Related Research Articles

The Davis Station, commonly called Davis, is one of three permanent bases and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Davis is situated on the coast of Cooperation Sea in Princess Elizabeth Land, Ingrid Christensen Coast in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Davis lies in the Antarctic oasis, a remarkable ice free area known as the Vestfold Hills.

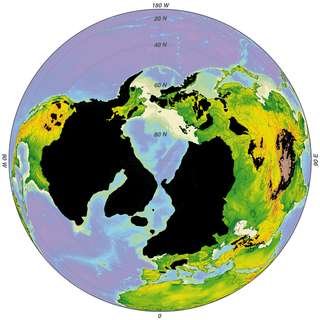
The Antarctic Plate is a tectonic plate containing the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and extending outward under the surrounding oceans. After breakup from Gondwana, the Antarctic plate began moving the continent of Antarctica south to its present isolated location causing the continent to develop a much colder climate. The Antarctic Plate is bounded almost entirely by extensional mid-ocean ridge systems. The adjoining plates are the Nazca Plate, the South American Plate, the African Plate, the Somali Plate, the Indo-Australian Plate, the Pacific Plate, and, across a transform boundary, the Scotia Plate.

The Last Glacial Period (LGP) occurred from the end of the Eemian to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago. The LGP is part of a larger sequence of glacial and interglacial periods known as the Quaternary glaciation which started around 2,588,000 years ago and is ongoing. The definition of the Quaternary as beginning 2.58 million years ago (Mya) is based on the formation of the Arctic ice cap. The Antarctic ice sheet began to form earlier, at about 34 Mya, in the mid-Cenozoic. The term Late Cenozoic Ice Age is used to include this early phase.

The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martin in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of the mainland Antarctica.
Alexander Island, which is also known as Alexander I Island, Alexander I Land, Alexander Land, Alexander I Archipelago, and Zemlja Alexandra I, is the largest island of Antarctica. It lies in the Bellingshausen Sea west of Palmer Land, Antarctic Peninsula from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. George VI Ice Shelf entirely fills George VI Sound and connects Alexander Island to Palmer Land. The island partly surrounds Wilkins Sound, which lies to its west. Alexander Island is about 390 kilometres (240 mi) long in a north–south direction, 80 kilometres (50 mi) wide in the north, and 240 kilometres (150 mi) wide in the south. Alexander Island is the second largest uninhabited island in the world, after Devon Island.

Bunger Hills, also known as Bunger Lakes or Bunger Oasis, is a coastal range on the Knox Coast in Wilkes Land in Antarctica, consisting of a group of moderately low, rounded coastal hills, overlain by morainic drift and notably ice free throughout the year, lying south of the Highjump Archipelago. The reasoning behind the minute amount of ice in the area is still relatively unknown and remains under intense debate amongst scientists today.
The Vestfold Hills are rounded, rocky, coastal hills, 411 square kilometres (159 sq mi) in extent, on the north side of Sorsdal Glacier on the Ingrid Christensen Coast of Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica. The hills are subdivided by three west-trending peninsulas bounded by narrow fjords. Most of the hills range between 30 and 90 metres in height, with the highest summit reaching nearly 160 metres (520 ft).

Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station is a Polish research station on King George Island, off the coast of Antarctica.
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma and is ongoing. Although geologists describe the entire time period up to the present as an "ice age", in popular culture the term "ice age" is usually associated with just the most recent glacial period during the Pleistocene or the Pleistocene epoch in general. Since planet Earth still has ice sheets, geologists consider the Quaternary glaciation to be ongoing, with the Earth now experiencing an interglacial period.

The geology of Antarctica covers the geological development of the continent through the Archean, Proterozoic and Phanerozoic eons.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic South Pole and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle, and is surrounded by the Southern Ocean. At 14,200,000 square kilometres, it is the fifth-largest continent and nearly twice the size of Australia. It is by far the least populated continent, with around 5,000 people in the summer and around 1,000 in the winter. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice that averages 1.9 km in thickness.
Citadel Bastion is a rocky, flat-topped, rocky elevation at the south side of the terminus of Saturn Glacier, facing towards George VI Sound and the Rymill Coast, situated on the east side of Alexander Island, Antarctica. Its maximum elevation is about 645 m. Citadel Bastion lies next to Hodgson Lake. This mountain was mapped from trimetrogon air photography taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and from survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1948–50. The name applied by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because it resembles a fortified structure with a watchtower at the end of a wall.
Mule Peninsula is an irregularly shaped rocky peninsula between Ellis Fjord and Krok Fjord in the southern part of the Vestfold Hills of Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica. It was mapped from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition of 1936–37 and named Breidnesmulen by Norwegian cartographers. Mule Peninsula is an adaptation of the original Norwegian name by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia.

Lake Burton, also known as Burton Lagoon, is a meromictic and saline lake in the Vestfold Hills of Princess Elizabeth Land in Eastern Antarctica. Princess Elizabeth Land, including the lake, is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. The lake has a surface area of 1.35 km2 (0.52 sq mi), a volume of 9.69 million m3, a maximum depth of 18.3 metres (60 ft) and a mean depth of 7.16 metres (23.5 ft). The lake is named after H. R. Burton, a biologist working in the Vestfold Hills of Antarctica.

Eduard Meine van Zinderen Bakker was a Dutch-born South African palynologist who made significant contributions to the fields of plant ecology, palynology and palaeo-ecology of Africa.

Leanne Armand is a Professor and marine scientist. She is expert in the identification of diatoms in the Southern Ocean. She is known for her contributions to the understanding of past Southern Ocean dynamics and sea ice as a result of her knowledge of diatom distributions and ecology.

Patricia Margaret Selkirk, is an Australian plant biologist and ecologist. Her career has focused on Antarctic and subantarctic terrestrial ecosystems and she is recognized as being a pioneering female Australian Antarctic scientist.

Dana Michelle Bergstrom is a senior researcher at the Australian Antarctic Division most notable for her work on identifying and mitigating risks against Antarctic and Sub Antarctic Ecosystems.

Adamussium is a genus of scallops belonging to the family Pectenidae from the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. There are three known species but only one is extant, the Antarctic scallop. Of the two extinct species A. jonkersi is from the Oligocene deposits on King George Island in the South Shetland Islands and the other, A. necopinatum, was described in 2016 from Pliocene marine deposits in the Vestfold Hills of East Antarctica.
References
- ↑ NSBHS Leaving Certificate 1948
- The Complete Encyclopedia: Antarctica and the Arctic, David McGonigal and Dr. Lynn Woodworth, Firefly Books, 2001
- Australian Antarctic Magazine, Spring, 2002, p. 54