Related Research Articles

A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay into pottery, tiles and bricks. Various industries use rotary kilns for pyroprocessing and to transform many other materials.

Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity. When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow.

Smoking is the process of flavoring, browning, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Meat, fish, and lapsang souchong tea are often smoked.

Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species, either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.

A furnace, referred to as a heater or boiler in British English, is an appliance used to generate heat for all or part of a building. Furnaces are mostly used as a major component of a central heating system. Furnaces are permanently installed to provide heat to an interior space through intermediary fluid movement, which may be air, steam, or hot water. Heating appliances that use steam or hot water as the fluid are normally referred to as a residential steam boilers or residential hot water boilers. The most common fuel source for modern furnaces in North America and much of Europe is natural gas; other common fuel sources include LPG, fuel oil, wood and in rare cases coal. In some areas electrical resistance heating is used, especially where the cost of electricity is low or the primary purpose is for air conditioning. Modern high-efficiency furnaces can be up to 98% efficient and operate without a chimney, with a typical gas furnace being about 80% efficient. Waste gas and heat are mechanically ventilated through either metal flue pipes or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes that can be vented through the side or roof of the structure. Fuel efficiency in a gas furnace is measured in AFUE.
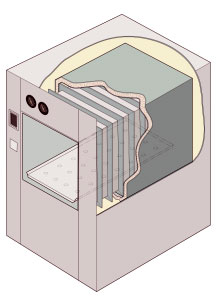
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites.
A clothes dryer, also known as tumble dryer or simply dryer, is a powered household appliance that is used to remove moisture from a load of clothing, bedding and other textiles, usually after they are washed in a washing machine.

Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic.

A convection oven is an oven that has fans to circulate air around food to create an evenly heated environment. The increased air circulation causes a fan-assisted oven to cook food faster than a conventional non-fan oven, which relies only on natural convection to circulate the hot air. Fan-assisted convection ovens are commonly used for baking as well as non-food, industrial applications. Small countertop convection ovens for household use are often marketed as air fryers.

A clothes line, also spelt clothesline and also known as a washing line, is a device for hanging clothes on for the purpose of drying them. It is any type of rope, cord, or twine that has been stretched between two points, outside or indoors, above the level of the ground. Clothing that has recently been washed is hung along the line to dry, using clothes pegs or clothespins. Washing lines are attached either from a post or a wall, and are frequently located in back gardens, or on balconies. Longer washing lines often have props holding up sections in the middle due to the weight of the usually wet clothing.

Dielectric heating, also known as electronic heating, radio frequency heating, and high-frequency heating, is the process in which a radio frequency (RF) alternating electric field, or radio wave or microwave electromagnetic radiation heats a dielectric material. At higher frequencies, this heating is caused by molecular dipole rotation within the dielectric.
Drying is a mass transfer process consisting of the removal of water or another solvent by evaporation from a solid, semi-solid or liquid. This process is often used as a final production step before selling or packaging products. To be considered "dried", the final product must be solid, in the form of a continuous sheet, long pieces, particles or powder. A source of heat and an agent to remove the vapor produced by the process are often involved. In bioproducts like food, grains, and pharmaceuticals like vaccines, the solvent to be removed is almost invariably water. Desiccation may be synonymous with drying or considered an extreme form of drying.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to food preparation:
A building envelope is the physical separator between the conditioned and unconditioned environment of a building including the resistance to air, water, heat, light, and noise transfer.

Wood drying reduces the moisture content of wood before its use. When the drying is done in a kiln, the product is known as kiln-dried timber or lumber, whereas air drying is the more traditional method.
Laboratory ovens are a common piece of equipment that can be found in electronics, materials processing, forensic, and research laboratories. These ovens generally provide pinpoint temperature control and uniform temperatures throughout the heating process. The following applications are some of the common uses for laboratory ovens: annealing, die-bond curing, drying or dehydrating, Polyimide baking, sterilizing, evaporating. Typical sizes are from one cubic foot to 0.9 cubic metres (32 cu ft). Some ovens can reach temperatures that are higher than 300 degrees Celsius. These temperatures are then applied from all sides of the oven to provide constant heat to sample.

A food dehydrator is a device that removes moisture from food to aid in its preservation. Food drying is a method of preserving fruit, vegetables and meats that has been practiced since antiquity.

Hot air ovens are electrical devices which use dry heat to sterilize. They were originally developed by Louis Pasteur. Generally, they use a thermostat to control the temperature. Their double walled insulation keeps the heat in and conserves energy, the inner layer being a poor conductor and outer layer being metallic. There is also an air filled space in between to aid insulation. An air circulating fan helps in uniform distribution of the heat. These are fitted with the adjustable wire mesh plated trays or aluminium trays and may have an on/off rocker switch, as well as indicators and controls for temperature and holding time. The capacities of these ovens vary. Power supply needs vary from country to country, depending on the voltage and frequency (hertz) used. Temperature sensitive tapes or biological indicators using bacterial spores can be used as controls, to test for the efficacy of the device during use.
Moist heat sterilization describes sterilization techniques that use hot water vapor as a sterilizing agent. Heating an article is one of the earliest forms of sterilization practiced. The various procedures used to perform moist heat sterilization process cause destruction of micro-organisms by denaturation of macromolecules.

An industrial furnace, also known as a direct heater or a direct fired heater, is a device used to provide heat for an industrial process, typically higher than 400 degrees Celsius. They are used to provide heat for a process or can serve as reactor which provides heats of reaction. Furnace designs vary as to its function, heating duty, type of fuel and method of introducing combustion air. Heat is generated by an industrial furnace by mixing fuel with air or oxygen, or from electrical energy. The residual heat will exit the furnace as flue gas. These are designed as per international codes and standards the most common of which are ISO 13705 / American Petroleum Institute (API) Standard 560. Types of industrial furnaces include batch ovens, vacuum furnaces, and solar furnaces. Industrial furnaces are used in applications such as chemical reactions, cremation, oil refining, and glasswork.
References
ISO 20857
Notes
- ↑ Textbook of Microbiology by Prof. C P Baveja, ISBN 81-7855-266-3
- ↑ Textbook of Microbiology by Ananthanarayan and Panikar, ISBN 81-250-2808-0
- ↑ "029 This page has moved | HAI | CDC".
- ↑ "HVHA TECH | UK | Metafix High Velocity Hot air Sterilisers".
General References
- Ninemeier J. Central Service Technical Manual (6th ed.). International Association of Healthcare Central Service Materiel Management. p. 159.[ permanent dead link ]