Related Research Articles

Drosophila is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies ; tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly.

Drosophila melanogaster is a species of fly in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly", "pomace fly", or "banana fly". In the wild, D. melanogaster are attracted to rotting fruit and fermenting beverages, and are often found in orchards, kitchens and pubs.

Obaid Siddiqi FRS was an Indian National Research Professor and the Founder-Director of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) National Center for Biological Sciences. He made seminal contributions to the field of behavioural neurogenetics using the genetics and neurobiology of Drosophila.

Drosophila simulans is a species of fly closely related to D. melanogaster, belonging to the same melanogaster species subgroup. Its closest relatives are D. mauritiana and D. sechellia.
The Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup contains 9 species of flies, including the best known species Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. The subgroup belongs to the Drosophila melanogaster species group within the subgenus Sophophora.
The Drosophila melanogaster species group belongs to the subgenus Sophophora and contains 10 subgroups. The phylogeny in this species group is poorly known despite many studies covering many of the species subgroups. The most likely explanation is that the various subgroups diverged from each other in a relatively short evolutionary time frame. Three subgroups have not yet been investigated in molecular studies, and their position in the phylogeny is unclear. The suzukii subgroup is paraphyletic as D. lucipennis is systematically placed within the elegans subgroup.
Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) is the largest class of small non-coding RNA molecules expressed in animal cells. piRNAs form RNA-protein complexes through interactions with piwi-subfamily Argonaute proteins. These piRNA complexes are mostly involved in the epigenetic and post-transcriptional silencing of transposable elements and other spurious or repeat-derived transcripts, but can also be involved in the regulation of other genetic elements in germ line cells.

Most animal testing involves invertebrates, especially Drosophila melanogaster, a fruit fly, and Caenorhabditis elegans, a nematode. These animals offer scientists many advantages over vertebrates, including their short life cycle, simple anatomy and the ease with which large numbers of individuals may be studied. Invertebrates are often cost-effective, as thousands of flies or nematodes can be housed in a single room.

Notch proteins are a family of type 1 transmembrane proteins that form a core component of the Notch signaling pathway, which is highly conserved in animals. The Notch extracellular domain mediates interactions with DSL family ligands, allowing it to participate in juxtacrine signaling. The Notch intracellular domain acts as a transcriptional activator when in complex with CSL family transcription factors. Members of this type 1 transmembrane protein family share several core structures, including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats and an intracellular domain transcriptional activation domain (TAD). Notch family members operate in a variety of different tissues and play a role in a variety of developmental processes by controlling cell fate decisions. Much of what is known about Notch function comes from studies done in Caenorhabditis elegans (C.elegans) and Drosophila melanogaster. Human homologs have also been identified, but details of Notch function and interactions with its ligands are not well known in this context.

In molecular biology the DM domain is a protein domain first discovered in the doublesex proteins of Drosophila melanogaster and is also seen in C. elegans and mammalian proteins. In D. melanogaster the doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides. These proteins are believed to function as transcription factors on downstream sex-determination genes, especially on neuroblast differentiation and yolk protein genes transcription.
A behaviour mutation is a genetic mutation that alters genes that control the way in which an organism behaves, causing their behavioural patterns to change.

Drosophila hydei (mosca casera) is a species of Diptera, or the order of flies, in the family Drosophilidae. It is a species in the hydei species subgroup, a group in the repleta species group. Bizarrely, it is also known for having approximately 23 mm long sperm, 10 times the length of the male's body. Drosophila hydei are commonly found on compost piles worldwide, and can be rudimentarily identified by eye owing to their large size and variegated pigment pattern on the thorax. The name derives from Dr R. R. Hyde, who first discovered that the species was distinct from Drosophila repleta. D. hydei are one of the more popular flies used as feeders in the pet trade. A few varieties are available, some flightless. They are very similar to Drosophila melanogaster, despite having separated 50 million years ago.

Drosophila synthetica refers to a genetically engineered population of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. This population was created under laboratory conditions to ensure it is morphologically and genetically different enough from its wild type to be a separate species. D. synthetica has small white eyes, strongly veined wings, and is unable to hybridize with D. melanogaster. This population was created in 2012 by the Spanish geneticist Eduardo Moreno, working at the University of Bern.
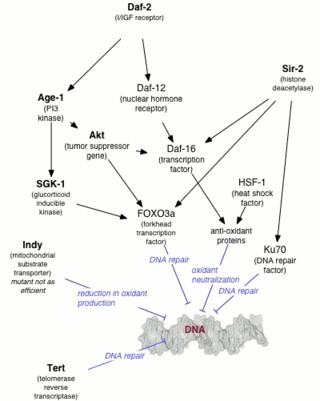
Genetics of aging is generally concerned with life extension associated with genetic alterations, rather than with accelerated aging diseases leading to reduction in lifespan.
Drosophila elegans is a flower-feeding species of fruit flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae. It is found in Taiwan and the Philippines in Asia.
The Drosophila saltans species group contains 21 described fly species, all of which are found in the neotropical region. It is one of the seven species groups in the subgenus Sophophora, the others being the D. willistoni, D. melanogaster, D. obscura, D. dispar, D. fima, and D. dentissima groups. The D. saltans species group is most closely related to the D. willistoni subgroup. The species are placed into five subgroups: the D. s. cordata, D. s. elliptica, D. s. parasaltans, D. s. saltans, and D. s. sturtevanti subgroups. It is thought that, like the D. willistoni species group, the D. saltans species group originated in tropical North America, colonized South America, and then diversified prior to the formation of the Isthmus of Panama. Some of these may have migrated back to North America within the last 4.5 million years ago (mya), and consequently the relationship between the species is unresolved due to the short amount of time that has elapsed since their divergence points.
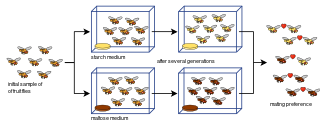
Laboratory experiments of speciation have been conducted for all four modes of speciation: allopatric, peripatric, parapatric, and sympatric; and various other processes involving speciation: hybridization, reinforcement, founder effects, among others. Most of the experiments have been done on flies, in particular Drosophila fruit flies. However, more recent studies have tested yeasts, fungi, and even viruses.
Metavirus is a genus of viruses in the family Metaviridae. They are retrotransposons that invade a eukaryotic host genome and may only replicate once the virus has infected the host. These genetic elements exist to infect and replicate in their host genome and are derived from ancestral elements unrelated from their host. Metavirus may use several different hosts for transmission, and has been found to be transmissible through ovule and pollen of some plants.
Semotivirus is the only genus of viruses in the family Belpaoviridae. Species exist as retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. BEL/pao transposons are only found in animals.
A mutation accumulation (MA) experiment is a genetic experiment in which isolated and inbred lines of organisms are maintained such that the effect of natural selection is minimized, with the aim of quantitatively estimating the rates at which spontaneous mutations occur in the studied organism. Spontaneous mutation rates may be directly estimated using molecular techniques such as DNA sequencing, or indirectly estimated using phenotypic assays.
References
- J. A. Coyne, S. Elwyn, S. Y. Kim & A. Llopart 2004. Genetic studies of two sister species in the Drosophila melanogaster subgroup, D. yakuba and D. santomea. Genetical Research 84: 11-26.