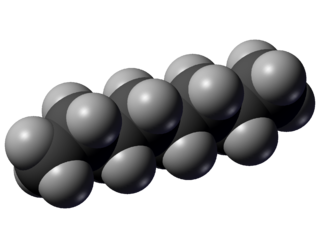
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane) is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.

Pentane is an organic compound with the formula C5H12—that is, an alkane with five carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of three structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, pentane means exclusively the n-pentane isomer; the other two are called isopentane (methylbutane) and neopentane (dimethylpropane). Cyclopentane is not an isomer of pentane because it has only 10 hydrogen atoms where pentane has 12.
Dihydroxybenzenes are organic chemical compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three isomer: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
There are two isomers of propanol.
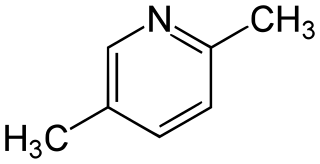
Lutidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are dimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Lutidine comes in several isomers:
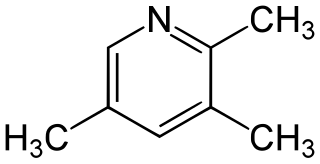
Collidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are trimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Collidine comes in several isomers:
1,4-Dimethoxybenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OCH3)2. It is one of three isomers of dimethoxybenzene. It is a white solid with an intensely sweet floral odor. It is produced by several plant species.
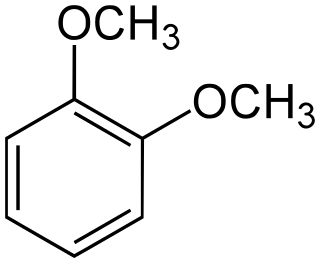
1,2-Dimethoxybenzene, commonly known as veratrole, is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OCH3)2. It is one of three isomers of dimethoxybenzene. It is a colorless liquid, with a pleasant odor and slight solubility in water. It is the dimethyl ether derived from pyrocatechol.
1,2-Dichlorobenzene, or orthodichlorobenzene (ODCB), is an organic compound with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colourless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. It is a derivative of benzene, consisting of two adjacent chlorine atoms.

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.
Dichlorophenols (DCPs) are any of several chemical compounds which are derivatives of phenol containing two chlorine atoms. There are six isomers:
Stilbene may refer to one of the two stereoisomers of 1,2-diphenylethene:

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulas — that is, same number of atoms of each element — but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
The molecular formula C8H10O2 (molar mass: 138.164 g/mol) may refer to:

Tetrahydroxybenzenes or Benzenetetrols are a group of organic compounds which are tetrahydroxy derivatives of benzene. Tetrahydroxybenzene comes in three isomers:
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.
Nonynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C9H16.

Benzenedicarboxylic acid is a group of chemical compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of benzene. Benzenedicarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:
Heptynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C7H12.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











