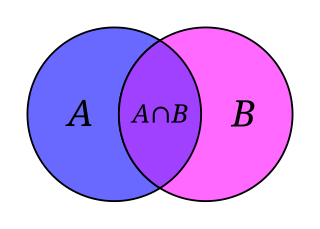
Set theory is a branch of mathematical logic that studies sets, which informally are collections of objects. Although any type of object can be collected into a set, set theory is applied most often to objects that are relevant to mathematics. The language of set theory can be used to define nearly all mathematical objects.
Leadership is both a research area and a practical skill encompassing the ability of an individual or organization to "lead" or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints, contrasting Eastern and Western approaches to leadership, and also United States versus European approaches. U.S. academic environments define leadership as "a process of social influence in which a person can enlist the aid and support of others in the accomplishment of a common task".

Acculturation is a process of social, psychological, and cultural change that stems from the balancing of two cultures while adapting to the prevailing culture of the society. Individuals of a differing culture try to incorporate themselves into the new more prevalent culture by participating in aspects of the more prevalent culture, such as their traditions, but still hold onto their original cultural values and traditions. The effects of acculturation can be seen at multiple levels in both the devotee of the prevailing culture and those who are assimilating into the culture.

Mobile Fighter G Gundam, also known in Japan as Mobile Fighting Legend G Gundam, is a 1994 Japanese animated television series produced by Sunrise and the fifth installment in the long running Gundam franchise. The series is set in the "Future Century", where space colonies representing countries have agreed to hold an organized fighting tournament known as the "Gundam Fight" every four years to settle their political differences in place of war. Each colony sends a representative fighter piloting a giant, humanoid mecha called a Gundam to battle on Earth until only one is left, and the winning nation earns the right to govern over all the colonies until the next tournament. The events of G Gundam follow Domon Kasshu, the pilot of Neo Japan's Shining Gundam during the 13th Gundam Fight. Domon's mission is to both win the tournament and to track down his older brother, who is believed to have stolen the mysterious Devil Gundam from the Neo Japan government.
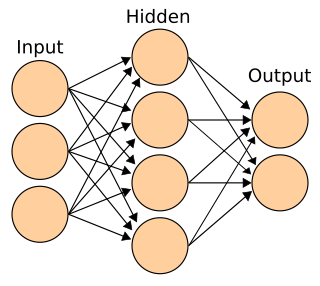
Connectionism is an approach in the fields of cognitive science, that hopes to explain mental phenomena using artificial neural networks (ANN).

Saharon Shelah is an Israeli mathematician. He is a professor of mathematics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Rutgers University in New Jersey.
In social psychology, group polarization refers to the tendency for a group to make decisions that are more extreme than the initial inclination of its members. These more extreme decisions are towards greater risk if individuals' initial tendencies are to be risky and towards greater caution if individuals' initial tendencies are to be cautious. The phenomenon also holds that a group's attitude toward a situation may change in the sense that the individuals' initial attitudes have strengthened and intensified after group discussion, a phenomenon known as attitude polarization.

In computer science, concurrency refers to the ability of different parts or units of a program, algorithm, or problem to be executed out-of-order or in partial order, without affecting the final outcome. This allows for parallel execution of the concurrent units, which can significantly improve overall speed of the execution in multi-processor and multi-core systems. In more technical terms, concurrency refers to the decomposability property of a program, algorithm, or problem into order-independent or partially-ordered components or units.
Distributed cognition is an approach to cognitive science research that deploys models of the extended mind by taking as the fundamental unit of analysis "a collection of individuals and artifacts and their relations to each other in a particular work practice". "DCog" is a specific approach to distributed cognition which takes a computational perspective towards goal-based activity systems. Dcog frameworks employed were originally developed in the mid-1980s by Edwin Hutchins, who continues to be the leading pioneer and whose research is based at the University of California at San Diego.
Nancy Ann Lynch is a mathematician, a theorist, and a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She is the NEC Professor of Software Science and Engineering in the EECS department and heads the "Theory of Distributed Systems" research group at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.

