Related Research Articles
Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh, also known as Dubhaltach Óg mac Giolla Íosa Mór mac Dubhaltach Mór Mac Fhirbhisigh, Duald Mac Firbis, Dudly Ferbisie, and Dualdus Firbissius was an Irish scribe, translator, historian and genealogist. He was one of the last traditionally trained Irish Gaelic scholars, and was a member of the Clan MacFhirbhisigh, a leading family of northern Connacht. His best-known work is the Leabhar na nGenealach, which was published in 2004 as The Great Book of Irish Genealogies, by Éamonn de Búrca, more than 300 years after it had been written.

The Annals of Inisfallen are a chronicle of the medieval history of Ireland.

The Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland or the Annals of the Four Masters are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,242 years after creation to AD 1616.

The Annals of Ulster are annals of medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, under his patron Cathal Óg Mac Maghnusa, on the island of Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa, also known as Senad or Ballymacmanus Island, near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of Fir Manach (Fermanagh). Later entries were added by others.
Fedelmid mac Crimthainn was the King of Munster between 820 and 846. He was numbered as a member of the Céli Dé, an abbot of Cork Abbey and Clonfert Abbey, and possibly a bishop. After his death, he was later considered a saint in some martyrologies.
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over time, the obituaries of priests, abbots and bishops were added, along with those of notable political events. Non-Irish models include Bede's Chronica maiora, Marcellinus Comes's Chronicle of Marcellinus and the Liber pontificalis.
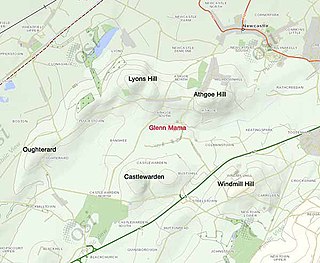
The Battle of Glenn Máma or Glenmama took place most probably near Lyons Hill in Ardclough, County Kildare, Ireland, in AD 999 between Windmill Hill and Blackchurch. It was the decisive and only engagement of the brief Leinster revolt of 999–1000 against the King of Munster, Brian Boru. In it, the combined forces of the Kingdoms of Munster and Meath, under King Brian Boru and the High King of Ireland, Máel Sechnaill II, inflicted a crushing defeat on the allied armies of Leinster and Dublin, led by King Máel Mórda of Leinster.

Secundinus, or Sechnall as he was known in Irish, was founder and patron saint of Domhnach Sechnaill, County Meath, who went down in medieval tradition as a disciple of St Patrick and one of the first bishops of Armagh. Historians have suggested, however, that the connection with St Patrick was a later tradition invented by Armagh historians in favour of their patron saint and that Secundinus is more likely to have been a separate missionary, possibly a companion of Palladius.
Gofraid ua Ímair or Guthfrith of Ivar was a Hiberno-Scandinavian and Viking leader who ruled Dublin and briefly Viking Northumbria in the early 10th century. He was a grandson of Ímar and a member of the Uí Ímair. Gofraid was most probably among those Vikings expelled from Dublin in 902, whereafter he helped his kinsman Ragnall conquer Northumbria. Another kinsman, Sitric Cáech, became ruler of Dublin around the same time. Ragnall died in 920, and so the following year Sitric left Dublin to rule in Northumbria, and Gofraid succeeded Sitric as ruler of Dublin. Sitric's early reign was marked by raids he conducted against the Gaelic (Native-Irish), including one at Armagh.
Canovee is the name of a rural region and a village nucleus in the Lee valley in County Cork, Ireland. The toponym 'Canovee' is synonymous with the official version Cannaway, and the electoral division of Cannaway.
Ivar of Limerick, was the last Norse king of the city-state of Limerick, and penultimate King of the Foreigners of Munster, reigning during the rise to power of the Dál gCais and the fall of the Eóganachta.

