Harmonic analysis is a branch of mathematics concerned with investigating the connections between a function and its representation in frequency. The frequency representation is found by using the Fourier transform for functions on the real line, or by Fourier series for periodic functions. Generalizing these transforms to other domains is generally called Fourier analysis, although the term is sometimes used interchangeably with harmonic analysis. Harmonic Analysis has become a vast subject with applications in areas as diverse as number theory, representation theory, signal processing, quantum mechanics, tidal analysis and neuroscience.

In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.

Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes . Although it is not possible to perfectly predict random events, much can be said about their behavior. Two major results in probability theory describing such behaviour are the law of large numbers and the central limit theorem.

In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events.

In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm designed to solve a search problem. Search algorithms work to retrieve information stored within particular data structure, or calculated in the search space of a problem domain, with either discrete or continuous values.

Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing signals, such as sound, images, potential fields, seismic signals, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal.
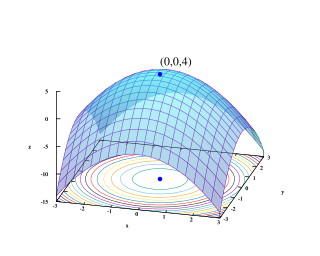
Mathematical optimization or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. Optimization problems arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries.

In probability and statistics, a probability mass function is a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value. Sometimes it is also known as the discrete density function. The probability mass function is often the primary means of defining a discrete probability distribution, and such functions exist for either scalar or multivariate random variables whose domain is discrete.

In dynamical systems theory and control theory, a phase space or state space is a space in which all possible "states" of a dynamical system or a control system are represented, with each possible state corresponding to one unique point in the phase space. For mechanical systems, the phase space usually consists of all possible values of position and momentum variables. It is the direct product of direct space and reciprocal space. The concept of phase space was developed in the late 19th century by Ludwig Boltzmann, Henri Poincaré, and Josiah Willard Gibbs.

In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Trajectory optimization is the process of designing a trajectory that minimizes some measure of performance while satisfying a set of constraints. Generally speaking, trajectory optimization is a technique for computing an open-loop solution to an optimal control problem. It is often used for systems where computing the full closed-loop solution is not required, impractical or impossible. If a trajectory optimization problem can be solved at a rate given by the inverse of the Lipschitz constant, then it can be used iteratively to generate a closed-loop solution in the sense of Caratheodory. If only the first step of the trajectory is executed for an infinite-horizon problem, then this is known as Model Predictive Control (MPC).
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
The Mathematics Subject Classification (MSC) is an alphanumerical classification scheme that has collaboratively been produced by staff of, and based on the coverage of, the two major mathematical reviewing databases, Mathematical Reviews and Zentralblatt MATH. The MSC is used by many mathematics journals, which ask authors of research papers and expository articles to list subject codes from the Mathematics Subject Classification in their papers. The current version is MSC2020.
Interpolation is a method of constructing new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points in the mathematical field of numerical analysis.
In mathematical physics, the concept of quantum spacetime is a generalization of the usual concept of spacetime in which some variables that ordinarily commute are assumed not to commute and form a different Lie algebra. The choice of that algebra still varies from theory to theory. As a result of this change some variables that are usually continuous may become discrete. Often only such discrete variables are called "quantized"; usage varies.
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled.

In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable may be continuous or discrete if they are typically obtained by measuring or counting, respectively. If it can take on two particular real values such that it can also take on all real values between them, the variable is continuous in that interval. If it can take on a value such that there is a non-infinitesimal gap on each side of it containing no values that the variable can take on, then it is discrete around that value. In some contexts a variable can be discrete in some ranges of the number line and continuous in others.
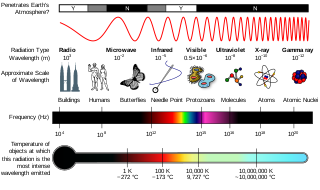
In the physical sciences, the term spectrum was introduced first into optics by Isaac Newton in the 17th century, referring to the range of colors observed when white light was dispersed through a prism. Soon the term referred to a plot of light intensity or power as a function of frequency or wavelength, also known as a spectral density plot.