Léonie Duquet was a French nun who was arrested in December 1977 in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and "disappeared". She was believed killed by the military regime of Argentine President Jorge Rafael Videla during the Dirty War. Alice Domon, a French nun working with Duquet, disappeared a few days later. They had been working in poor neighborhoods of Buenos Aires in the 1970s and supported the Mothers of the Plaza de Mayo, founded in 1977. Despite repeated efforts by France to trace the sisters, the Argentine military dictatorship was unresponsive. In 1990 a French court in Paris tried Argentine Captain Alfredo Astiz, known to have arrested Duquet and believed implicated in the "disappearance" of Domon, for kidnapping the two sisters. He was convicted and sentenced to life imprisonment in absentia. In Argentina at the time, he and other military and security officers were shielded from prosecution by Pardon Laws passed in 1986 and 1987. These were repealed in 2003 and ruled unconstitutional in 2005, and the government re-opened prosecution of war crimes.

Kenneth Noble Stevens was the Clarence J. LeBel Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and Professor of Health Sciences and Technology at the Research Laboratory of Electronics at MIT. Stevens was head of the Speech Communication Group in MIT's Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE), and was one of the world's leading scientists in acoustic phonetics.
Transactive memory is a psychological hypothesis first proposed by Daniel Wegner in 1985 as a response to earlier theories of "group mind" such as groupthink. A transactive memory system is a mechanism through which groups collectively encode, store, and retrieve knowledge. Transactive memory was initially studied in couples and families where individuals had close relationships but was later extended to teams, larger groups, and organizations to explain how they develop a "group mind", a memory system that is more complex and potentially more effective than that of any of its individual constituents. A transactive memory system includes memory stored in each individual, the interactions between memory within the individuals, as well as the processes that update this memory. Transactive memory, on the other hand, is merely the shared store of knowledge.
Hierarchical temporal memory (HTM) is a biologically constrained theory of intelligence, originally described in the 2004 book On Intelligence by Jeff Hawkins with Sandra Blakeslee. HTM is based on neuroscience and the physiology and interaction of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex of the mammalian brain.
The goal of most research on group development is to learn why and how small groups change over time. To do this, researchers examine patterns of change and continuity in groups over time. Aspects of a group that might be studied include the quality of the output produced by a group, the type and frequency of its activities, its cohesiveness, the existence of group conflict.
Domon is a surname, belonging to several languages, and may refer to:
Connectivism is a theory of learning in a digital age that emphasizes the role of social and cultural context in how and where learning occurs. Learning does not simply happen within an individual, but within and across the networks. What sets connectivism apart from theories such as constructivism is the view that "learning can reside outside of ourselves, is focused on connecting specialized information sets, and the connections that enable us to learn more are more important than our current state of knowing". Connectivism sees knowledge as a network and learning as a process of pattern recognition. Connectivism has similarities with Vygotsky's zone of proximal development (ZPD) and Engeström's Activity theory. The phrase "a learning theory for the digital age" indicates the emphasis that connectivism gives to technology's effect on how people live, communicate, and learn.
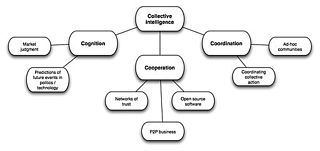
Collective intelligence (CI) is shared or group intelligence that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision making. The term appears in sociobiology, political science and in context of mass peer review and crowdsourcing applications. It may involve consensus, social capital and formalisms such as voting systems, social media and other means of quantifying mass activity. Collective IQ is a measure of collective intelligence, although it is often used interchangeably with the term collective intelligence. Collective intelligence has also been attributed to bacteria and animals.
Groupthink is a psychological phenomenon that occurs within a group of people in which the desire for harmony or conformity in the group results in an irrational or dysfunctional decision-making outcome. Group members try to minimize conflict and reach a consensus decision without critical evaluation of alternative viewpoints by actively suppressing dissenting viewpoints, and by isolating themselves from outside influences.