Ivar of Waterford was the Norse king of Waterford from at least 969 until his death in the year 1000, and also reigned as King of Dublin, possibly from 989 to 993, and certainly again for less than a year between 994 and 995, returning after his expulsion from the city in 993 by Sigtrygg Silkbeard, who would expel him for good the next time.
Máel Muad mac Brain, commonly anglicised Molloy and referred to in several texts as Maelmuadh son of Bran, was King of Munster, first possibly from 959 or alternatively 963 to around 970, when he may have been deposed (usurped) by Mathgamain mac Cennétig of the Dál gCais, and then again from 976, following his putting to death of the latter, until his own death in the Battle of Belach Lechta against Mathgamain's brother Brian Bóruma in 978. From around 970 to 976, he is referred to in the sources only as King of Desmond, but remained "in opposition" to Mathgamain throughout his career. Máel Muad's chief ally in Munster was Donnubán mac Cathail, to whom he partly owed his second reign, and with whom he is also associated earlier. Along with Donnubán he was also allied, according to the not contemporary saga and political tract Cogad Gáedel re Gallaib, with Ivar of Limerick, who may himself have temporarily been overlord of the province.
The Battle of Belach Lechta or Bealach Leachta was a major battle fought in Munster in 978 between Máel Muad mac Brain, King of Munster, and Brian Bóruma. In the battle, the king was killed and Bóruma took over the role as the de facto King of Munster. Bóruma was the younger brother of Mathgamain mac Cennétig and in line to be the next High King of Ireland.
AI978.2: The battle of Belach Lechta, in which Mael Muad son of Brain, king of Caisel, and many others, fell. Brian, son of Cennétig, was victor.
The Battle of Cathair Cuan refers to a perhaps extended conflict fought in or between 977 and 978, or simply to a single battle in one or the other year, in Munster in Ireland. Attacking were Brian Bóruma and the Dál gCais, while defending were Donnubán mac Cathail and the remainder of the Viking army of Limerick. The latter were probably the followers of the newly elected and final King of the Foreigners of Munster Harald Ivarsson, son of the recently slain Ivar of Limerick, although it is possible Donnubán was in overall command.

Fingal mac Gofraid, and his father, Gofraid mac Sitriuc, were late eleventh-century rulers of the Kingdom of the Isles. Although one source states that Gofraid mac Sitriuc's father was named Sitriuc, there is reason to suspect that this could be an error of some sort. There is also uncertainty as to which family Gofraid mac Sitriuc belonged to. One such family, descended from Amlaíb Cúarán, King of Northumbria and Dublin, appears to have cooperated with Diarmait mac Maíl na mBó, King of Leinster. Another family, that of Echmarcach mac Ragnaill, King of Dublin and the Isles, opposed Amlaíb Cúarán's apparent descendants, and was closely connected with Diarmait's adversaries, the Uí Briain kindred.
Bárid mac Ímar ; Old Norse: Bárðr or Bárǫðr ; d. 881) was a ninth-century King of Dublin. He was a son of Ivar (Ímar) Ragnarsson and a member of the Uí Ímair.
Domnall mac Taidc was the ruler of the Kingdom of the Isles, the Kingdom of Thomond, and perhaps the Kingdom of Dublin as well. His father was Tadc, son of Toirdelbach Ua Briain, King of Munster, which meant that Domnall was a member of the Meic Taidc, a branch of the Uí Briain. Domnall's mother was Mór, daughter of Echmarcach mac Ragnaill, King of Dublin and the Isles, which may have given Domnall a stake to the kingship of the Isles.
Domnall mac Murchada, also known as Domnall mac Murchada meic Diarmata, was a leading late eleventh-century claimant to the Kingdom of Leinster, and a King of Dublin. As a son of Murchad mac Diarmata, King of Dublin and the Isles, Domnall was a grandson of Diarmait mac Máel na mBó, King of Leinster, and thus a member of the Uí Chennselaig. Domnall was also the first of the Meic Murchada, a branch of the Uí Chennselaig named after his father.
Harald Sigtryggsson was a Viking leader who ruled Limerick in the early 10th century. He was the son of Sitric Cáech and great-grandson of Ímar, making him one of the Uí Ímair. He was installed as king of Limerick following the capture of the previous king Olaf Scabby-head by Harald's cousin Olaf Guthfrithson, king of Dublin, during a battle at Lough Ree in 937. Harald died in 940 and was ultimately succeeded by Ivar of Limerick.
References
- ↑ Hennessy, W. M. (15 November 2012). The Annals of Loch Cé: A Chronicle of Irish Affairs from AD 1014 to AD 1590. Cambridge University Press. p. 154. ISBN 978-1-108-04888-0.
- ↑ Koch, John T.; Minard, Antone (8 August 2012). The Celts [2 volumes]: History, Life, and Culture [2 volumes]. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-59884-965-3.