This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
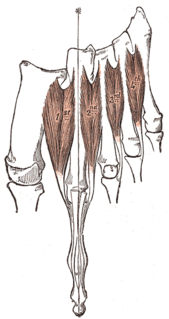
In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.

The superficial palmar arch is formed predominantly by the ulnar artery, with a contribution from the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. However, in some individuals the contribution from the radial artery might be absent, and instead anastomoses with either the princeps pollicis artery, the radialis indicis artery, or the median artery, the former two of which are branches from the radial artery.
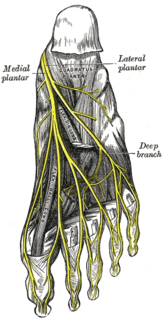
The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.

The radialis indicis artery is a branch of the radial artery that provides blood to the index finger.

Most of the dorsal metacarpal arteries arise from the dorsal carpal arch and run downward on the second, third, and fourth dorsal interossei of the hand and bifurcate into the dorsal digital arteries. Near their origin, they anastomose with the deep palmar arch by perforating arteries. They also anastomose with common palmar digital arteries, also via perforating arteries.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

In the palm of the hand the median nerve is covered by the skin and the palmar aponeurosis, and rests on the tendons of the Flexor muscles. Immediately after emerging from under the transverse carpal ligament the median nerve becomes enlarged and flattened and splits into a smaller, lateral, and a larger, medial portion.

The proper palmar digital arteries travel along the sides of the phalanges, each artery lying just below its corresponding digital nerve.
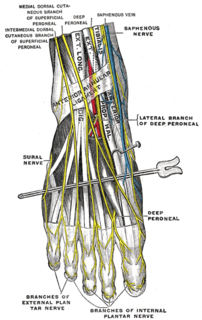
The proper plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot that arise from the superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve. The superficial branch splits into a proper digital nerve and a common digital nerve:

The common plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. The common digital nerve communicates with the third common digital branch of the medial plantar nerve and divides into two proper digital nerves which supply the adjoining sides of the fourth and fifth toes.

The proper plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. They primarily arise from the medial plantar nerve's superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the medial plantar nerve turns into a proper digital nerve and is responsible for supplies the medial side of the great toe.

The common plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. The three common digital nerves pass between the divisions of the plantar aponeurosis, and each splits into two proper digital nerves:
Plantar digital arteries may refer to:
Common artery may refer to:
Proper artery may refer to:
Proper digital arteries may refer to:
Common digital arteries may refer to:
Palmar arteries may refer to:
Dorsal digital arteries arise from the bifurcation of dorsal metacarpal arteries. They travel along the sides and dorsal aspects of the phalanges of the middle finger, ring finger, and little finger. They communicate with the proper palmar digital arteries.






