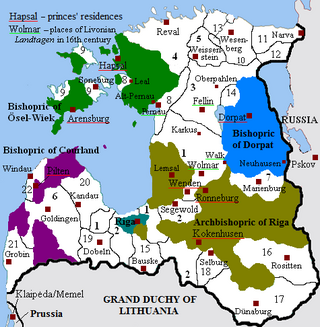
Livonia or in earlier records Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.

The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Christian military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the pagan Baltic, Finnic and West Slavic peoples around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, and also against Orthodox Christian East Slavs.
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204 for the second time. The membership of the crusading order comprised warrior monks, mostly from northern Germany, who fought Baltic and Finnic polytheists in the area of modern-day Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Alternative names of the Order include Christ Knights, Swordbrothers, Sword Brethren, Order of the Brothers of the Sword, and The Militia of Christ of Livonia. The seal reads: +MAGISTRI ETFRM MILICIE CRI (Christi) DE LIVONIA.

Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the south central part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) against the German crusaders and Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades. Semigallians had close linguistic and cultural ties with Samogitians.
The Battle of Aizkraukle or Ascheraden was fought on 5 March 1279 between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led by Traidenis, and the Livonian branch of the Teutonic Order near Aizkraukle in present-day Latvia. The order suffered a great defeat: 71 knights, including the grand master, Ernst von Rassburg, and Eilart Hoberg, leader of the knights from Danish Estonia, were killed. It was the second-largest defeat of the order in the 13th century. After the battle Duke Nameisis of the Semigallians recognized Traidenis as his suzerain.

Jelgava is a state city in central Latvia about 41 kilometres southwest of Riga. It is the largest town in the region of Zemgale (Semigalia). Jelgava was the capital of the united Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1578–1795) and was the administrative center of the Courland Governorate (1795–1918).

Semigallia, also spelt Semigalia, is one of the Historical Latvian Lands located to the south of the Daugava river and to the north of the Saule region of Samogitia. The territory is split between Latvia and Lithuania, previously inhabited by the Semigallian Baltic tribe. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) against the German crusaders and Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades. Semigallians had close linguistic and cultural ties with Samogitians.

Koknese is a town in Aizkraukle Municipality in the Vidzeme region of Latvia, on the right bank of the Daugava River. It has a population of nearly 3,000.

Dobele is a town in the cultural region Zemgale in Latvia, and is located near the center of Latvia on the banks of the river Bērze. It received town rights in 1917 whilst being a part of the German occupied Courland Governorate during the First World War. As of 2020, the population was 8,856.

Viestards was one of the greatest Semigallian dukes in the 13th century, referred to as King Vester.

Bauska Castle is a complex consisting of the ruins of an earlier castle and a later palace on the outskirts of the Latvian city of Bauska.

The Battle of Skuodas or Schoden was a medieval battle fought in ca. 1259 near Skuodas in present-day Lithuania during the Lithuanian Crusade. The Samogitian army of 3,000 invaded Courland and on their way back defeated the Livonian Order, killing 33 knights and many more low-rank soldiers. In terms of knights killed, it was the eighth largest defeat of the Livonian Order in the 13th century. This victory led to a Semigallian insurrection against the Livonian crusaders, which lasted from 1259 to 1272.

The Battle of Durbe was a medieval battle fought near Durbe, 23 km (14 mi) east of Liepāja, in present-day Latvia during the Livonian Crusade. On 13 July 1260, the Samogitians soundly defeated the joint forces of the Teutonic Knights from Prussia and the Livonian Order from Livonia. Some 150 knights were killed, including Livonian master Burkhard von Hornhausen and Prussian land marshal Heinrich Botel. It was by far the largest defeat of the knights in the 13th century: in the second-largest, the Battle of Aizkraukle, 71 knights were killed. The battle inspired the Great Prussian Uprising and the rebellions of the Semigallians, the Couronians, and the Oeselians. The battle undid two decades of Livonian conquests and it took some thirty years for the Livonian Order to restore its control.

Tērvete is a village in Tērvete Parish, Dobele Municipality in the Semigallia region of Latvia. It is famous for the historic hillfort built for the kings of Western Semigallia (Zemgale) in the Middle Ages.

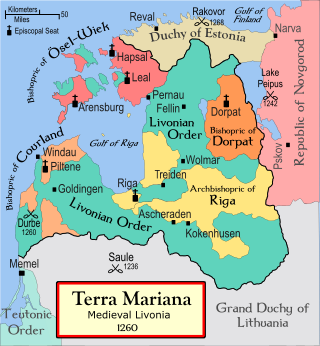
The Livonian crusade consists of the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – modern Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal-sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12th–13th century. The Livonian crusade was conducted mostly by the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Denmark. It ended with the creation of Terra Mariana and the Danish duchy of Estonia. The lands on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea were one of the last parts of Europe to be Christianised. The available information is largely based on Livonian Chronicle of Henry.

Kandava is a town in Tukums Municipality, in the Courland region of Latvia. It had a population of 3,656 people as of January 2020.

Grobiņa Castle is a medieval castle located in the town of Grobiņa, in South Kurzeme Municipality in the Courland region of Latvia. The ancient Curonian castle hill is located only 100 m from the castle. It is supposed to be the famous Seeburg, which is mentioned in Scandinavian sources as early as the 9th century.

The ruins of Embūte Castle are located in Embūte, Embūte Parish, South Kurzeme Municipality in the Courland region of Latvia, not far from an ancient hillfort erected by Curonians. It was an ancient Curonian settlement and is mentioned in ancient chronicles as a place with strong Curonian resistance to German crusaders. The bishop's castle was built as a border castle with Lithuania by Livonian Order on a steep hill on the right bank of the Lanka river, which flows into left tributary of the Venta. Later manor house was built using the walls of the former castle, which can be seen in the division of the rooms and the building material. Today, the ruins are surrounded by trees and are in poor condition.

Dinaburga Castle, also known as Vecdaugavpils or Vecpils, is a castle located in Naujene Parish, Augšdaugava Municipality in the Latgale region of Latvia, east of Daugavpils. It is strategically situated on a high bank of the Daugava River. It was built between 1273 and 1277 by the Livonian Order, and destroyed by Russian troops before 1577. Nowadays, fragments of the foundation are exposed.

Nameisis or Namejs was a Semigallian duke in the second half of the 13th century. He ruled in the western part of Semigallia, with his capital at Tērvete. In 1279–81, he led a Semigallian uprising against the Livonian Order, a crusading military order. Very little is known about his life. He is mentioned only in the Livonian Rhymed Chronicle and in some documents from the 14th century. For this reason he is sometimes referred as semi legendary ruler in Latvian historiography.





















