Related Research Articles
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the eastern border area of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-speaking peoples, Teso people also known as Iteso or people of Teso, Karo peoples, Luo peoples, Ateker peoples, Kalenjin peoples, Karamojong people also known as the Karamojong or Karimojong, Datooga, Dinka, Nuer, Atwot, Lotuko, and the Maa-speaking peoples.

Sir Edward Evan Evans-Pritchard FBA FRAI was an English anthropologist who was instrumental in the development of social anthropology. He was Professor of Social Anthropology at the University of Oxford from 1946 to 1970.
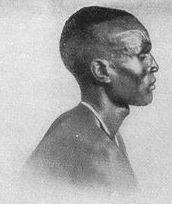
The Dinka people are a Nilotic ethnic group native to South Sudan. The Dinka mostly live along the Nile, from Mangalla-Bor to Renk, in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, Upper Nile, and the Abyei Area of the Ngok Dinka in South Sudan.

The Nuer people are a Nilotic ethnic group concentrated in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. They also live in the Ethiopian region of Gambella. The Nuer speak the Nuer language, which belongs to the Nilotic language family. They are the second-largest ethnic group in South Sudan and the largest ethnic group in Gambella, Ethiopia. The Nuer people are pastoralists who herd cattle for a living. Their cattle serve as companions and define their lifestyle. The Nuer call themselves "Naath".
Terence "Terry" Osborn Ranger was a prominent British Africanist, best known as a historian of Zimbabwe. Part of the post-colonial generation of historians, his work spanned the pre- and post-Independence (1980) period in Zimbabwe, from the 1960s to the present. He published and edited dozens of books and wrote hundreds of articles and book chapters, including co-editing The Invention of Tradition (1983) with Eric Hobsbawm. He was the Rhodes Professor of Race Relations at the University of Oxford and the first Africanist fellow of the British Academy.

Juma Abdalla Oris was a Ugandan military officer and government minister during the dictatorship of Idi Amin. After fleeing his country during the Uganda–Tanzania War, he became leader of the West Nile Bank Front (WNBF), a rebel group active in the West Nile region of Uganda during the 1990s.
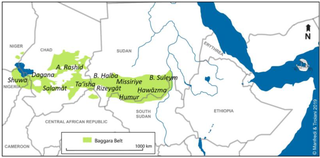
The Messiria, known also under the name of Misseriya Arabs, are a branch of the Baggara ethnic grouping of Arab tribes. Their language is Sudanese Arabic. Numbering over one million, the Baggara are the second largest ethnic group in Western Sudan, extending into Eastern Chad. They are primarily nomadic cattle herders and their journeys are dependent upon the seasons of the year. The use of the term Baggara carries negative connotations as slave raiders, so they prefer to be called instead Messiria.

The Abyei Area is an area of 10,546 km2 or 4,072 sq mi on the border between South Sudan and Sudan that has been accorded "special administrative status" by the 2004 Protocol on the Resolution of the Abyei Conflict in the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War. The capital of the Abyei Area is Abyei Town. Under the terms of the Abyei Protocol, the Abyei Area is considered, on an interim basis, to be simultaneously part of both the Republic of South Sudan and Republic of Sudan, effectively a condominium.
Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, also known as Daarood, Dawud or Da'ud, is the common ancestor of the Somali Darod clan and the Harla people. According to local tradition, Abdirahman descended from Aqil ibn Abi Talib, a member of the Banu Hashim and a cousin of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Bor County is a county of Jonglei State in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan.
Ronald Godfrey Lienhardt was a British anthropologist. He took many photographs of the Dinka people he studied. He wrote about their religion in Divinity and Experience: the Religion of the Dinka.
The history of South Sudan comprises the history of the territory of present-day South Sudan and the peoples inhabiting the region.
Ethnic violence in South Sudan has a long history among South Sudan's varied ethnic groups. South Sudan has 64 tribes with the largest being the Dinka, who constitute about 35% of the population and predominate in government. The second largest are the Nuers. Conflict is often aggravated among nomadic groups over the issue of cattle and grazing land and is part of the wider Sudanese nomadic conflicts.
Ngundeng Bong was a prophet of the Nuer people of South Sudan. He presented himself as being an earthly representative of Deng, the sky god of the Nuer religion. His prophecies of the breakup of Sudan are still a factor in the politics of modern South Sudan.

Terje Tvedt is a Norwegian academic, author and documentary film maker.
Afonso V of the Congo was a Kinlaza manikongo of the Kingdom of Kongo from 1785 to 1787.

The Nuer: A Description of the Modes of Livelihood and Political Institutions of a Nilotic People is an ethnographical study by the British anthropologist E. E. Evans-Pritchard (1902–73) first published in 1940. The work examined the political and familial systems of the Nuer people in the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan and is considered a landmark work of social anthropology. It was the first of three books authored by Evans-Pritchard on Nuer culture.
Wendy Rosalind James, was a British social anthropologist and academic. She was Professor of Social Anthropology at the University of Oxford from 1996 to 2007, and President of the Royal Anthropological Institute from 2001 to 2004.
The Ugandan Nubians, alternatively known as Nubis or Nubi, are a people who traditionally live in northern Uganda, and generally include those who identify as Nubians. In addition, the Nubian identity is also linked to ethnical, linguistical, cultural, and societal elements, but these do not apply to all Ugandan Nubians.

The Sabean colonisation of Africa was a process of colonization by Sabeans that occurred in the Horn of Africa during the first millennium BC.
References
- ↑ Dorina Bekoe, Kelly Campbell, Nicholas Howenstein, "Resolving the Boundary Dispute in Sudan's Abyei Region", United States Institute of Peace, October 2005, accessed 3 January 2023
- ↑ "Why Abyei Matters", oxfordjournals.org, 2007
- ↑ "JAMES, Prof. Wendy Rosalind, (Mrs D. H. Johnson)". Who's Who 2017. Oxford University Press. November 2016. Retrieved 4 February 2017.