Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes.The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.

The ECOPEACE Party is a national environmentalist political party in South Africa founded in 1995. The party was formerly known as eThekwini ECOPEACE and eThekwini Ecoparty—eThekwini is the Zulu name for Durban, where the party is based. The Zulu party motto is Buhlakuleni uButhi, Yitshaleni iMithi, which translates to "Uproot Poisons, Replant Trees ".

A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent. Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carbon dioxide and methane, can be emitted through the burning of fossil fuels, land clearance and the production and consumption of food, manufactured goods, materials, wood, roads, buildings, transportation and other services. The term was popularised by a $250 million ad campaign by the oil and gas company BP in an attempt to move public attention away from restricting the activities of fossil fuel companies and onto individual responsibility for solving climate change.
Business action on climate change includes a range of activities relating to global warming, and to influencing political decisions on global-warming-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of global warming, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of global warming deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of global warming, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.
A low-carbon economy (LCE), low-fossil-fuel economy (LFFE), or decarbonised economy is an economy based on low-carbon power sources that therefore has a minimal output of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions into the atmosphere, specifically carbon dioxide. GHG emissions due to anthropogenic (human) activity are the dominant cause of observed global warming since the mid-20th century. Continued emission of greenhouse gases may cause long-lasting changes around the world, increasing the likelihood of severe, pervasive, and irreversible effects for people and ecosystems.
The G8 Climate Change Roundtable was formed in January 2005 at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland. Its purpose was to address the global climate change issue facing governments, business and civil society. The first meeting was held in Gleneagles, Scotland, from 6–8 July 2005, to coincide with the 31st G8 summit.
This is a list of climate change topics.

Adaptation to climate change is important because the risks are particularly severe in some regions of Australia, such as the Great Barrier Reef in Queensland, the Macquarie Marshes in New South Wales. The Department of Climate Change said in its Climate Change Impacts and Costs fact sheet: "...ecologically rich sites, such as the Great Barrier Reef, Queensland Wet Tropics, Kakadu Wetlands, Australian Alpine areas, south-western Australia and sub- Antarctic islands are all at risk, with significant loss of biodiversity projected to occur by 2020". It also said: "Very conservatively, 90 Australian animal species have so far been identified at risk from climate change, including mammals, insects, birds, reptiles, fish, and amphibians from all parts of Australia." Australia is already the driest populated continent in the world.

See Also: climate change mitigation, emissions trading.
The Global Climate Network (GCN) is an alliance of influential think tanks and research institutes in different countries that collaborate on research into climate change policy and whose stated aim is to help address the political blockages to ambitious action to tackle global warming.

Belgrave Trust is a social enterprise firm that uses carbon offsets to allow individuals to live carbon neutral, through subscriptions and environmentally conscious products bundled with offsets. The firm's principal business is conducted through a retail website that offers a curated selection of physical items as well as personal and gift subscriptions. Revenues derived from subscribers and through the sale of products are used to offset greenhouse gasses through the purchase and retirement of carbon offset securities that fund projects creating clean energy or reducing emissions.

The International Day of Forests was established on the 21st day of March, by resolution of the United Nations General Assembly on November 28, 2012. Each year, various events celebrate and raise awareness of the importance of all types of forests, and trees outside forests, for the benefit of current and future generations. Countries are encouraged to undertake efforts to organize local, national, and international activities involving forests and trees, such as tree planting campaigns, on International Day of Forests. The Secretariat of the United Nations Forum on Forests, in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization, facilitates the implementation of such events in collaboration with governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests, and international, regional and subregional organizations. International Day of Forests was observed for the first time on March 21, 2013.

eThekwini Metropolitan Municipality is a metropolitan municipality created in 2000, that includes the city of Durban, South Africa and surrounding towns. eThekwini is one of the 11 districts of KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa. The majority of its 3,442,361 people speak Zulu. It was formed from seven formerly independent local councils and tribal land.
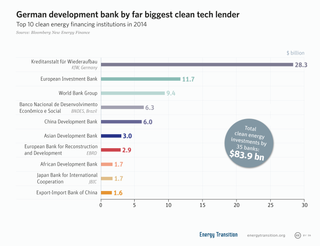
Climate finance is “finance that aims at reducing emissions, and enhancing sinks of greenhouse gases and aims at reducing vulnerability of, and maintaining and increasing the resilience of, human and ecological systems to negative climate change impacts”, as defined by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Standing Committee on Finance. The term has been used in a narrow sense to refer to transfers of public resources from developed to developing countries, in light of their UN Climate Convention obligations to provide "new and additional financial resources", and in a wider sense to refer to all financial flows relating to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
The Urbanization and Global Environmental Change Project (UGEC) is one of the core research projects of the International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental Change (IHDP). UGEC aims to understand the bi-directional interactions between urbanization and global environmental change. The UGEC International Project Office is located at Arizona State University.

The Climate and Development Knowledge Network (CDKN) works to enhance the quality of life for the poorest and most vulnerable to climate change. CDKN does this by combining research, advisory services and knowledge management in support of locally owned and managed policy processes. It works in partnership with decision-makers in the public, private and non-governmental sectors nationally, regionally and globally.
The Buffelsdraai Landfill Site Community Reforestation Project (BLSCRP) was initiated in 2008 to alleviate climate change impacts associated with hosting elements of the 2010 FIFA World Cup in Durban. The proposed carbon offset was to be achieved through the planting of more than 500 000 indigenous trees within the buffer zone of the Buffelsdraai Landfill Site. Restoring the forest ecosystem was identified as a way of "absorbing event-related greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing the capacity of people and biodiversity to adapt to the inevitable effects of climate change".

Alfred Park is a small wetland swamp forest in New Germany, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It is managed by the Ethekwini Municipality.
Debra C. Roberts is a South African government worker and one of the six co-chairs of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. She was elected co-chair of Working Group II for the sixth assessment in 2015.










