Distal interphalangeal joints are the articulations between the phalanges of the hand or foot. This term therefore includes:
Distal interphalangeal joints are the articulations between the phalanges of the hand or foot. This term therefore includes:

The lumbricals are intrinsic muscles of the hand that flex the metacarpophalangeal joints, and extend the interphalangeal joints.

A hammer toe or contracted toe is a deformity of the muscles and ligaments of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the second, third, fourth, or fifth toe causing it to be bent, resembling a hammer. In the early stage a flexible hammertoe is movable at the joints; a rigid hammertoe joint cannot be moved and usually requires surgery.

The phalanges are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.
PIJ may refer to:

The extensor digitorum muscle is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the radial nerve.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.
The knuckles are the joints of the fingers. The word is cognate to similar words in other Germanic languages, such as the Dutch "knokkel" (knuckle) or German "Knöchel" (ankle), i.e., Knöchlein, the diminutive of the German word for bone (Knochen). Anatomically, it is said that the knuckles consist of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints of the finger. The knuckles at the base of the fingers may be referred to as the 1st or major knuckles while the knuckles at the midfinger are known as the 2nd and 3rd, or minor, knuckles. However, the ordinal terms are used inconsistently and may refer to any of the knuckles.

The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow cavities on the proximal ends of the proximal phalanges. Being condyloid, they allow the movements of flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction at the joint.

A hinge joint is a bone joint in which the articular surfaces are molded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane. According to one classification system they are said to be uniaxial. The direction which the distal bone takes in this motion is seldom in the same plane as that of the axis of the proximal bone; there is usually a certain amount of deviation from the straight line during flexion.
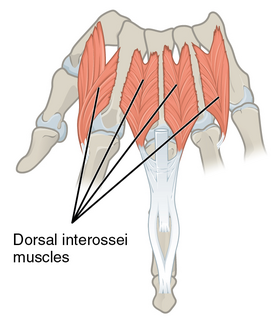
In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

The interphalangeal joints of the hand also known as Bitals, are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand.

Boutonniere deformity is a deformed position of the fingers or toes, in which the joint nearest the knuckle is permanently bent toward the palm while the farthest joint is bent back away. Causes include injury, inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, and genetic conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Interphalangeal joint may refer to:

The interphalangeal joints of the foot are between the phalanx bones of the toes in the feet.
Collateral ligament can refer to:

The collateral ligaments of interphalangeal joints are ligaments of the interphalangeal joints of the hand.
The collateral ligaments of the interphalangeal joints of the foot are fibrous bands that are situated on both sides of the interphalangeal joints of the toes.
Plantar ligament refer to ligaments in the sole of the foot:

An ulnar claw, also known as claw hand, or 'spinster's claw' is a deformity or an abnormal attitude of the hand that develops due to ulnar nerve damage causing paralysis of the lumbricals. A claw hand presents with a hyperextension at the metacarpophalangeal joints and flexion at the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints of the 4th and 5th fingers. The patients with this condition can make a full fist but when they extend their fingers, the hand posture is referred to as claw hand. The ring- and little finger can usually not fully extend at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP).