
macOS, originally Mac OS X, previously shortened as OS X, is a Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers, it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS and SteamOS. As of 2024, the most recent release of macOS is macOS 15 Sequoia, the 21st major version of macOS.

The Finder is the default file manager and graphical user interface shell used on all Macintosh operating systems. Described in its "About" window as "The Macintosh Desktop Experience", it is responsible for the launching of other applications, and for the overall user management of files, disks, and network volumes. It was introduced with the Macintosh 128K—the first Macintosh computer—and also exists as part of GS/OS on the Apple IIGS. It was rewritten completely with the release of Mac OS X in 2001.
The history of macOS, Apple's current Mac operating system formerly named Mac OS X until 2011 and then OS X until 2016, began with the company's project to replace its "classic" Mac OS. That system, up to and including its final release Mac OS 9, was a direct descendant of the operating system Apple had used in its Mac computers since their introduction in 1984. However, the current macOS is a UNIX operating system built on technology that had been developed at NeXT from the 1980s until Apple purchased the company in early 1997.

Safari is a web browser developed by Apple. It is built into several of Apple's operating systems, including macOS, iOS, iPadOS and visionOS, and uses Apple's open-source browser engine WebKit, which was derived from KHTML.
The Dock is a prominent feature of the graphical user interface of macOS. It is used to launch applications and to switch between running applications. The Dock is also a prominent feature of macOS's predecessor NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP operating systems. The earliest known implementations of a dock are found in operating systems such as RISC OS and NeXTSTEP. iOS has its own version of the Dock for the iPhone and iPod Touch, as does iPadOS for the iPad.

Mission Control is a feature of the macOS operating system. Dashboard, Exposé, and Spaces were combined and renamed Mission Control in 2011 with the release of Mac OS X 10.7 Lion. Exposé was first previewed on June 23, 2003, at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference as a feature of the then forthcoming Mac OS X 10.3 Panther.
The taskbar is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, displaying and facilitating switching between running programs. The taskbar and the associated Start Menu were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

Aqua is the graphical user interface, design language and visual theme of Apple's macOS and iOS operating systems. It was originally based on the theme of water, with droplet-like components and a liberal use of reflection effects and translucency. Its goal is to "incorporate color, depth, translucence, and complex textures into a visually appealing interface" in macOS applications. At its introduction, Steve Jobs noted that "... it's liquid, one of the design goals was when you saw it you wanted to lick it".
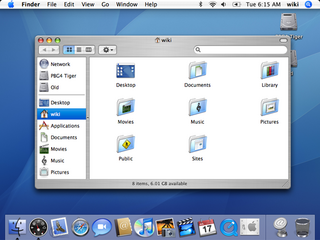
Mac OS X Tiger is the 5th major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Mac computers. Tiger was released to the public on April 29, 2005, for US$129.95 as the successor to Mac OS X 10.3 Panther. Included features were a fast searching system called Spotlight, a new version of the Safari web browser, Dashboard, a new 'Unified' theme, and improved support for 64-bit addressing on Power Mac G5s. Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger also had a number of additional features that Microsoft had spent several years struggling to add to Windows with acceptable performance, such as fast file search and improved graphics processing.

Dashboard is a discontinued feature of Apple Inc.'s macOS operating systems, used as a secondary desktop for hosting mini-applications known as widgets. These are intended to be simple applications that do not take time to launch. Dashboard applications supplied with macOS included a stock ticker, weather report, calculator, and notepad; while users could create or download their own.
SpringBoard is the standard application that manages the iPhone's home screen. Other tasks include starting WindowServer, launching and bootstrapping applications, and setting some of the device's settings on startup.

OS X Lion, also known as Mac OS X Lion, is the eighth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server system for Mac computers.
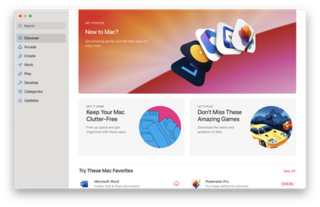
The Mac App Store is a digital distribution platform for macOS apps, often referred to as Mac apps, created and maintained by Apple. The platform was announced on October 20, 2010, at Apple's "Back to the Mac" event. Apple began accepting app submissions from registered developers on November 3, 2010, in preparation for its launch.

OS X El Capitan is the twelfth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh. It focuses mainly on performance, stability, and security. Following the California location-based naming scheme introduced with OS X Mavericks, El Capitan was named after a rock formation in Yosemite National Park. El Capitan is the final version to be released under the name OS X. OS X El Capitan received far better reviews than Yosemite.

tvOS is an operating system developed by Apple for the Apple TV, a digital media player. In the first-generation Apple TV, Apple TV Software was based on Mac OS X. The software for the second-generation and later Apple TVs is based on the iOS operating system and has many similar frameworks, technologies, and concepts.

macOS Sierra is the thirteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. The name "macOS" stems from the intention to unify the operating system's name with that of iOS, watchOS and tvOS. Sierra is named after the Sierra Nevada mountain range in California and Nevada. Specifically, Lone Pine Peak is the location for macOS Sierra's default wallpaper. Its major new features concern Continuity, iCloud, and windowing, as well as support for Apple Pay and Siri.

iOS 11 is the eleventh major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple, being the successor to iOS 10. It was announced at the company's Worldwide Developers Conference on June 5, 2017, and was released on September 19, 2017. It was succeeded by iOS 12 on September 17, 2018.

macOS Mojave is the fifteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. Mojave was announced at Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference on June 4, 2018, and was released to the public on September 24. The operating system's name refers to the Mojave Desert, continuing the use of California-themed names that began with OS X Mavericks. It succeeded macOS High Sierra and was followed by macOS Catalina. macOS Mojave is the last version of macOS that features the iTunes and Dashboard apps.
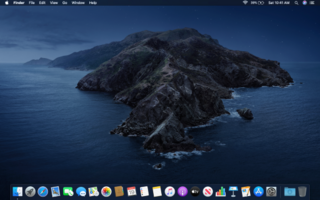
macOS Catalina is the sixteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. It is the successor to macOS Mojave and was announced at WWDC 2019 on June 3, 2019 and released to the public on October 7, 2019. Catalina is the first version of macOS to support only 64-bit applications and the first to include Activation Lock. It is also the last version of macOS to have the major version number of 10; its successor, Big Sur, released on November 12, 2020, is version 11. In order to increase web compatibility, Safari, Chromium and Firefox have frozen the OS in the user agent running in subsequent releases of macOS at 10.15.7 Catalina.















