
H2 antagonists, sometimes referred to as H2RA and also called H2 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the histamine H2 receptors of the parietal cells in the stomach. This decreases the production of stomach acid. H2 antagonists can be used in the treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease. They have been surpassed by proton pump inhibitors (PPIs); the PPI omeprazole was found to be more effective at both healing and alleviating symptoms of ulcers and reflux oesophagitis than the H2 blockers ranitidine and cimetidine.
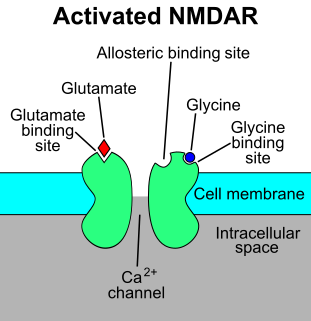
The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors. The other receptors are the AMPA and kainate receptors. It is activated when glutamate and glycine bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.
An antagonist is the character in a story who is against the protagonist.

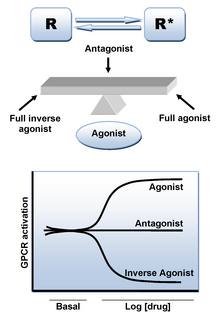
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers. In pharmacology, antagonists have affinity but no efficacy for their cognate receptors, and binding will disrupt the interaction and inhibit the function of an agonist or inverse agonist at receptors. Antagonists mediate their effects by binding to the active site or to the allosteric site on a receptor, or they may interact at unique binding sites not normally involved in the biological regulation of the receptor's activity. Antagonist activity may be reversible or irreversible depending on the longevity of the antagonist–receptor complex, which, in turn, depends on the nature of antagonist–receptor binding. The majority of drug antagonists achieve their potency by competing with endogenous ligands or substrates at structurally defined binding sites on receptors.

A dopamine antagonist (antidopaminergic) is a type of drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism. Most antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists, and as such they have found use in treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and stimulant psychosis. Several other dopamine antagonists are antiemetics used in the treatment of nausea and vomiting.
An endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) is a drug that blocks endothelin receptors.

Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists are a class of medications that antagonize the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor and thus the action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). They are used in the treatment of prostate cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, female infertility in assisted reproduction, and for other indications.
An opioid antagonist, or opioid receptor antagonist, is a receptor antagonist that acts on one or more of the opioid receptors.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of anesthetics that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.
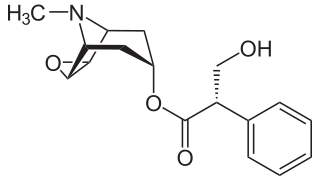
A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter whose receptor is a protein found in synapses and other cell membranes. Besides responding to their primary neurochemical, neurotransmitter receptors can be sensitive to a variety of other molecules. Acetylcholine receptors are classified into two groups based on this:

Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis and other allergies. Antihistamines can give relief when a person has nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives because of pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy. Typically people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic, over-the-counter drug with few side effects. As an alternative to taking an antihistamine, people who suffer from allergies can instead avoid the substance which irritates them. However, this is not always possible as some substances, such as pollen, are carried in the air, thus making allergic reactions caused by them generally unavoidable. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Doctors recommend that people talk to them before any longer term use of antihistamines.
An adrenergic antagonist is a drug that inhibits the function of adrenergic receptors. There are five adrenergic receptors, which are divided into two groups. The first group of receptors are the beta (β) adrenergic receptors. There are β1, β2, and β3 receptors. The second group contains the alpha (α) adrenoreceptors. There are only α1 and α2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors are located near the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. There are also α-adreno receptors that are located on vascular smooth muscle.
The orexin receptor (also referred to as the hypocretin receptor) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds the neuropeptide orexin. There are two variants, OX1 and OX2, each encoded by a different gene (HCRTR1, HCRTR2).

Bemesetron (MDL-72222) is a drug which acts as an antagonist at the 5HT3 receptor. It has antiemetic effects comparable to metoclopramide, however it is not used clinically, instead its main application is in scientific research studying the involvement of the 5HT3 receptor in the actions of drugs of abuse.

SB-399885 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 9.0nM. SB-399885 and other 5-HT6 antagonists show nootropic effects in animal studies, as well as antidepressant and anxiolytic effects which are comparable to and synergistic with drugs such as imipramine and diazepam, and have been proposed as potential novel treatments for cognitive disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease.

SB-271046 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It was one of the first selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonists to be discovered, and was found through high-throughput screening of the SmithKline Beecham Compound Bank using cloned 5-HT6 receptors as a target, with an initial lead compound being developed into SB-271046 through a structure-activity relationship (SAR) study. SB-271046 was found to be potent and selective in vitro and had good oral bioavailability in vivo, but had poor penetration across the blood–brain barrier, so further SAR work was then conducted, which led to improved 5-HT6 antagonists such as SB-357,134 and SB-399,885.
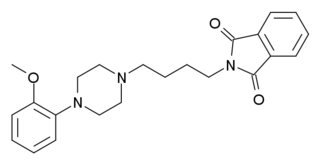
NAN-190 is a drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was previously believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but a subsequent discovery showed that it also potently blocks the α2-adrenergic receptor. The new finding has raised significant concerns about studies using NAN-190 as a specific serotonin receptor antagonist.

CGS-15943 is a drug which acts as a potent and reasonably selective antagonist for the adenosine receptors A1 and A2A, having a Ki of 3.3nM at A2A and 21nM at A1. It was one of the first adenosine receptor antagonists discovered that is not a xanthine derivative, instead being a triazoloquinazoline. Consequently, CGS-15943 has the advantage over most xanthine derivatives that it is not a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and so has more a specific pharmacological effects profile. It produces similar effects to caffeine in animal studies, though with higher potency.

AM-6545 is a drug which acts as a peripherally selective silent antagonist for the CB1 receptor, and was developed for the treatment of obesity. Other cannabinoid antagonists such as rimonabant have been marketed for this application, but have subsequently been withdrawn from sale because of centrally mediated side effects such as depression and nausea. Because AM-6545 does not cross the blood–brain barrier to any significant extent, it does not produce these kinds of side effects, but has still been shown to effectively reduce appetite and food consumption in animal studies.
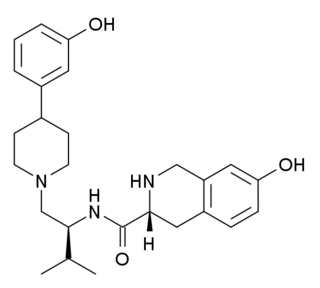
AT-076 is a so-called opioid "pan" antagonist and is the first reasonably balanced antagonist known of all four opioid receptor types. It acts as a silent antagonist of all four of the opioid receptors, behaving as a competitive antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor and δ-opioid receptor and as a noncompetitive antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor and nociceptin receptor. AT-076 was derived from the selective κ-opioid receptor antagonist JDTic via removal of the 3,4-dimethyl group of the trans-(3R,4R)-dimethyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperidine antagonist scaffold, which increased affinity for the nociceptin receptor by 10-fold and for the μ- and δ-opioid receptors by 3-6-fold.


















