Related Research Articles

Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines, at one time acridine dyes were popular but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.

Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
2. Isomers include various quinone derivatives. The term anthraquinone, however refers to the isomer, 9,10-anthraquinone wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is a building block of many dyes and is used in bleaching pulp for papermaking. It is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite.

Phenanthrenoids are chemical compounds formed with a phenanthrene backbone. Those compound are naturally occurring in plants, although they can also be synthetized.
In enzymology, juglone 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a fluorescent organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a white solid. It is an isomer of 2-naphthol differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, with the hydroxyl group being more reactive than in the phenols. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds. Naphthols (both 1 and 2 isomers) are used as biomarkers for livestock and humans exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.

2,3,5,6,7,8-Hexahydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione, also called hexahydroxynaphthoquinone or spinochrome E, is an organic compound with formula C
10H
6O
8. It is formally derived from naphthoquinone (1,4-naphtalenedione) through replacement of all six hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. The numerical prefixes "2,3,5,6,7,8" are superfluous, since there is no other hexahydroxy derivative of 1,4-naphthoquinone.

1,3-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called purpuroxanthin or xanthopurpurin, is an organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
4 that occurs in the plant Rubia cordifolia. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers. Its molecular structure can be viewed as being derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms (H) by hydroxyl groups (-OH).
A dihydroxyanthraquinone is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula C
14H
8O
4, formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Dihyroxyantraquinones have been studied since the early 1900s, and include some compounds of historical and current importance. The isomers differ in the position of the hydroxyl groups, and of the carbonyl oxygens (=O) of the underlying anthraquinone.
A hydroxynaphthoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of a naphthoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).

Naphthazarin, often called 5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone or 5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione (IUPAC), is a naturally occurring organic compound with formula C
10H
6O
4, formally derived from 1,4-naphthoquinone through replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is thus one of many dihydroxynaphthoquinone structural isomers.
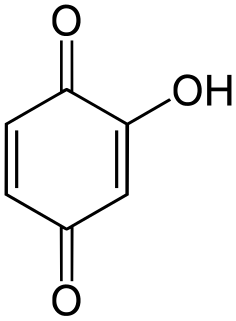
Hydroxyquinone often refers to a hydroxybenzoquinone, any organic compound with formula C
6H
4O
3 which can be viewed as a derivative of a benzoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH). When unqualified, the terms usually mean specifically the compound 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, derived from 1,4-benzoquinone or para-benzoquinone.
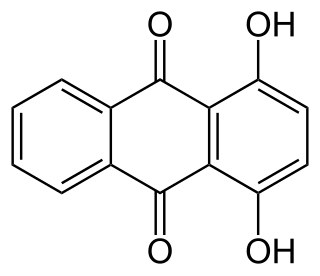
A hydroxyanthraquinone (formula: C14H9O2(OH)) is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of an anthraquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).
A hydroxybenzoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of a benzoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).
The molecular formula C10H6O4 may refer to:

Naphthoquinone is a class of organic compounds structurally related to naphthalene. Two isomers are common for the parent naphthoquinones:

1,4-Naphthoquinone or para-naphthoquinone is an organic compound derived from naphthalene. It forms volatile yellow triclinic crystals and has a sharp odor similar to benzoquinone. It is almost insoluble in cold water, slightly soluble in petroleum ether, and more soluble in polar organic solvents. In alkaline solutions it produces a reddish-brown color. Vitamin K is a derivative of 1,4-naphthoquinone. It is a planar molecule with one aromatic ring fused to a quinone subunit. It is an isomer of 1,2-naphthoquinone.

Coronaric acid (isoleukotoxin) is a mono-unsaturated, epoxide derivative of the di-saturated fatty acid, linoleic acid (i.e. 9 ,12 octadecadienoic acid. It is a mixture of the two optically active isomers of 12 9,10-epoxy-octadecenoic acid. This mixture is also termed 9,10-epoxy-12Z-octadecenoic acid or 9 -EpOME and when formed by or studied in mammalians, isoleukotoxin.
A cyclohexanetetrol is a chemical compound consisting of a cyclohexane molecule with four hydroxyl groups (–OH) replacing four of the twelve hydrogen atoms. It is therefore a cyclitol. Its generic formula is C
6H
12O
4 or C
6H
8(OH)
4.
References
- ↑ J. Khalafy and J.M. Bruce (2002), Oxidative dehydrogenation of 1-tetralones: Synthesis of juglone, naphthazarin, and α-hydroxyanthraquinones. Journal of Sciences, Islamic Republic of Iran, volume 13 issue 2, pages 131-139.