
A ramjet is a form of airbreathing jet engine that requires forward motion of the engine to provide air for combustion. Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds around Mach 3 and can operate up to Mach 6.
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (abbreviated as UDMH; also known as 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, heptyl or Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is primarily used as a rocket propellant. At room temperature, UDMH is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical of organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. At concentrations between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock.
Monomethylhydrazine (MMH) is a highly toxic, volatile hydrazine derivative with the chemical formula CH6N2. It is used as a rocket propellant in bipropellant rocket engines because it is hypergolic with various oxidizers such as nitrogen tetroxide and nitric acid. As a propellant, it is described in specification MIL-PRF-27404.

RP-1 and similar fuels like RG-1 and T-1 are highly refined kerosene formulations used as rocket fuel. Liquid-fueled rockets that use RP-1 as fuel are known as kerolox rockets. In their engines, RP-1 is atomized, mixed with liquid oxygen (LOX), and ignited to produce thrust. Developed in the 1950s, RP-1 is outwardly similar to other kerosene-based fuels like Jet A and JP-8 used in turbine engines but is manufactured to stricter standards. While RP-1 is widely used globally, the primary rocket kerosene formulations in Russia and other former Soviet countries are RG-1 and T-1, which have slightly higher densities.
Aerozine 50 is a 50:50 mix by weight of hydrazine and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH), developed in the late 1950s by Aerojet General Corporation as a storable, high-energy, hypergolic fuel for the Titan II ICBM rocket engines. Aerozine continues in wide use as a rocket fuel, typically with dinitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer, with which it is hypergolic. Aerozine 50 is more stable than hydrazine alone, and has a higher density and boiling point than UDMH alone.

Otto fuel II is a monopropellant mixture of chiefly propylene glycol dinitrate that is used to drive torpedoes and other weapon systems. It was invented by Otto Reitlinger in 1963. Otto fuel II, sometimes known simply as Otto fuel, is not related to the Otto cycle; it is named after Reitlinger and for being the second iteration of the fuel. It was developed by the US Navy and the first torpedo to use it was the Mark 48 torpedo in the 1960s.

The Beechcraft AQM-37 Jayhawk is an air-launched supersonic target drone manufactured by Beechcraft capable of simulating inbound ICBM warhead packages for fleet shoot-down exercises.

In organic and inorganic chemistry, nitroamines or nitramides are chemical compounds with the general chemical structure R1R2N−NO2. They consist of a nitro group bonded to the nitrogen of an amine. The R groups can be any group, typically hydrogen and organyl. An example of inorganic nitroamine is chloronitroamine, Cl−NH−NO2. The parent inorganic compound, where both R substituents are hydrogen, is nitramide or nitroamine, H2N−NO2.

The AGM-12 Bullpup is a short-range air-to-ground missile developed by Martin Marietta for the US Navy. It is among the earliest precision guided air-to-ground weapons and the first to be mass produced. It first saw operational use in 1959 on the A-4 Skyhawk, but soon found use on the A-6 Intruder, F-100 Super Sabre, F-105 Thunderchief, F-4 Phantom II, F-8 Crusader, and P-3 Orion in both Navy and US Air Force service, as well as NATO allies. The weapon was guided manually via a small joystick in the aircraft cockpit, which presented a number of problems and its ultimate accuracy was on the order of 10 metres (33 ft), greater than desired. In the 1960s it was increasingly supplanted by fully automatic weapons like the AGM-62 Walleye and AGM-65 Maverick.
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. Like triethanolamine and tetraethylammonium, it is often abbreviated TEA. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base.

Diethylenetriamine (abbreviated Dien or DETA) and also known as 2,2’-Iminodi(ethylamine)) is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2NH2)2. This colourless hygroscopic liquid is soluble in water and polar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons. Diethylenetriamine is structural analogue of diethylene glycol. Its chemical properties resemble those for ethylene diamine, and it has similar uses. It is a weak base and its aqueous solution is alkaline. DETA is a byproduct of the production of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride.

Furfuryl alcohol is an organic compound containing a furan substituted with a hydroxymethyl group. It is a colorless liquid, but aged samples appear amber. It possesses a faint odor of burning and a bitter taste. It is miscible with but unstable in water. It is soluble in common organic solvents.
UH 25 is a fuel mixture for rockets. It was developed for the European Ariane 2–4 launch vehicles.
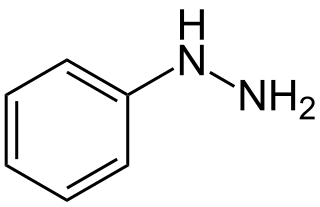
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine (H2N−NH2), in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by hydrocarbon groups.
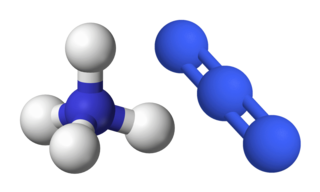
Ammonium azide is the chemical compound with the formula [NH4]N3, being the salt of ammonia and hydrazoic acid. Like other inorganic azides, this colourless crystalline salt is a powerful explosive, although it has a remarkably low sensitivity. [NH4]N3 is physiologically active and inhalation of small amounts causes headaches and palpitations. It was first obtained by Theodor Curtius in 1890, along with other azides.
Hydyne is a mixture of 60% unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) and 40% diethylenetriamine (DETA), developed in 1957 at Rocketdyne for use in liquid-fuel rockets. Hydyne was used as the fuel for the first stage of the Juno I rocket that launched Explorer 1, the first successful satellite launch conducted by the United States. As part of Mixed Amine Fuel series of rocket fuels, it was designated as MAF-4.
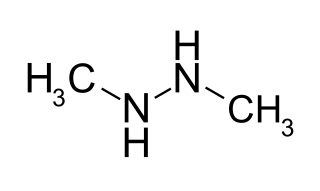
Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine (SDMH), or 1,2-dimethylhydrazine, is the organic compound with the formula (CH3NH)2. It is one of the two isomers of dimethylhydrazine. Both isomers are colorless liquids at room temperature, with properties similar to those of methylamines. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine is a potent carcinogen that acts as a DNA methylating agent. The compound has no commercial value, in contrast to its isomer unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (1,1-dimethylhydrazine, UDMH), which is used as a rocket fuel. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine is more toxic than unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and is therefore an unwanted impurity in UDMH.

The Société d'Études pour la Propulsion par Réaction (SEPR) was a French research and manufacturing company founded in 1944 which specialised in the development of liquid-fuelled rocket engines during the 1950s, 60s, 70s and 80s.
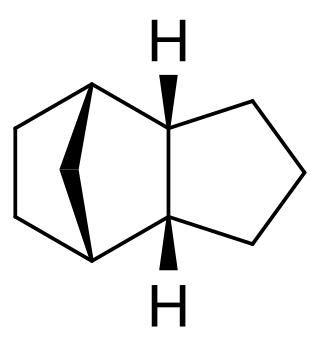
Tricyclodecane (TCD) is an organic compound with the formula C10H16. It is classed as a hydrocarbon. It has two main stereoisomers–the endo and exo forms. Its primary use in the exo form is as a component of jet fuel. It is used here primarily because of its high energy density. The exo isomer also has a low freezing point. Because of this, its properties have been studied extensively. It is often called tetrahydrodicyclopentadiene.
JP-10 is a synthetic jet fuel, specified and used mainly as fuel in missiles. Being designed for military purposes, it is not a kerosene based fuel.













