
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare applications. BME is also traditionally logical sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy. Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment in hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards. This involves procurement, routine testing, preventive maintenance, and making equipment recommendations, a role also known as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) or as a clinical engineer.

Positive airway pressure (PAP) is a mode of respiratory ventilation used in the treatment of sleep apnea. PAP ventilation is also commonly used for those who are critically ill in hospital with respiratory failure, in newborn infants (neonates), and for the prevention and treatment of atelectasis in patients with difficulty taking deep breaths. In these patients, PAP ventilation can prevent the need for tracheal intubation, or allow earlier extubation. Sometimes patients with neuromuscular diseases use this variety of ventilation as well. CPAP is an acronym for "continuous positive airway pressure", which was developed by Dr. George Gregory and colleagues in the neonatal intensive care unit at the University of California, San Francisco. A variation of the PAP system was developed by Professor Colin Sullivan at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney, Australia, in 1981.

Oxygen therapy, also referred to as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Supplemental oxygen can also refer to the use of oxygen enriched air at altitude. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia, carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactically given to maintain blood oxygen levels during the induction of anesthesia. Oxygen therapy is often useful in chronic hypoxemia caused by conditions such as severe COPD or cystic fibrosis. Oxygen can be delivered via nasal cannula, face mask, or endotracheal intubation at normal atmospheric pressure, or in a hyperbaric chamber. It can also be given through bypassing the airway, such as in ECMO therapy.

The Cigna Group is an American multinational for-profit managed healthcare and insurance company based in Bloomfield, Connecticut. Its insurance subsidiaries are major providers of medical, dental, disability, life and accident insurance and related products and services, the majority of which are offered through employers and other groups. Cigna is incorporated in Delaware.
Disease management is defined as "a system of coordinated healthcare interventions and communications for populations with conditions in which patient self-care efforts are significant."

Lift chairs, also known as lift recliners or riser armchairs, are chairs that feature a powered lifting mechanism that pushes the entire chair up from its base and so assists the user to a standing position.
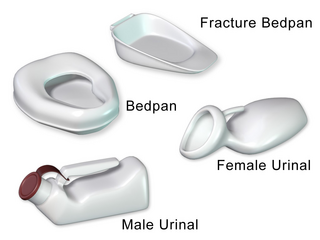
A bedpan or bed pan is a device used as a receptacle for the urine and/or feces of a person who is confined to a bed and therefore not able to use a toilet or chamber pot.

ResMed Inc. is an American medical equipment company based in San Diego, California. It primarily provides cloud-connectable medical devices for the treatment of sleep apnea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory conditions. ResMed produced hundreds of thousands of ventilators and bilevel devices to help treat the respiratory symptoms of patients with COVID-19. ResMed also provides software to out-of-hospital care agencies to streamline transitions of care into and between these care settings for seniors and their care providers.
Health technology is defined by the World Health Organization as the "application of organized knowledge and skills in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of lives". This includes pharmaceuticals, devices, procedures, and organizational systems used in the healthcare industry, as well as computer-supported information systems. In the United States, these technologies involve standardized physical objects, as well as traditional and designed social means and methods to treat or care for patients.

For health issues in Iran see Health in Iran.
In the US a certificate of medical necessity is a document required by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to substantiate in detail the medical necessity of an item of durable medical equipment or a service to a Medicare beneficiary. There are different types of CMN for different requirements, e.g., insulin pumps, home health and private duty nursing services, etc.
This article discusses the definitions and types of home medical equipment (HME), also known as durable medical equipment (DME), and durable medical equipment and prosthetics and orthotics (DMEPOS).
In the United States, Medicare fraud is the claiming of Medicare health care reimbursement to which the claimant is not entitled. There are many different types of Medicare fraud, all of which have the same goal: to collect money from the Medicare program illegitimately.

A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical medical laboratories are an example of applied science, as opposed to research laboratories that focus on basic science, such as found in some academic institutions.
Health care in Australia operates under a shared public-private model underpinned by the Medicare system, the national single-payer funding model. State and territory governments operate public health facilities where eligible patients receive care free of charge. Primary health services, such as GP clinics, are privately owned in most situations, but attract Medicare rebates. Australian citizens, permanent residents, and some visitors and visa holders are eligible for health services under the Medicare system. Individuals are encouraged through tax surcharges to purchase health insurance to cover services offered in the private sector, and further fund health care.
The Compliance Team (TCT) Inc., is a US for-profit organization that provides Exemplary Provider accreditation and certification services to healthcare providers across the United States. It was set up in 1994 and is based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
The Healthcare Quality Association on Accreditation (HQAA) is a US not-for-profit health care accrediting body and is an alternative to the Community Health Accreditation Partner (CHAP), Accreditation Commission for Health Care and Joint Commission. The organization provides an accreditation option specifically designed with the durable medical equipment (DME).

A standing wheelchair is assistive technology, similar to a standing frame, that allows a wheelchair user to raise the chair from a seated to a standing position. The standing wheelchair supports the person in a standing position and enables interaction with people and objects at eye level.

Ekso Bionics Holdings Inc. is a company that develops and manufactures powered exoskeleton bionic devices that can be strapped on as wearable robots to enhance the strength, mobility, and endurance of industrial workers and people experiencing paralysis and mobility issues after a brain injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis (MS) or spinal cord injury. They enable individuals with any amount of lower extremity weakness, including those who are paralyzed, to stand up and walk.
A hospital readmission is an episode when a patient who had been discharged from a hospital is admitted again within a specified time interval. Readmission rates have increasingly been used as an outcome measure in health services research and as a quality benchmark for health systems. Generally, higher readmission rate indicates ineffectiveness of treatment during past hospitalizations. Hospital readmission rates were formally included in reimbursement decisions for the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) as part of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2010, which penalizes health systems with higher than expected readmission rates through the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program. Since the inception of this penalty, there have been other programs that have been introduced, with the aim to decrease hospital readmission. The Community Based Care Transition Program, Independence At Home Demonstration Program, and Bundled Payments for Care Improvement Initiative are all examples of these programs. While many time frames have been used historically, the most common time frame is within 30 days of discharge, and this is what CMS uses.












