Related Research Articles

Diego Garcia is an island of the British Indian Ocean Territory, a disputed overseas territory of the United Kingdom also claimed by Mauritius. It is a militarised atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of the 60 small islands of the Chagos Archipelago. Portuguese sailors under Pedro Mascarenhas were the first Europeans to discover the island, finding it uninhabited in 1512. After a 1786 British colony failed, the French began using the island as a leper colony and, starting in 1793, coconut cultivation by enslaved labor. It was transferred to British rule after the Napoleonic Wars. It was one of the "Dependencies" of the British Colony of Mauritius until the Chagos Islands were detached for inclusion in the newly created British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965.

Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about 2,000 kilometres off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island, as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon. The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion, are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans 2,040 square kilometres (790 sq mi) and has an exclusive economic zone covering 2,300,000 square kilometres.

The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons.

The Chagossians are an Indo-African ethnic group originating from French slaves brought to the Chagos Islands, specifically Diego Garcia, Peros Banhos, and the Salomon island chain, in the late 18th century. Under international law, they are the indigenous people of the Chagos archipelago. Most Chagossians now live in Mauritius and the United Kingdom after being forcibly removed by the British government in the late 1960s and early 1970s so that Diego Garcia, the island where most Chagossians lived, could serve as the location for a United States military base. Today, no Chagossians are allowed to live on the island of Diego Garcia or anywhere in the Chagos archipelago, despite many of the islands they used to inhabit being over 160 km away from Diego Garcia.

The Salomon Islands or Salomon Atoll is a small atoll of the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).

Stealing a Nation is a 2004 Granada Television documentary about the British–American clandestine operation that saw the expulsion of the Chagossian population who have lived on Diego Garcia and neighbouring islands since the late 18th century. More than 2,000 people were exiled to Mauritius between 1967 and 1973, so that Diego Garcia could become a United States military airbase (see depopulation of Chagossians from the Chagos Archipelago). The film contains a series of interviews with Chagossians, who have been deprived of their right of return and forced to live in abject poverty. Stealing a Nation was written and directed by Australian journalist John Pilger, and produced and directed by Christopher Martin; reconstruction footage was directed by Sean Crotty.
The United Kingdom, at the request of the United States, began expelling the inhabitants of the Chagos Archipelago in 1968, concluding its forced deportations on 27 April 1973 with the expulsion of the remaining Chagossians on the Peros Banhos atoll. The inhabitants, known at the time as the Ilois, are today known as Chagos Islanders or Chagossians.
Mauritian Creoles are the people on the island of Mauritius and in the wider overseas Mauritian diaspora who trace their roots to Black Africans who were brought to Mauritius under slavery from the seventeenth to the nineteenth century. It can also refer to and include members of the island's mixed race or Métis community, especially if they are Christian. In government records, creoles along with Franco-Mauritians form part of the broader group known as Population Générale.
Chagossian creole is a French-based creole that was still spoken in 1994 by the 1,800 or so Chagossians, the former inhabitants of the Chagos Archipelago evicted in the early 1970s. Ilwa is a variety of Mauritian Creole with influences from Seychellois Creole. It is currently spoken mainly in Mauritius and the Seychelles. There is also a small minority community speaking the language in the United Kingdom.

The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 individual islands, many very small, amounting to a total land area of 60 square kilometres. The largest and most southerly island is Diego Garcia, 27 square kilometres, the site of a Joint Military Facility of the United Kingdom and the United States. Official administration is remote from London, though the local capital is often regarded as being on Diego Garcia.

R v Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs, ex parte Bancoult [2008] UKHL 61 is a UK constitutional law case in the House of Lords concerning the removal of the Chagos Islanders and the exercise of the Royal Prerogative. The Chagos Islands, acquired by the United Kingdom in 1814, were reorganised as the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965 for the purpose of removing its inhabitants. Under a 1971 ordinance, the Chagossians were forcibly removed, and the central island of Diego Garcia leased to the United States for use as a military outpost.
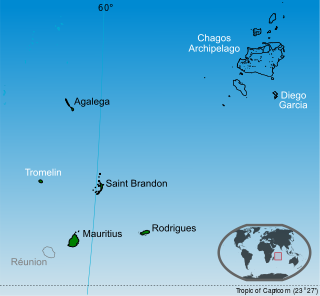
Sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago is disputed between Mauritius and the United Kingdom. Mauritius has repeatedly stated that the Chagos Archipelago is part of its territory and that the United Kingdom claim is a violation of United Nations resolutions banning the dismemberment of colonial territories before independence. On 22 May 2019, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a non-binding resolution declaring that the archipelago was part of Mauritius, with 116 countries voted in favor of Mauritius while six opposed it.

Allen Vincatassin is a Chagossian activist who is the first and current President of the Diego Garcia and Chagos Islands Council. He was arrested and jailed in 2020 and 2021 for fraud.
Aurélie Marie-Lisette Talate, also known as Lisette Talate or Aurelie Talate in her community was a Chagossian activist and emblematic figure of the Chagossian struggle to regain their islands; which they were forcibly exiled from by the occupying US military with permission from the UK in order to establish the Diego Garcia military base. Despite strong desire from the community to return to their land, the US and UK governments have patently refused to allow right of return.
The British Indian Ocean Territory, sometimes known as the Chagos Archipelago has had many threats of occupation by various groups, especially since the Depopulation of Chagossians from the Chagos Archipelago, as well as being a joint UK-US facility that is used in countering terrorism. The UK maintains that there is a low risk of terrorism in this territory.
Charlesia Alexis was a Chagossian singer and activist, notable for helping establish the Chagos Refugee Group.

The Maldives–Lakshadweep–Chagos Archipelago tropical moist forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in South Asia. It spans a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean, including Lakshadweep, a union territory of India; the Maldives, an independent country; and the British Indian Ocean Territory, an overseas territory of the United Kingdom.
Sabrina Jean is a second-generation Chagossian and activist for the Chagossian community to return home to the Chagos Islands in the Indian Ocean, administered as part of the British Indian Ocean Territory.

Sega tambour Chagos is one of the types of Sega music of Mauritius, with origins in the Chagos Archipelago. It is sung in the Chagossian creole language of the islands.
Clément Siatous is a Mauritian and British painter of Chagossian origin. He is known for his paintings depicting the daily life of the Chagossians before their exile.
References
- African Film Festival of Cordoba-FCAT (license CC BY-SA-3.0)
