Canvas is an extremely durable plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, shelters, as a support for oil painting and for other items for which sturdiness is required, as well as in such fashion objects as handbags, electronic device cases, and shoes. It is popularly used by artists as a painting surface, typically stretched across a wooden frame.

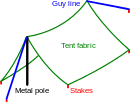
A tent is a shelter consisting of sheets of fabric or other material draped over, attached to a frame of poles or a supporting rope. While smaller tents may be free-standing or attached to the ground, large tents are usually anchored using guy ropes tied to stakes or tent pegs. First used as portable homes by nomads, tents are now more often used for recreational camping and as temporary shelters.

A tipi, often called a lodge in English, is a conical tent, historically made of animal hides or pelts, and in more recent generations of canvas, stretched on a framework of wooden poles. The word is Siouan, and in use in Dakhótiyapi, Lakȟótiyapi, and as a loanword in US and Canadian English, where it is sometimes spelled phonetically as teepee and tepee.

A tarpaulin or tarp is a large sheet of strong, flexible, water-resistant or waterproof material, often cloth such as canvas or polyester coated with polyurethane, or made of plastics such as polyethylene. Tarpaulins often have reinforced grommets at the corners and along the sides to form attachment points for rope, allowing them to be tied down or suspended.

A shelter-half is a simple kind of partial tent designed to provide temporary shelter and concealment when combined with one or more sections. Two sheets of canvas or a similar material are fastened together with snaps, straps or buttons to form a larger surface. The shelter-half is then erected using poles, ropes, pegs, and whatever tools are on hand, forming an inverted V structure. Small tents like these are often called pup tents in American English.
Helsinki slang or stadin slangi is a local dialect and a sociolect of the Finnish language mainly used in the capital city of Helsinki. It is characterized by its abundance of foreign loan words not found in the other Finnish dialects.

Bushcraft is the use and practice of skills, thereby acquiring and developing knowledge and understanding, in order to survive and thrive in a natural environment.

A bivouac shelter is any of a variety of improvised camp site, or shelter that is usually of a temporary nature, used especially by soldiers, or people engaged in backpacking, bikepacking, scouting, or mountain climbing. It may often refer to sleeping in the open with a bivouac sack, but it may also refer to a shelter constructed of natural materials like a structure of branches to form a frame, which is then covered with leaves, ferns, and similar material for waterproofing and duff for insulation. Modern bivouacs often involve the use of one- or two-man tents but may also be without tents or full cover. In modern mountaineering the nature of the bivouac shelter will depend on the level of preparedness, in particular whether existing camping and outdoor gear may be incorporated into the shelter. A bivouac shelter is colloquially known as a bivvy.

A lean-to is a type of simple structure originally added to an existing building with the rafters "leaning" against another wall. Free-standing lean-to structures are generally used as shelters. One traditional type of lean-to is known by its Finnish name laavu.

An awning or overhang is a secondary covering attached to the exterior wall of a building. It is typically composed of canvas woven of acrylic, cotton or polyester yarn, or vinyl laminated to polyester fabric that is stretched tightly over a light structure of aluminium, iron or steel, possibly wood or transparent material. The configuration of this structure is something of a truss, space frame or planar frame. Awnings are also often constructed of aluminium understructure with aluminium sheeting. These aluminium awnings are often used when a fabric awning is not a practical application where snow load as well as wind loads may be a factor.

Lavvu is a temporary dwelling used by the Sami people of northern extremes of Northern Europe. It has a design similar to a Native American tipi but is less vertical and more stable in high winds. It enables the indigenous cultures of the treeless plains of northern Scandinavia and the high arctic of Eurasia to follow their reindeer herds. It is still used as a temporary shelter by the Sami, and increasingly by other people for camping. It should not be confused with the goahti, another type of Sami dwelling, or the Finnish laavu.

The Volkswagen Westfalia Camper was a conversion of the Volkswagen Type 2, and then, the Volkswagen Type 2 (T3), sold from the early 1950s to 2003. Volkswagen subcontracted the modifications to the company Westfalia-Werke in Rheda-Wiedenbrück.

A bell tent is a human shelter for inhabiting, traveling or leisure that has been used since 600AD. The design is a simple structure, supported by a single central pole, covered with cotton canvas. The stability of the tent is reinforced with tension by guy ropes connected around the top of the walls and being held down by pegs around the circumference to the ground. It has a circular floor plan of some 10 ft and larger.
The multiple sizes of bell tents can be suited to their use or preference and most have a spacious interior, with room to sleep a number of people.

Ultralight backpacking is a subset of lightweight backpacking, a style of backpacking which emphasizes carrying the lightest and least amount of gear. While no technical standards exist, some United States hikers consider "ultralight" to mean an initial base weight of less than 4.5kg. Base weight is the weight of a fully loaded backpack at the start of a trip, plus the gear inside and outside it, excluding consumables such as food, water, and fuel. Base weight can be lowered by reducing the weight of individual items of gear, or by choosing not to carry that gear. Ultralight backpacking is most popular among thru-hikers—those hikers on extended trips requiring resupply.
Iittala, founded as a glassworks in 1881, is a Finnish design brand specialising in design objects, tableware and cookware. Iittala's official i-logo was designed by Timo Sarpaneva in 1956.

A tarp tent is a tarpaulin, a plastic or nylon sheet, used in place of a tent. It is usually rigged with poles, tent pegs, and guy lines. Ultralight backpackers use tarp tents because they are lightweight compared to other backpacking shelters.

A goahti, goahte, gåhte, gåhtie or gåetie, ,, is a Sami hut or tent of three types of covering: fabric, peat moss or timber. The fabric-covered goahti looks very similar to a Sami lavvu, but often constructed slightly larger. In its tent version the goahti is also called a 'curved pole' lavvu, or a 'bread box' lavvu as the shape is more elongated while the lavvu is in a circular shape.

A pole marquee or pole tent is a variety of large tent often used to shelter summer events such as shows, festivals, and weddings. They are particularly associated with typical English country garden weddings and village fetes.

A Whymper tent is a ridge tent of A-frame construction used for mountaineering which was designed by English mountaineer Edward Whymper (1840–1911) and named after him. Whymper was the first person to ascend the Matterhorn. Tents using his general design were in common use from the later part of the nineteenth century to the mid-twentieth century and were referred to generically as "Whymper tents". A later smaller variant of the design was called the Meade tent.
The Forester tent is meant for canoeing and hiking, especially in wilderness areas. It is spacious for its weight, providing a comfortable shelter with standing room at the front and storage room at the back. It is well suited to inclement weather.