
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight trains.

The Panama Canal Railway is a railway line linking the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean in Central America. The route stretches 47.6 miles (76.6 km) across the Isthmus of Panama from Colón (Atlantic) to Balboa. Because of the difficult physical conditions of the route and state of technology, the construction was renowned as an international engineering achievement, one that cost US$8 million and the lives of an estimated 5,000 to 10,000 workers. Opened in 1855, the railway preceded the Panama Canal by half a century; the railway was vital in assisting the construction of the canal in the early 1900s. With the opening of the canal, the railroad's route was changed as a result of the creation of Gatun Lake, which flooded part of the original route. Following World War II, the railroad's importance declined and much of it fell into a state of neglect until 1998, when a project to rebuild the railroad to haul intermodal traffic began; the new railroad opened in 2001.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The 4-6-2 locomotive became almost globally known as a Pacific type after a New Zealand locomotive that was shipped across the Pacific Ocean.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type was first used by the Northern Pacific Railway, and initially named the Northern Pacific, but railfans and railroad employees have shortened the name since its introduction. It is most-commonly known as a Northern.

The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923.

The Chicago Tunnel Company was the builder and operator of a 2 ft narrow-gauge railway freight tunnel network under downtown Chicago, Illinois. This was regulated by the Interstate Commerce Commission as an interurban even though it operated entirely under central Chicago, did not carry passengers, and was entirely underground. It inspired the construction of the London Post Office Railway.

The McKeen Motor Car Company of Omaha, Nebraska, was a builder of internal combustion-engined railroad motor cars (railcars), constructing 152 between 1905 and 1917. Founded by William McKeen, the Union Pacific Railroad's Superintendent of Motive Power and Machinery, the company was essentially an offshoot of the Union Pacific and the first cars were constructed by the UP before McKeen leased shop space in the UP's Omaha Shops in Omaha, Nebraska. The UP had asked him to develop a way of running small passenger trains more economically and McKeen produced a design that was ahead of its time. Unfortunately, internal combustion engine technology was not and the McKeen cars never found a truly reliable powerplant.

The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to November 21, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980. Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.

The Pioneer Zephyr is a diesel-powered trainset built by the Budd Company in 1934 for the Chicago, Burlington & Quincy Railroad (CB&Q), commonly known as the Burlington Route. The trainset was the second internal combustion-powered streamliner built for mainline service in the United States, the first such train powered by a diesel engine, and the first to enter revenue service.
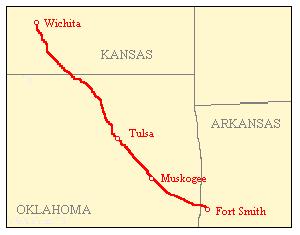
The Midland Valley Railroad (MV) was a railroad company incorporated on June 4, 1903 for the purpose of building a line from Hope, Arkansas, through Muskogee and Tulsa, Oklahoma to Wichita, Kansas. It was backed by C. Jared Ingersoll, a Philadelphia industrialist who owned coal mining properties in Indian Territory. The railroad took its name from Midland, Arkansas, a coal mining town in western Arkansas, which was served by the railroad. The Midland Valley gained access to Fort Smith, Arkansas via trackage rights over the Frisco from Rock Island, Oklahoma.
The Kansas, Oklahoma and Gulf Railway (“KO&G”) had at its height 310.5 miles of track from Denison, Texas through Oklahoma to Baxter Springs, Kansas. Its various predecessor companies built the line between 1904 and 1913. The railroad was consolidated into a Missouri Pacific Railroad subsidiary—the Texas and Pacific Railway—in 1963.
The Oklahoma City – Ada – Atoka Railway (OCAA) was formed from trackage from Oklahoma City to Atoka via Shawnee, Ada, and Coalgate, Oklahoma. Atoka to Coalgate had been built between 1882 and 1886 as feeder to the old Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad (Katy) main line, and Coalgate-Shawnee-Oklahoma City had been constructed by Katy affiliates, and specifically the first 40 miles northwest out of Coalgate having been built by the Texas and Oklahoma Railroad in 1902. The remaining 78 miles into Oklahoma City were built in the 1903-1904 timeframe by that line’s successor, the Missouri, Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad Company. These properties were not included in the 1923 reorganization of the Katy, and were put in the OCAA instead. The OCAA was sold to the Muskogee Company in 1929, becoming one of the Muskogee Roads.

The Muskogee Turnpike, also designated State Highway 351 (SH-351), is a controlled-access toll road in eastern Oklahoma.
The Sand Springs Railway is a class III railroad operating in Oklahoma. It was originally formed in 1911 by industrialist Charles Page to connect his newly formed city of Sand Springs to Tulsa, operating both as a passenger carrying interurban and a freight carrier. At Sand Springs, the company also served his children's home, and Page directed all railroad profits to support the home's operations.

The Ohio Railway Museum is a railway museum that was founded in 1948. It is located in Worthington, Ohio, near Columbus, Ohio.

The Mitsubishi ESR (Ecological Science Research) is a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) concept exhibited by Mitsubishi Motors at the 30th Tokyo Motor Show in 1993. It was designed to demonstrate the company's technological developments in alternative energy, and used a 70 kW AC induction motor to drive the front wheels. 28 alkaline batteries housed under the passenger compartment, and a rear-mounted 1.5-litre gasoline engine powered an onboard electrical generator system. It also recycled its own kinetic energy, and absorbed solar power through roof-mounted cells.

The Eureka Springs & North Arkansas Railway is a for-profit passenger tourist railway established by the late Robert Dortch, Jr. and his wife Mary Jane in 1981 in Eureka Springs, Arkansas. The railway offers one-hour excursion tours, a catered luncheon train and a catered dinner train - each lasting a little more than one hour, from April through October. It operates along 2.5 miles (4.0 km) of restored track right-of-way formerly belonging to the defunct Arkansas & Ozarks Railway Co - the last incarnation of the North Arkansas Line.

Idealia was America's first diesel powered yacht built and owned by the Electric Launch Company (ELCO). The yacht was built in 1911, launched in 1912 and demonstrated the potential for use of diesel engines in yachts for several years thereafter. She yacht performed a public trial on the Hudson River on 22 October 1913 under the supervision of ELCO's manager Henry R. Sutphen with a gathering of naval architects and engineers as observers. Idealia was sold to individual owners after its period of demonstrating the diesel engine's pleasure craft utility.

The second USS Juniata (SP-602) was a United States Navy patrol vessel in commission from 1 June 1917 to 13 July 1918. Juniata was built as the private gasoline-powered motor yacht Josephine for Edward Shearson of New York by Robert Jacobs at City Island in the Bronx, New York, in 1911. She was sold in 1914 to George W. Elkins of Philadelphia and renamed Juniata.
The Muskogee Electric Traction Company (“Traction”) was an electrified streetcar line operating in and around Muskogee, Oklahoma from 1904 to 1941, with bus passenger service continuing under that name to 1958.
















