Related Research Articles
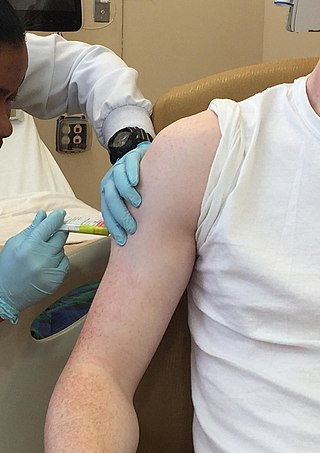
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.
The therapeutic index is a quantitative measurement of the relative safety of a drug with regard to risk of overdose. It is a comparison of the amount of a therapeutic agent that causes toxicity to the amount that causes the therapeutic effect. The related terms therapeutic window or safety window refer to a range of doses optimized between efficacy and toxicity, achieving the greatest therapeutic benefit without resulting in unacceptable side-effects or toxicity.
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is a branch of clinical chemistry and clinical pharmacology that specializes in the measurement of medication levels in blood. Its main focus is on drugs with a narrow therapeutic range, i.e. drugs that can easily be under- or overdosed. TDM aimed at improving patient care by individually adjusting the dose of drugs for which clinical experience or clinical trials have shown it improved outcome in the general or special populations. It can be based on a a priori pharmacogenetic, demographic and clinical information, and/or on the a posteriori measurement of blood concentrations of drugs (pharmacokinetic monitoring) or biological surrogate or end-point markers of effect (pharmacodynamic monitoring).

A vaccine trial is a clinical trial that aims at establishing the safety and efficacy of a vaccine prior to it being licensed.

In drug development, preclinical development is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials and during which important feasibility, iterative testing and drug safety data are collected, typically in laboratory animals.
Palifermin is a truncated human recombinant keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) produced in Escherichia coli. KGF stimulates the growth of cells that line the surface of the mouth and intestinal tract.

H5N1 clinical trials are clinical trials concerning H5N1 vaccines, which are intended to provide immunization to influenza A virus subtype H5N1. They are intended to discover pharmacological effects and identify any adverse reactions the vaccines may achieve in humans.
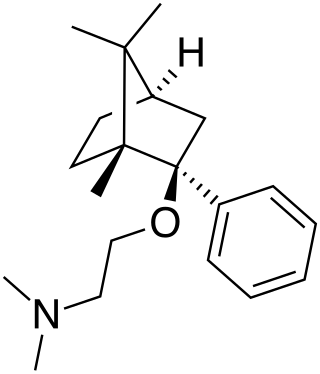
Deramciclane (EGIS-3886) is a non-benzodiazepine-type anxiolytic drug to treat various types of anxiety disorders. Deramciclane is a unique alternative to current anxiolytics on the market because it has a novel chemical structure and target. It acts as an antagonist at the 5-HT2A receptor, as an inverse agonist at the 5-HT2C receptor, and as a GABA reuptake inhibitor. The two serotonin receptors are G protein-coupled receptors and are two of the main excitatory serotonin receptor types. Their excitation has been implicated in anxiety and mood. Deramciclane does not affect CYP3A4 activity in metabolizing other drugs, but it is a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6. Some studies also show the drug to have moderate affinity to dopamine D2 receptors and low affinity to dopamine receptor D1. Researchers are looking for alternatives to benzodiazepines for anxiolytic use because benzodiazepine drugs have sedative and muscle relaxant side effects.
A glossary of terms used in clinical research.

Riociguat, sold under the brand name Adempas, is a medication by Bayer that is a stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC). It is used to treat two forms of pulmonary hypertension (PH): chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Riociguat constitutes the first drug of the class of sGC stimulators. The drug has a half-life of 12 hours and will decrease dyspnea associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension.
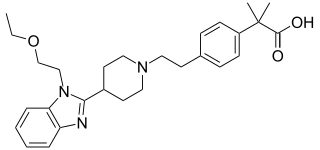
Bilastine is an antihistamine medication used to treat hives (urticaria), allergic rhinitis and itchy inflamed eyes (allergic conjunctivitis) caused by an allergy. It is a second-generation antihistamine and takes effect by selectively inhibiting the histamine H1 receptor, preventing these allergic reactions. Bilastine has an effectiveness similar to cetirizine, fexofenadine, and desloratadine.
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for drug safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.

Gemigliptin (rINN), sold under the brand name Zemiglo, is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor class of drugs. Glucose lowering effects of DPP-4 inhibitors are mainly mediated by GLP-1 and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) incretin hormones which are inactivated by DPP-4.
Demcizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody which is used to treat patients with pancreatic cancer or non-small cell lung cancer. Demcizumab has completed phase 1 trials and is currently undergoing phase 2 trials. Demcizumab was developed by OncoMed Pharmaceuticals in collaboration with Celgene.

Filgotinib, sold under the brand name Jyseleca, is a medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It was developed by the Belgian-Dutch biotech company Galapagos NV.

BIA 10-2474 is an experimental fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor developed by the Portuguese pharmaceutical company Bial-Portela & Ca. SA. It interacts with the human endocannabinoid system. The drug was in development for the treatment of a range of different medical conditions from anxiety disorder to Parkinson's disease, also for the treatment of chronic pain of multiple sclerosis, cancer, hypertension or the treatment of obesity. A clinical trial with this drug was underway in Rennes, France, in January 2016, in which serious adverse events occurred affecting five participants, including the death of one man. The underlying mechanism that caused the acute neurotoxicity of this molecule remains unknown.

ZF2001, trade-named Zifivax or ZF-UZ-VAC-2001, is an adjuvanted protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom in collaboration with the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The vaccine candidate is in Phase III trials with 29,000 participants in China, Ecuador, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan.
Donanemab, sold under the brand name Kisunla, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Donanemab was developed by Eli Lilly and Company.

Sonlicromanol (KH176) is a clinical-stage oral drug compound developed by Khondrion as a potential treatment for inherited mitochondrial diseases, such as Leigh's Disease, MELAS and LHON. Due to dysfunctional mitochondria, an increased level of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) is observed in these patients, causing a wide range of symptoms. The active metabolite of Sonlicromanol has several mechanisms of action, acting both as antioxidant and as reactive oxygen species (ROS)-redox modulator. Through selective suppression of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1), Sonlicromanol even has potency as anti-cancer drug for mPGES-1 overexpressing cancer like prostate cancer. Currently, Sonlicromanol is in phase II clinical trial in the KHENERGYZE, KHENEREXT and KHENERGYC studies as potent candidate in treatment for mitochondrial diseases.
References
- ↑ Ting, Naitee (2006). Dose Finding in Drug Development. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-29074-5.
- ↑ Lee, Chi-Jen (2005). Clinical Trials Of Drugs And Biopharmaceuticals. CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-2185-9.
- ↑ Schmidt, R. (1988). "Dose-finding studies in clinical drug development". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 34: 15–19. doi:10.1007/bf01061410.