Fly fishing is an angling technique that uses an ultralight-weight lure called an artificial fly, which typically mimics small invertebrates such as flying and aquatic insects to attract and catch fish. Because the mass of the fly lure is insufficient to overcome air resistance, it cannot be launched far using conventional gears and techniques, so specialized tackles are used instead and the casting techniques are significantly different from other forms of angling. It is also very common for the angler to wear waders, carry a hand net, and stand in the water when fishing.

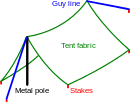
A tent is a shelter consisting of sheets of fabric or other material draped over, attached to a frame of poles or a supporting rope. While smaller tents may be free-standing or attached to the ground, large tents are usually anchored using guy ropes tied to stakes or tent pegs. First used as portable homes by nomads, tents are now more often used for recreational camping and as temporary shelters.
In literature and writing, stylistically elements are the use of any of a variety of techniques to give an auxiliary meaning, ideas, or feeling to the literalism or written.
A story arc is the chronological construction of a plot in a novel or story. It can also mean an extended or continuing storyline in episodic storytelling media such as television, comic books, comic strips, board games, video games, and films with each episode following a dramatic arc. On a television program, for example, the story would unfold over many episodes. In television, the use of the story arc is common in sitcoms, and even more so in soap operas. In a traditional Hollywood film, the story arc usually follows a three-act structure. Webcomics are more likely to use story arcs than newspaper comics, as most webcomics have readable archives online that a newcomer to the strip can read in order to understand what is going on. Although story arcs have existed for decades, one of the first appearances of the term was in 1973 by Time Magazine for a synopsis of the movie The Friends of Eddie Coyle: "He accomplishes this with no sacrifice to the pacing of his action sequences or the suspenseful development of his story's arc."
Orr is a fictional character in the classic 1961 novel Catch-22 by Joseph Heller. Orr is a World War II bomber pilot who shares a tent with his good friend, the protagonist of the novel, Yossarian. Described as "a warm-hearted, simple-minded gnome," Orr is generally considered crazy. His most notable feature is repeatedly being shot down over water, but, until his final flight, always managing to survive along with his entire crew. On his final flight, perhaps two-thirds of the way through the novel, he is again shot down into the Mediterranean, and is lost at sea. Only in the last ten pages of the novel does Heller reveal that Orr's crashes were part of an elaborate plot to escape the war.

Myiasis, also known as flystrike or fly strike, is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) that grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species can create an infestation even on unbroken skin and have been known to use moist soil and non-myiatic flies as vector agents for their parasitic larvae.

A carport is a covered structure used to offer limited protection to vehicles, primarily cars, from rain and snow. The structure can either be free standing or attached to a wall. Unlike most structures, a carport does not have four walls, and usually has one or two. Carports offer less protection than garages but allow for more ventilation. In particular, a carport prevents frost on the windshield. A "mobile" and/or "enclosed" carport has the same purpose as a standard carport. However, it may be removed/relocated and is typically framed with tubular steel and may have canvas or vinyl type covering which encloses the complete frame, including walls. It may have an accessible front entry or open entryway not typically attached to any structure or fastened in place by permanent means put held in place by stakes. It is differentiated from a tent by its main purpose: to house vehicles and/or motorized equipment.

A rash guard, also known as rash vest or rashie, is an athletic shirt made of spandex and nylon or polyester. The name rash guard reflects the fact that the shirt protects the wearer against rashes caused by abrasion, or by sunburn from extended exposure to the sun, as sun protective clothing.

In aviation, instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) are weather conditions that require pilots to fly primarily by reference to flight instruments, and therefore under instrument flight rules (IFR), as opposed to flying by outside visual references under visual flight rules (VFR). Typically, this means flying in cloud or poor weather, where little or nothing can be seen or recognised when looking out of the window. Simulated IMC can be achieved for training purposes by wearing view-limiting devices, which restrict outside vision and force the trainee to rely on instrument indications only.

