Related Research Articles

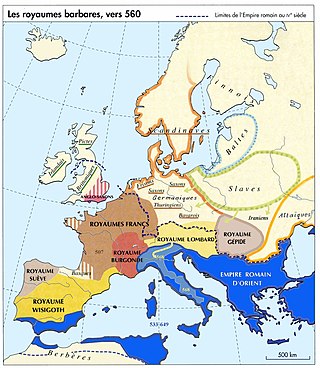
The Lombards or Longobards were a Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
Pope Stephen II was born a Roman aristocrat and member of the Orsini family. Stephen was the bishop of Rome from 26 March 752 to his death. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzantine Papacy and the Frankish Papacy. During Stephen's pontificate, Rome was facing invasion by the Lombards when Stephen II went to Paris to seek assistance from Pepin the Short. Pepin defeated the Lombards and made a gift of land to the pope, eventually leading to the establishment of the Papal States.
Year 744 (DCCXLIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 744 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into conflict with the Merovingian Franks, and it later came under their influence and Frankish control. The name is still used for one of modern Germany's federal states (Bundesländer).
The term Lombard refers to people or things related to Lombardy, a region in northern Italy.

Cividale del Friuli is a town and comune (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, part of the North-Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. The town lies 135 metres (443 ft) above sea-level in the foothills of the eastern Alps, 15 kilometres (9 mi) by rail from the city of Udine and close to the Slovenian border. It is situated on the river Natisone, which forms a picturesque ravine here. Formerly an important regional power, it is today a quiet, small town that attracts tourists thanks to its medieval center.
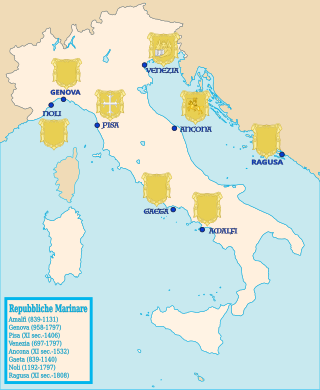
The history of Italy in the Middle Ages can be roughly defined as the time between the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and the Italian Renaissance. Late antiquity in Italy lingered on into the 7th century under the Ostrogothic Kingdom and the Byzantine Empire under the Justinian dynasty, the Byzantine Papacy until the mid 8th century. The "Middle Ages" proper begin as the Byzantine Empire was weakening under the pressure of the Muslim conquests, and most of the Exarchate of Ravenna finally fell under Lombard rule in 751. From this period, former states that were part of the Exarchate and were not conquered by the Lombard Kingdom, such as the Duchy of Naples, became de facto independent states, having less and less interference from the Eastern Roman Empire.
Cleph was king of the Lombards from 572 to 574.

Agilulf, called the Thuringian and nicknamed Ago, was a duke of Turin and king of the Lombards from 591 until his death.
Arioald was the Lombard king of Italy from 626 to 636. Duke of Turin, he married the princess Gundeberga, daughter of King Agilulf and his queen Theodelinda. He was, unlike his father-in-law, an Arian who did not accept Catholicism.
Rodoald, was a Lombard king of Italy, who succeeded his father Rothari on the throne in 652. He was said to be lecherous and he was assassinated after a reign of just six months in 653 by the husband of one of his lovers. Paul the Deacon writes that Rodoald "had reigned five years and seven days, ", although historians note that this length of reign is suspect. Aripert, a rival claimant, was elected with the support of the Catholic Church, which opposed the Arian monarchy.

Liutpert was the Lombard king of Italy between 700 and 702, with interruption. Upon succeeding his father, King Cunincpert, at a young age, he ruled together with his tutor, Ansprand, the duke of Asti. After eight months, he was deposed by Raginpert, the duke of Turin and son of Godepert, Liutpert's great-uncle, but succeeded in returning to the throne several months later upon Raginpert's death, only to be deposed again, taken captive from Pavia, and drowned by Aripert II, Raginpert's son. He was buried in the Basilica of Santissimo Salvatore in Pavia.

Aripert I was king of the Lombards (653–661) in Italy. He was the son of Gundoald, Duke of Asti, who had crossed the Alps from Bavaria with his sister Theodelinda. As a relative of the Bavarian ducal house, his was called the Bavarian Dynasty.

Ansprand was king of the Lombards briefly in 712. Before that, he was the duke of Asti and regent during the minority of Liutpert (700–701). He was defeated at Novara by Raginpert and exiled during the subsequent war over the succession, fleeing to the court of Theudebert, duke of Bavaria, in 702.

Aripert II was the king of the Lombards from 701 to 712. Duke of Turin and son of King Raginpert, and thus a scion of the Bavarian Dynasty, he was associated with the throne as early as 700. He was removed by Liutpert, who reigned from 700 to 702, with the exception of the year 701, when Raginpert seized the throne. After his father's death, he tried to take the throne, too. He defeated Liutpert and the regent Ansprand's men at Pavia and captured the king, whom he later had strangled in his bath. He seized the capital and forced Ansprand over the Alps. He was firmly in power by 703.
Alduin was king of the Lombards from 547 to 560.

Perctarit was the first Catholic king of the Lombards who lead a religiously divided kingdom during the 7th Century. He ruled from 661 to 662 the first time and later from 671 to 688. He is significant for making Catholicism the official religion, sparing the life of an invading leader, and building projects around the capital.
Raginpert was the Duke of Turin and then King of the Lombards briefly in 701. He was the son of Godepert and grandson of Aripert I. He usurped the throne in 701 and removed Liutpert, his grandnephew, putting his son Aripert in line for the succession. He and his Neustrians went out to meet the regent, Ansprand, in battle and defeated him at Novara, but died shortly after. His son Aripert did not succeed in taking the throne right away.
Garibald was the young son of Grimoald I of Benevento, king of the Lombards, and Theodota, daughter of Aripert I. After his father's death in 671, he reigned briefly for three months until the numerous adherents of Perctarit, his uncle, who had been exiled by Grimoald nine years earlier, besought their candidate to return and elected him, deposing the young king. He was the last Arian king in Europe.
References
- 1 2 Kleinhenz, Christopher (2004). Medieval Italy: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. pp. 5, 37. ISBN 9781135948801.
- ↑ "German Tribes org Lombard Kings". GermanTribes.org. Archived from the original on 2010-07-18. Retrieved 2017-06-29.