Related Research Articles

Filter paper is a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow. It is used to separate fine solid particles from liquids or gases.

A cleanroom or clean room is an engineered space that maintains a very low concentration of airborne particulates. It is well isolated, well controlled from contamination, and actively cleansed. Such rooms are commonly needed for scientific research and in industrial production for all nanoscale processes, such as semiconductor manufacturing. A cleanroom is designed to keep everything from dust to airborne organisms or vaporised particles away from it, and so from whatever material is being handled inside it.

A sieve, fine mesh strainer, or sift, is a tool used for separating wanted elements from unwanted material or for controlling the particle size distribution of a sample, using a screen such as a woven mesh or net or perforated sheet material. The word sift derives from sieve.

A media filter is a type of filter that uses a bed of sand, peat, shredded tires, foam, crushed glass, geo-textile fabric, anthracite, crushed granite or other material to filter water for drinking, swimming pools, aquaculture, irrigation, stormwater management, oil and gas operations, and other applications.

HEPA filter, also known as high-efficiency particulate absorbing filter and high-efficiency particulate arrestance filter, is an efficiency standard of air filters.
Drip irrigation or trickle irrigation is a type of micro-irrigation system that has the potential to save water and nutrients by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either from above the soil surface or buried below the surface. The goal is to place water directly into the root zone and minimize evaporation. Drip irrigation systems distribute water through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. Depending on how well designed, installed, maintained, and operated it is, a drip irrigation system can be more efficient than other types of irrigation systems, such as surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation.

A water filter removes impurities by lowering contamination of water using a fine physical barrier, a chemical process, or a biological process. Filters cleanse water to different extents, for purposes such as: providing agricultural irrigation, accessible drinking water, public and private aquariums, and the safe use of ponds and swimming pools.

A particulate air filter is a device composed of fibrous, or porous materials which removes particulates such as smoke, dust, pollen, mold, viruses and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbon) may also remove odors and gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds or ozone. Air filters are used in applications where air quality is important, notably in building ventilation systems and in engines.

A cloth filter is a simple and cost-effective appropriate technology method for reducing the contamination of drinking water, developed for use mainly in Bangladesh. Water collected in this way has a greatly reduced pathogen count. Though not always perfectly safe, it is an improvement for poor people with limited options.
Ultra-low particulate air (ULPA) is a type of air filter. A ULPA filter can remove from the air at least 99.999% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria and any airborne particles with a minimum particle penetration size of 120 nanometres. A ULPA filter can remove—to a large extent but not 100%—oil smoke, tobacco smoke, rosin smoke, smog, and insecticide dust. It can also remove carbon black to some extent. Some fan filter units incorporate ULPA filters. The EN 1822 and ISO 29463 standards may be used to rate ULPA filters.
A particle counter is used for monitoring and diagnosing particle contamination within specific clean media, including air, water and chemicals. Particle counters are used in a variety of applications in support of clean manufacturing practices, industries include: electronic components and assemblies, pharmaceutical drug products and medical devices, and industrial technologies such as oil and gas.
Mechanical screening, often just called screening, is the practice of taking granulated or crushed ore material and separating it into multiple grades by particle size.