Fly tying is the process of producing an artificial fly used by fly fishing anglers to catch fish. Fly tying is a manual process done by a single individual using hand tools and a variety of natural and manmade materials that are attached to a hook. Although the recent history of fly tying dates from the middle 1800s, fly tyers were engaged in tying flys since at least 200 AD.

A horse blanket or rug is a blanket or animal coat intended for keeping a horse or other equine warm or otherwise protected from wind or other elements. They are tailored to fit around a horse's body from chest to rump, with straps crossing underneath the belly to secure the blanket yet allowing the horse to move about freely. Most have one or two straps that buckle in front, but a few designs have a closed front and must be slipped over a horse's head. Some designs also have small straps that loop lightly around the horse's hind legs to prevent the blanket from slipping sideways.
Text linguistics is a branch of linguistics that deals with texts as communication systems. Its original aims lay in uncovering and describing text grammars. The application of text linguistics has, however, evolved from this approach to a point in which text is viewed in much broader terms that go beyond a mere extension of traditional grammar towards an entire text. Text linguistics takes into account the form of a text, but also its setting, i. e. the way in which it is situated in an interactional, communicative context. Both the author of a text as well as its addressee are taken into consideration in their respective roles in the specific communicative context. In general it is an application of discourse analysis at the much broader level of text, rather than just a sentence or word.

A bivouac shelter or bivvy is any of a variety of improvised camp site or shelter that is usually of a temporary nature, used especially by soldiers or people engaged in backpacking, bikepacking, scouting or mountain climbing. It may often refer to sleeping in the open with a bivouac sack, but it may also refer to a shelter constructed of natural materials like a structure of branches to form a frame, which is then covered with leaves, ferns and similar material for waterproofing and duff for insulation. Modern bivouacs often involve the use of one- or two-person tents but may also be without tents or full cover. In modern mountaineering the nature of the bivouac shelter will depend on the level of preparedness, in particular whether existing camping and outdoor gear may be incorporated into the shelter.

A hut is a small dwelling, which may be constructed of various local materials. Huts are a type of vernacular architecture because they are built of readily available materials such as wood, snow, ice, stone, grass, palm leaves, branches, clay, hides, fabric, or mud using techniques passed down through the generations.

The Aussie salute, otherwise known as the Barcoo salute, is the gesture commonly deployed all across Australia to deter bush flies from the human face.
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the complement is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a predicate-argument structure. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call arguments actants, following Lucien Tesnière (1959).

Fishing tackle is the equipment used by anglers when fishing. Almost any equipment or gear used in fishing can be called fishing tackle, examples being hooks, lines, baits/lures, rods, reels, floats, sinkers/feeders, nets, spears, gaffs and traps, as well as wires, snaps, beads, spoons, blades, spinners, clevises and tools that make it easy to tie knots.

A fly or flye is a strength training exercise in which the hand and arm move through an arc while the elbow is kept at a constant angle. Flies are used to work the muscles of the upper body. Because these exercises use the arms as levers at their longest possible length, the amount of weight that can be moved is significantly less than equivalent press exercises for the same muscles . Due to this leverage, fly exercises of all types have a large potential to damage the shoulder joint and its associated ligaments and the tendons of the muscles connecting to it. They should be done with caution and their effects first tested while using very light weights; which are gradually incremented after more strength is gained.

A pandal in India and neighbouring countries, is a fabricated structure, either temporary or permanent, that is used at many places such as either outside a building or in an open area such as along a public road or in front of a house. This canopy or big tent is often used in a religious or other events that gathers people together, such as a wedding, fair, exhibition or festival.
The friendly fly or large flesh fly, Sarcophaga aldrichi, is a fly that is a parasitoid of the forest tent caterpillar. It strongly resembles the house fly but is in a different family, the Sarcophagidae, or flesh-flies. It is a little larger than the house fly, and has the same three black stripes on its thorax. It has red eyes, a grayish body, and a checkered abdomen.