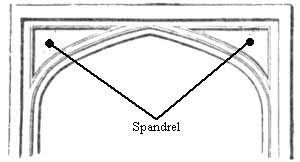
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements.
Flag terminology is the nomenclature, or system of terms, used in vexillology, the study of flags, to describe precisely the parts, patterns, and other attributes of flags and their display.

A dome is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them.

A tent is a shelter consisting of sheets of fabric or other material draped over, attached to a frame of poles or a supporting rope. While smaller tents may be free-standing or attached to the ground, large tents are usually anchored using guy ropes tied to stakes or tent pegs. First used as portable homes by nomads, tents are now more often used for recreational camping and as temporary shelters.

Stairs are a structure designed to bridge a large vertical distance between lower and higher levels by dividing it into smaller vertical distances. This is achieved as a diagonal series of horizontal platforms called steps which enable passage to the other level by stepping from one to another step in turn. Steps are very typically rectangular. Stairs may be straight, round, or may consist of two or more straight pieces connected at angles.
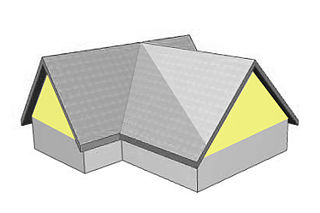
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesthetic concerns. The term gable wall or gable end more commonly refers to the entire wall, including the gable and the wall below it. Some types of roof do not have a gable. One common type of roof with gables, the gable roof, is named after its prominent gables.
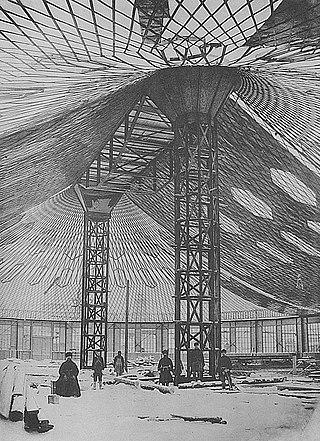
A tensile structure is a construction of elements carrying only tension and no compression or bending. The term tensile should not be confused with tensegrity, which is a structural form with both tension and compression elements. Tensile structures are the most common type of thin-shell structures.

A wigwam, wickiup, wetu (Wampanoag), or wiigiwaam is a semi-permanent domed dwelling formerly used by certain Native American tribes and First Nations people and still used for ceremonial events. The term wickiup is generally used to refer to these kinds of dwellings in the Southwestern United States and Western United States and Northwest Alberta, Canada, while wigwam is usually applied to these structures in the Northeastern United States as well as Ontario and Quebec in central Canada. The names can refer to many distinct types of Indigenous structures regardless of location or cultural group. The wigwam is not to be confused with the Native Plains tipi, which has a different construction, structure, and use.

Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel. The alternative to framed construction is generally called mass wall construction, where horizontal layers of stacked materials such as log building, masonry, rammed earth, adobe, etc. are used without framing.

An awning or overhang is a secondary covering attached to the exterior wall of a building. It is typically composed of canvas woven of acrylic, cotton or polyester yarn, or vinyl laminated to polyester fabric that is stretched tightly over a light structure of aluminium, iron or steel, possibly wood or transparent material. The configuration of this structure is something of a truss, space frame or planar frame. Awnings are also often constructed of aluminium understructure with aluminium sheeting. These aluminium awnings are often used when a fabric awning is not a practical application where snow load as well as wind loads may be a factor.

A lampshade is a fixture that covers the lightbulb on a lamp to diffuse the light it emits. Lampshades can be made out of a wide variety of materials like paper, glass, fabric or stone. Usually conical or cylindrical in shape, lampshades can be found on floor, desk, tabletop, or suspended lamps. The term can also apply to the glass hung under many designs of ceiling lamp. Beyond its practical purpose, significant emphasis is also usually given to decorative and aesthetic features. A lamp shade also serves to "shade" human eyes from the direct glare of the light bulbs used to illuminate the lamp. Some lamp shades are also lined with a hard-backed opaque lining, often white or gold, to reflect as much light as possible through the top and bottom of the shade while blocking light from emitting through the walls of the shade itself. In other cases, the shade material is deliberately decorative so that upon illumination it may emphasize a display of color and light emitting through the shade surface itself.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

The Volkswagen Westfalia Camper was a conversion of the Volkswagen Type 2, and then, the Volkswagen Type 2 (T3), sold from the early 1950s to 2003. Volkswagen subcontracted the modifications to the company Westfalia-Werke in Rheda-Wiedenbrück.

In architecture, a vault is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed.

A window valance is a form of window treatment that covers the uppermost part of the window and can be hung alone or paired with other window blinds, or curtains. Valances are a popular decorative choice in concealing drapery hardware. Window valances were popular in Victorian interior design. In draping or bunting form they are commonly referred to as swag.

A goahti, goahte, gåhte, gåhtie or gåetie, ,, is a Sami hut or tent of three types of covering: fabric, peat moss or timber. The fabric-covered goahti looks very similar to a Sami lavvu, but often constructed slightly larger. In its tent version the goahti is also called a 'curved pole' lavvu, or a 'bread box' lavvu as the shape is more elongated while the lavvu is in a circular shape.

A pole marquee or pole tent is a variety of large tent often used to shelter summer events such as shows, festivals, and weddings. They are particularly associated with typical English country garden weddings and village fetes.

A hip roof, hip-roof or hipped roof, is a type of roof where all sides slope downwards to the walls, usually with a fairly gentle slope. Thus, a hipped roof has no gables or other vertical sides to the roof.

The Forester tent is meant for canoeing and hiking, especially in wilderness areas. It is spacious for its weight, providing a comfortable shelter with standing room at the front and storage room at the back. It is well suited to inclement weather.


