Swimming pool sanitation is the process of ensuring healthy conditions in swimming pools. Proper sanitation is needed to maintain the visual clarity of water and to prevent the transmission of infectious waterborne diseases.
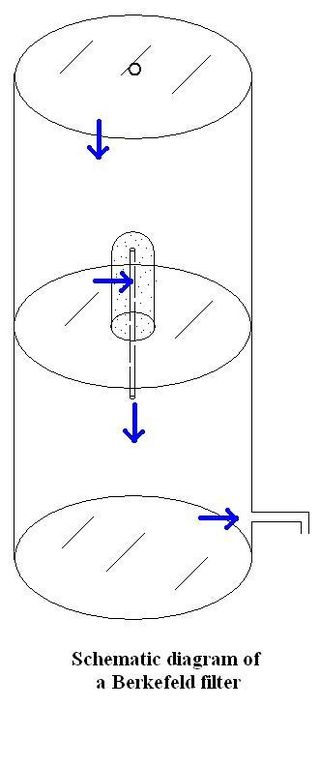
A Berkefeld filter is a water filter made of diatomaceous earth (Kieselguhr). It was invented in Germany in 1891, and by 1922 was being marketed in the United Kingdom by the Berkefeld Filter Co. Berkefeld was the name of the owner of the mine in Hanover, Germany, where the ceramic material was obtained.
A vacuum ceramic filter is designed to separate liquids from solids for dewatering of ore concentrates purposes. The device consists of a rotator, slurry tank, ceramic filter plate, distributor, discharge scraper, cleaning device, frame, agitating device, pipe system, vacuum system, automatic acid dosing system, automatic lubricating system, valve and discharge chute. The operation and construction principle of vacuum ceramic filter resemble those of a conventional disc filter, but the filter medium is replaced by a finely porous ceramic disc. The disc material is inert, has a long operational life and is resistant to almost all chemicals. Performance can be optimized by taking into account all those factors which affect the overall efficiency of the separation process. Some of the variables affecting the performance of a vacuum ceramic filter include the solid concentration, speed rotation of the disc, slurry level in the feed basin, temperature of the feed slurry, and the pressure during dewatering stages and filter cake formation.
Spa filters work continuously to keep debris and sediments from the water in a spa pool.

Micro-irrigation, also called Micro-spray,localized, low-volume, low-flow, or trickle irrigation, is an irrigation method with lower water pressure and flow than a traditional sprinkler system. Low-volume irrigation is used in agriculture for row crops, orchards, and vineyards. It is also used in horticulture in wholesale nurseries, in landscaping for civic, commercial, and private landscapes and gardens, and in the science and practice of restoration ecology and environmental remediation. The lower volume allows the water to be absorbed into slow-percolation soils such as clay, minimizing runoff.
Gyratory equipment, used in mechanical screening and sieving is based on a circular motion of the machine. Unlike other methods, gyratory screen operates in a gentler manner and is more suited to handle fragile things, enabling it to produce finer products. This method is applicable for both wet and dry screening.
A conical plate centrifuge is a type of centrifuge that has a series of conical discs which provides a parallel configuration of centrifugation spaces.
Pile Cloth Media Filtration is a mechanical process for the separation of organic and inorganic solids from liquids. It belongs to the processes of surface filtration and cake filtration where, in addition to the sieve effect, real filtration effects occur over the depth of the pile layer. Pile Cloth Media Filtration represents a branch of cloth filtration processes and is used for water and wastewater treatment in medium and large scale. In Pile Cloth Media Filtration, three-dimensional textile fabrics are used as filter media. During the filter cleaning of the pile layer the filtration process continues and is not interrupted.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Drip Irrigation of Processing Tomatoes. UCANR Publications. 2008. p. 46. ISBN 978-1-60107-436-2 . Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- 1 2 Stryker, Jess. "Irrigation Water Filtration & Filter Recommendations". Irrigation Tutorials. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- 1 2 Robert N. Carrow; Ronny R. Duncan; Michael T. Huck (17 December 2008). Turfgrass and Landscape Irrigation Water Quality: Assessment and Management. CRC Press. p. 275. ISBN 978-1-4200-8194-7 . Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- 1 2 Burt, Charles M.; Styles, Stuart W. (1999). Drip and Micro Irrigation for Trees, Vines, and Row Crops (2nd ed.). San Luis Obispo, California: ITRC, Cal Poly. pp. 140–142. ISBN 0-9643634-2-9.
- 1 2 3 Allhands, Marcus; Prochaska, James. "Disc Filtration: Something Old, Something New" (PDF). K-State Research and Extension. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- 1 2 3 Maintaining Microirrigation Systems. UCANR Publications. 2008. pp. 33, 37–38. ISBN 978-1-60107-488-1 . Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- ↑ "ISO 9912-2:2013 Agricultural irrigation equipment -- Filters for microirrigation -- Part 2: Strainer-type filters and disc filters". International Organization for Standardization. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- ↑ "Device For Filtering Solid Particles For Liquids Containing Such Particles". Google Patents. Retrieved 8 August 2017.