis of an applied force by a fluid on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure in an integral unit are called pressure meters or pressure gauges or vacuum gauges. A manometer is a good example, as it uses the surface area and weight of a column of liquid to both measure and indicate pressure. Likewise the widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge.
The stethoscope is an acoustic medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. A stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds made by the heart, lungs or intestines, as well as blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a manual sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used when measuring blood pressure.
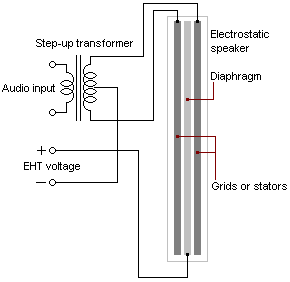
An electrostatic loudspeaker (ESL) is a loudspeaker design in which sound is generated by the force exerted on a membrane suspended in an electrostatic field.
Mechanical ventilation, or assisted ventilation, sometimes abbreviated as IMV, is the medical term for artificial ventilation where mechanical means are used to assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator, or the breathing may be assisted manually by a suitably qualified professional, such as an anesthesiologist, Registered Nurse (RN), paramedic or other first responder, or in some parts of the United States, by a respiratory therapist (RT), by compressing a bag valve mask device.

The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm.

The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm, is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity and performs an important function in respiration: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs.

A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.

Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central tendon defects of the diaphragm. Malformation of the diaphragm allows the abdominal organs to push into the chest cavity, hindering proper lung formation.
Optoelectronic plethysmography (OEP) is a method to evaluate ventilation through an external measurement of the chest wall surface motion.

A respiratory examination, or lung examination, is performed as part of a physical examination, in response to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, and is often carried out with a cardiac examination.

Diaphragmatic breathing, or deep breathing, is breathing that is done by contracting the diaphragm, a muscle located horizontally between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Air enters the lungs, the chest does not rise and the belly expands during this type of breathing. Diaphragmatic breathing is also known scientifically as eupnea, which is a natural and relaxed form of breathing in all mammals. Eupnea occurs in mammals whenever they are in a state of relaxation, i.e. when there is no clear and present danger in their environment.

The costodiaphragmatic recess, also called the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus, is a potential space in the pleural cavity, at the posterior-most tips of the cavity, located at the junction of the costal pleura and diaphragmatic pleura. It measures approximately 5 cm vertically and extends from the eighth to the tenth rib along the mid-axillary line.
Lung compliance, or pulmonary compliance, is a measure of the lung's ability to stretch and expand. In clinical practice it is separated into two different measurements, static compliance and dynamic compliance. Static lung compliance is the change in volume for any given applied pressure. Dynamic lung compliance is the compliance of the lung at any given time during actual movement of air.
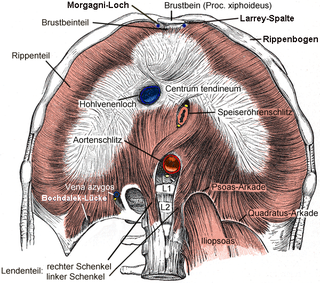
A Bochdalek hernia is one of two forms of a congenital diaphragmatic hernia, the other form being Morgagni hernia. A Bochdalek hernia is a congenital abnormality in which an opening exists in the infant's diaphragm, allowing normally intra-abdominal organs to protrude into the thoracic cavity. In the majority of patients, the affected lung will be deformed, and the resulting lung compression can be life-threatening. Bochdalek hernias occur more commonly on the posterior left side. This type of hernia was first studied and documented by the Czech Anatomist and Pathologist, Vincenz Alexander Bochdalek (1801–1883).

Diaphragmatic rupture is a tear of the diaphragm, the muscle across the bottom of the ribcage that plays a crucial role in respiration. Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic tears result from physical trauma. Diaphragmatic rupture can result from blunt or penetrating trauma and occurs in about 5% of cases of severe blunt trauma to the trunk.

Diaphragm pacing,, is the rhythmic application of electrical impulses to the diaphragm to provide artificial ventilatory support for respiratory failure or sleep apnea. Historically, this has been accomplished through the electrical stimulation of a phrenic nerve by an implanted receiver/electrode, though today an alternative option of attaching percutaneous wires to the diaphragm exists.
A subpulmonic effusion is excess fluid that collects at the base of the lung, in the space between the pleura and diaphragm. It is a type of pleural effusion in which the fluid collects in this particular space, but can be "layered out" with decubitus chest radiographs. There is minimal nature of costophrenic angle blunting usually found with larger pleural effusions. The occult nature of the effusion can be suspected indirectly on radiograph by elevation of the right diaphragmatic border with a lateral peak and medial flattening. The presence of the gastric bubble on the left with an abnormalagm of more than 2 cm can also suggest the diagnosis. Lateral decubitus views, with the patient lying on their side, can confirm the effusion as it will layer along the lateral chest wall. Subpulmonic space refers to the space below the lungs in which the subpulmonic fluid fills. Subpulmonic fluid is common particularly in trauma cases where the apparent hemidiaphragm appears defieted and the apex is displaced laterally.

Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.
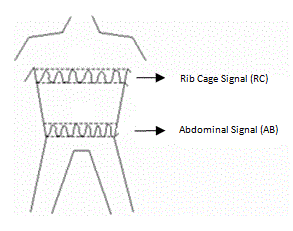
Respiratory inductance plethysmography (RIP) is a method of evaluating pulmonary ventilation by measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal wall.
The cardiovascular examination is a portion of the physical examination that involves evaluation of the cardiovascular system. The exact contents of the examination will vary depending on the presenting complaint but a complete examination will involve the heart, lungs, belly and the blood vessels.













