RNA polymerase, both abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, official name DNA-directed RNA polymerase, is a member of a family of enzymes that are essential to life: they are found in all living organisms and many viruses. RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP has intrinsic helicase activity, therefore no separate enzyme is needed to unwind the DNA. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides.

DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes DNA molecules from deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.
A sigma factor is a protein needed for initiation of transcription in bacteria. It is a bacterial transcription initiation factor that enables specific binding of RNA polymerase (RNAP) to gene promoters. It is homologous to archaeal transcription factor B and to eukaryotic factor TFIIB. The specific sigma factor used to initiate transcription of a given gene will vary, depending on the gene and on the environmental signals needed to initiate transcription of that gene. Selection of promoters by RNA polymerase is dependent on the sigma factor that associates with it.

DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the primary enzyme complex involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. It was discovered by Thomas Kornberg and Malcolm Gefter in 1970. The complex has high processivity and, specifically referring to the replication of the E.coli genome, works in conjunction with four other DNA polymerases. Being the primary holoenzyme involved in replication activity, the DNA Pol III holoenzyme also has proofreading capabilities that corrects replication mistakes by means of exonuclease activity working 3'→5'. DNA Pol III is a component of the replisome, which is located at the replication fork.
dnaQ is the gene encoding the ε subunit of DNA polymerase III in Escherichia coli. The ε subunit is one of three core proteins in the DNA polymerase complex. It functions as a 3’→5’ DNA directed proofreading exonuclease that removes incorrectly incorporated bases during replication. dnaQ may also be referred to as mutD.

Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is the RNA component of the ribosome, and is essential for protein synthesis in all living organisms. It constitutes the predominant material within the ribosome, which is approximately 60% rRNA and 40% protein by weight, or 3/5 of ribosome mass. Ribosomes contain two major rRNAs and 50 or more proteins. The ribosomal RNAs form two subunits, the large subunit (LSU) and small subunit (SSU). The LSU rRNA acts as a ribozyme, catalyzing peptide bond formation. The SSU and LSU rRNA sequences are widely used for working out evolutionary relationships among organisms, since they are of ancient origin and are found in all known forms of life.
Prokaryotic translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in prokaryotes.
Translational frameshifting or ribosomal frameshifting refers to an alternative process of protein translation. A protein is translated from one end of the mRNA to the other, from the 5' to the 3' end. Normally a protein is translated from a template mRNA with consecutive blocks of 3 nucleotides being read as single amino acids. However, certain organisms may exhibit a change or shift in the ribosomes frame by one or two nucleotides when translating the genetic code. This is deemed translational or ribosomal frameshifting. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary or tertiary mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses, retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes.
The gene rpoS encodes the sigma factor sigma-38, a 37.8 kD protein in Escherichia coli. Sigma factors are proteins that regulate transcription in bacteria. Sigma factors can be activated in response to different environmental conditions. rpoS is transcribed in late exponential phase, and RpoS is the primary regulator of stationary phase genes. RpoS is a central regulator of the general stress response and operates in both a retroactive and a proactive manner: it not only allows the cell to survive environmental challenges, but it also prepares the cell for subsequent stresses (cross-protection). The transcriptional regulator CsgD is central to biofilm formation, controlling the expression of the curli structural and export proteins, and the diguanylate cyclase, adrA, which indirectly activates cellulose production. The rpoS gene most likely originated in the gammaproteobacteria.
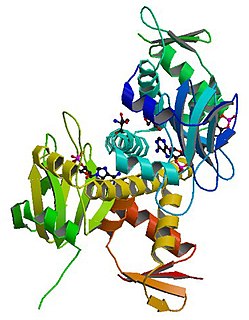
cAMP receptor protein is a regulatory protein in bacteria. CRP protein binds cAMP, which causes a conformational change that allows CRP to bind tightly to a specific DNA site in the promoters of the genes it controls. CRP then activates transcription through direct protein–protein interactions with RNA polymerase.
fis is an E. coli gene encoding the Fis protein. The regulation of this gene is more complex than most other genes in the E. coli genome, as Fis is an important protein which regulates expression of other genes. It is supposed that fis is regulated by H-NS, IHF and CRP. It also regulates its own expression (autoregulation). Fis is one of the most abundant DNA binding proteins in Escherichia coli under nutrient-rich growth conditions.
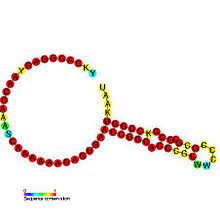
The hok/sok system is a postsegregational killing mechanism employed by the R1 plasmid in Escherichia coli. It was the first type I toxin-antitoxin pair to be identified through characterisation of a plasmid-stabilising locus. It is a type I system because the toxin is neutralised by a complementary RNA, rather than a partnered protein.

39S ribosomal protein L24, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRPL24 gene.
The gal operon is a prokaryotic operon, which encodes enzymes necessary for galactose metabolism. The operon contains two operators, OE and OI. The former is just before the promoter, and the latter is just after the galE gene.
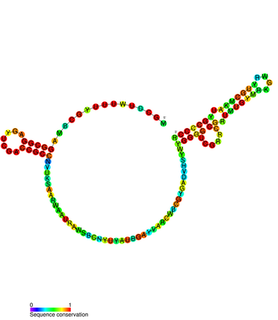
ALIL pseudoknot is an RNA element that induces frameshifting in bacteria. The expression of a minority of genes requires frameshifting to occur where the frequency of frameshifting is increased by a RNA secondary structure located on the 3' side of the shift site. This structure can be either a pseudoknot or a stem-loop and acts as a physical barrier to mRNA translocation so therefore causes ribosome pausing.

The JUMPstart RNA motif describes a conserved RNA-based secondary structure associated with JUMPstart elements. The 39-base-pair JUMPstart sequence describes a conserved element upstream of genes that participate in polysaccharide synthesis. The JUMPstart element has been shown to function as an RNA, and is present in the 5' untranslated regions of the genes it regulates.
16S rRNA (adenine1518-N6/adenine1519-N6)-dimethyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.182, S-adenosylmethionine-6-N',N'-adenosyl (rRNA) dimethyltransferase, KsgA, ksgA methyltransferase) is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:16S rRNA (adenine1518-N6/adenine1519-N6)-dimethyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
A slippery sequence is a small section of codon nucleotide sequences that controls the rate of ribosomal frameshifting. A slippery sequence causes a faster ribosomal transfer which in turn can cause the reading ribosome to "slip." This allows a tRNA to shift by 1 base after it has paired with its anticodon, changing the reading frame.
The locus of enterocyte effacement-encoded regulator (Ler) is a regulatory protein that controls bacterial pathogenicity of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC). More specifically, Ler regulates the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) pathogenicity island genes, which are responsible for creating intestinal attachment and effacing lesions and subsequent diarrhea: LEE1, LEE2, and LEE3. LEE1, 2, and 3 carry the information necessary for a type III secretion system. The transcript encoding the Ler protein is the open reading frame 1 on the LEE1 operon.