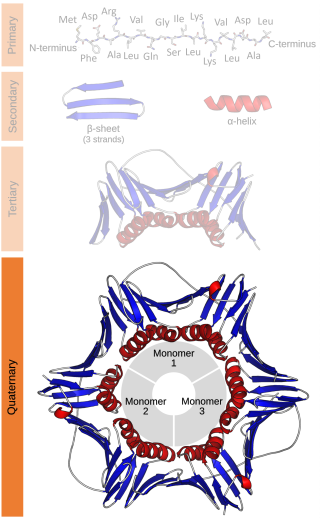
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains. Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple dimers to large homooligomers and complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other cofactors.
In chemistry, dimerization is the process of joining two identical or similar molecular entities by bonds. The resulting bonds can be either strong or weak. Many symmetrical chemical species are described as dimers, even when the monomer is unknown or highly unstable.
β-Fructofuranosidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of the table sugar sucrose into fructose and glucose. Alternative names for β-fructofuranosidase EC 3.2.1.26 include invertase, saccharase, glucosucrase, β-fructosidase, invertin, fructosylinvertase, alkaline invertase, and acid invertase. The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. Related to invertases are sucrases. Invertases and sucrases hydrolyze sucrose to give the same mixture of glucose and fructose. Invertase is a glycoprotein that hydrolyses (cleaves) the non-reducing terminal β-fructofuranoside residues. Invertases cleave the O-C(fructose) bond, whereas the sucrases cleave the O-C(glucose) bond. Invertase cleaves the α-1,2-glycosidic bond of sucrose.

A basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) is a protein structural motif that characterizes one of the largest families of dimerizing transcription factors. The word "basic" does not refer to complexity but to the chemistry of the motif because transcription factors in general contain basic amino acid residues in order to facilitate DNA binding.

A leucine zipper is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization.
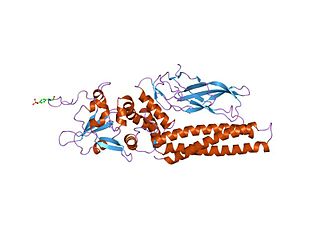
Members of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) protein family are intracellular transcription factors that mediate many aspects of cellular immunity, proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. They are primarily activated by membrane receptor-associated Janus kinases (JAK). Dysregulation of this pathway is frequently observed in primary tumors and leads to increased angiogenesis which enhances the survival of tumors and immunosuppression. Gene knockout studies have provided evidence that STAT proteins are involved in the development and function of the immune system and play a role in maintaining immune tolerance and tumor surveillance.
Bacterial translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in bacteria.
SMC complexes represent a large family of ATPases that participate in many aspects of higher-order chromosome organization and dynamics. SMC stands for Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes.

Pyrimidine dimers represent molecular lesions originating from thymine or cytosine bases within DNA, resulting from photochemical reactions. These lesions, commonly linked to direct DNA damage, are induced by ultraviolet light (UV), particularly UVC, result in the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent nitrogenous bases along the nucleotide chain near their carbon–carbon double bonds, the photo-coupled dimers are fluorescent. Such dimerization, which can also occur in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) involving uracil or cytosine, leads to the creation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6–4 photoproducts. These pre-mutagenic lesions modify the DNA helix structure, resulting in abnormal non-canonical base pairing and, consequently, adjacent thymines or cytosines in DNA will form a cyclobutane ring when joined together and cause a distortion in the DNA. This distortion prevents DNA replication and transcription mechanisms beyond the dimerization site.

Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) refers to two highly related proteins, STAT5A and STAT5B, which are part of the seven-membered STAT family of proteins. Though STAT5A and STAT5B are encoded by separate genes, the proteins are 90% identical at the amino acid level. STAT5 proteins are involved in cytosolic signalling and in mediating the expression of specific genes. Aberrant STAT5 activity has been shown to be closely connected to a wide range of human cancers, and silencing this aberrant activity is an area of active research in medicinal chemistry.

The retroviral psi packaging element, also known as the Ψ RNA packaging signal, is a cis-acting RNA element identified in the genomes of the retroviruses Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). It is involved in regulating the essential process of packaging the retroviral RNA genome into the viral capsid during replication. The final virion contains a dimer of two identical unspliced copies of the viral genome.
The ErbB family of proteins contains four receptor tyrosine kinases, structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), its first discovered member. In humans, the family includes Her1, Her2 (ErbB2), Her3 (ErbB3), and Her4 (ErbB4). The gene symbol, ErbB, is derived from the name of a viral oncogene to which these receptors are homologous: erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene. Insufficient ErbB signaling in humans is associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease, while excessive ErbB signaling is associated with the development of a wide variety of types of solid tumor.
Iterons are directly repeated DNA sequences which play an important role in regulation of plasmid copy number in bacterial cells. It is one among the three negative regulatory elements found in plasmids which control its copy number. The others include antisense RNAs and ctRNAs. Iterons complex with cognate replication (Rep) initiator proteins to achieve the required regulatory effect.

CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein gamma (C/EBPγ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPG gene. This gene has no introns.
EF-Ts is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B.
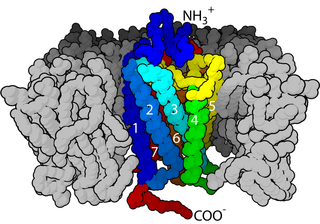
Cell surface receptors are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral membrane proteins that allow communication between the cell and the extracellular space. The extracellular molecules may be hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, or nutrients; they react with the receptor to induce changes in the metabolism and activity of a cell. In the process of signal transduction, ligand binding affects a cascading chemical change through the cell membrane.
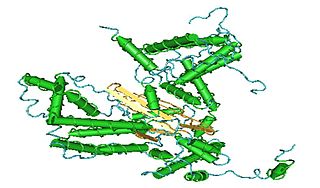
C7orf38 is a gene located on chromosome 7 in the human genome. The gene is expressed in nearly all tissue types at very low levels. Evolutionarily, it can be found throughout the kingdom animalia. While the function of the protein is not fully understood by the scientific community, bioinformatic tools have shown that the protein bares much similarity to zinc finger or transposase proteins. Many of its orthologs, paralogs, and neighboring genes have been shown to possess zinc finger domains. The protein contains a hAT dimerization domain nears its C-terminus. This domain is highly conserved in transposase enzymes.

In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word dimer has roots meaning "two parts", di- + -mer. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure.

Autophosphorylation is a type of post-translational modification of proteins. It is generally defined as the phosphorylation of the kinase by itself. In eukaryotes, this process occurs by the addition of a phosphate group to serine, threonine or tyrosine residues within protein kinases, normally to regulate the catalytic activity. Autophosphorylation may occur when a kinases' own active site catalyzes the phosphorylation reaction, or when another kinase of the same type provides the active site that carries out the chemistry. The latter often occurs when kinase molecules dimerize. In general, the phosphate groups introduced are gamma phosphates from nucleoside triphosphates, most commonly ATP.

FK1012 is a dimer consisting of two molecules of tacrolimus (FK506) linked via their vinyl groups. It is used as a research tool in chemically induced dimerization applications. FK1012 is a chemical inducer of dimerization (CID) which makes the protein capable of dimerization or oligomerization of fusion proteins containing one or more FKBP12 domains. It is used in pharmacology to act as a mediator in the formation of FK506 dimer. FK506 binding proteins (FKBPs) do not normally form dimers but can be caused to dimerize in the presence of FK1012. Genetically engineered proteins based on FKBPs can be used to manipulate protein localization, signaling pathways and protein activation.












