
Al-Jawf Province, also spelled Al-Jouf, is one of the provinces of Saudi Arabia, located in the north of the country, partially bordered by Jordan to the west. It is one of the earliest inhabited regions of Arabian Peninsula, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Stone Age and the Acheulean tool culture. Human settlement continued unbroken throughout the Copper Age, a period that saw the kingdom of Qidar fight against the Assyrian state for its independence. It is also in this period that references to Arabs first appear in historical texts. A Christian kingdom later emerged under the rule of the Bani Kalb tribe and survived until the arrival of Islam and the Islamic conquest of Al-Jawf. Following the region's Islamization it fell under the control of the Tayy tribe. Al-Jawf was incorporated into the third Saudi state at the time of its formation in 1932. In the 20th century the region was a site of conflict between the Al-Rashid family and the Al-Shaalan family, though it eventually came under the rule of King Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud.

Dumat al-Jandal, also known as Al-Jawf or Al-Jouf, which refers to Wadi Sirhan, is an ancient city of ruins and the historical capital of the Al Jawf Province, today in northwestern Saudi Arabia. It is located 37 km from Sakakah.
The Battle of Daumat al-Jandal took place between Muslims and Rebel Arab tribes in August 633 CE. This was a part of the Riddah wars. Daumat al-Jandal was given to Iyad ibn Ghanm to crush the rebels, but he failed in doing so, and send for help to Khalid ibn Walid who was in Iraq in those days.

Tarout or Tārūt Island is an island in the Persian Gulf belonging to the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, connected by three causeways to Qatif. It is six kilometers from the coast, and is the longest island in the Persian Gulf after Qeshm Island, extending from Ra’s Tannurah in the north to Qatif in the west. The island has an area of 70 square kilometers, and a population (2010) of 77,757. It contains a number of towns and villages, including Tārūt itself, Deyrah, and Darīn.

Saudi Arabia is the second biggest tourist destination in the Middle East with over 16 million visiting in 2017. Although most tourism in Saudi Arabia still largely involves religious pilgrimages, there is growth in the leisure tourism sector. As the tourism sector has been largely boosted lately, the sector is expected to a significant industry for Saudi Arabia, reducing its dependence on oil revenues. This is proved as tourism sector is expected to generate $25 billion in 2019. Potential tourist areas include the Hijaz and Sarawat Mountains, Red Sea diving and a number of ancient ruins.
Marid Castle is a historic military fortress located in the city of Dumat al-Jandal in the Al-Jawf region of Saudi Arabia, about 50 km from Sakaka. Built in the first century AD, it was first mentioned in the third century in the context of Queen Zenobia's campaign against Dumat al-Jandal and Tayma's rebellion, when her troops weren't able to capture the fortress.

Sakākā, often spelled Sakakah is a city in northwestern Saudi Arabia which is the capital of Al-Jawf Province. located just to the north of the An Nafud desert. Sakakah had a population of 209,174 at the 2024 census.
Thirteen ancient towns have been discovered in Saudi Arabia up to the present day. These include Qaryat al-Fāw, the Al-Ukhdūd archeological area, Hegra, Jubbah, Tārūt, Al-Shuwayḥaṭiyah, Thāj, Taimaa and Dūmat Al-Jandal. There are still more ancient towns in Saudi Arabia, but little information is currently available on them. Saudi Arabia occupies a unique and distinctive geographic location, bridging civilizations between continents. In ancient times the Arabian peninsula served as a corridor for trade; therefore it saw the beginning of many civilizations, the relics of which are still evident today. The Saudi government has recently established the Saudi Commission for Tourism and Antiquities, which is responsible for the preservation of these cities.
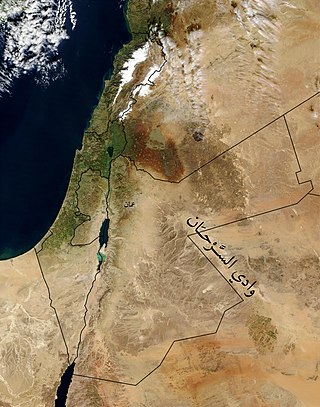
Wadi Sirhan is a wide depression in the northwestern Arabian Peninsula. It runs from the Aljouf Oasis in Saudi Arabia northwestward into Jordan. It historically served as a major trade and transportation route between Syria and Arabia. From antiquity until the early 20th century, control of Wadi Sirhan was often contested by various Arab tribes. The valley is named after the Sirhan tribe which migrated there in the mid-17th century.

Tarut Castle, also known as Tarut Palace, Tarut Fort, Portuguese Fort, or simply "The Fort," is an archaeological site
Al-Jandal Sport Club is a professional Saudi-Arabian football club based in Dumat al-Jandal, They currently play in the FD League, the second tier of Saudi football.

Qasr Ibrahim is a historic fort in the north of Alqoat neighborhood, Hofuf, Al-Ahsa, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It is also called the Dome Palace, AlQoat Palace or Ibrahim Castle and is the region's main architectural heritage site from the Ottoman period. It served as a Turkish military base. It was seized by King Abdul-Aziz Al Saud on April 13, 1913.

The Rajajel Columns is an archaeological site of pillars carved from sandstone thought to be 6,000 years old. It is located in the Al Jawf Region in Saudi Arabia. Specifically situated in the suburb of Qara south of Sakakah, it consists of 50 groups of erected stone columns called Rajajil. Some of the existing columns are higher than three meters, while they are about 60 cm thick.

Zabal Castle is a castle in the north of the city of Sakaka in the Al-Jouf region in the north of Saudi Arabia.

The Mosque of Umar ibn al-Khattab is a Sunni Islam mosque, located within the historic city of Dumat al-Jandal in the Al Jawf Province of Saudi Arabia. The mosque is named after the Rashidun caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab, who is believed to have constructed the mosque, although this claim has been contested. The mosque's minaret is the first of its kind to be built in North Arabia as well.

The Sisera well is one of the ancient wells in the Al-Jawf region in Saudi Arabia.
The archaeology of Saudi Arabia includes the following archaeological sites:
The Dūmat al-Jandal inscription is an Arabic Christian graffito written in the Paleo-Arabic script, and discovered at the Arabian site of Dumat al-Jandal. It was carved into the middle-left of a sandstone bolder, above a Nabataean Arabic inscription found a little lower. The rock also contains drawings of four female camels, one male camel, and an ibex.
Lake Dumat al-Jandal is an anthropogenic body of water, created in Dumat al-Jandal, Al-Jawf Province, northern Saudi Arabia, as a means of mitigating the risk of flooding caused by excess irrigation water from palm plantations. To accommodate the excess water, surface wells were constructed to facilitate its elevation and subsequent discharge over a neighboring hill, thereby forming the basis of this artificial lake. Lake Dumat al-Jandal is the largest unnatural lake in the Arabian Peninsula and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in particular.













