Dynamics or dynamic may refer to:

In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics. Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation.
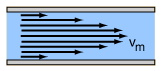
Laminar flow is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another smoothly. There are no cross-currents perpendicular to the direction of flow, nor eddies or swirls of fluids. In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface. Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection.

Aeroelasticity is the branch of physics and engineering studying the interactions between the inertial, elastic, and aerodynamic forces occurring while an elastic body is exposed to a fluid flow. The study of aeroelasticity may be broadly classified into two fields: static aeroelasticity dealing with the static or steady state response of an elastic body to a fluid flow, and dynamic aeroelasticity dealing with the body's dynamic response.
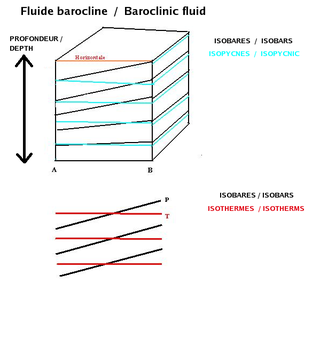
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology a baroclinic flow is one in which the density depends on both temperature and pressure. A simpler case, barotropic flow, allows for density dependence only on pressure, so that the curl of the pressure-gradient force vanishes.
Bifurcation or bifurcated may refer to:

In dynamical systems instability means that some of the outputs or internal states increase with time, without bounds. Not all systems that are not stable are unstable; systems can also be marginally stable or exhibit limit cycle behavior.

Faraday waves, also known as Faraday ripples, named after Michael Faraday (1791–1867), are nonlinear standing waves that appear on liquids enclosed by a vibrating receptacle. When the vibration frequency exceeds a critical value, the flat hydrostatic surface becomes unstable. This is known as the Faraday instability. Faraday first described them in an appendix to an article in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London in 1831.
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure refers to a term in Bernoulli's equation written words as static pressure + dynamic pressure = total pressure. Since pressure measurements at any single point in a fluid always give the static pressure value, the 'static' is often dropped. In the design and operation of aircraft, static pressure is the air pressure in the aircraft's static pressure system.

Horizontal convective rolls, also known as horizontal roll vortices or cloud streets, are long rolls of counter-rotating air that are oriented approximately parallel to the ground in the planetary boundary layer. Although horizontal convective rolls, also known as cloud streets, have been clearly seen in satellite photographs for the last 30 years, their development is poorly understood, due to a lack of observational data. From the ground, they appear as rows of cumulus or cumulus-type clouds aligned parallel to the low-level wind. Research has shown these eddies to be significant to the vertical transport of momentum, heat, moisture, and air pollutants within the boundary layer. Cloud streets are usually more or less straight; rarely, cloud streets assume paisley patterns when the wind driving the clouds encounters an obstacle. Those cloud formations are known as von Kármán vortex streets.
Static stability is the ability of a robot to remain upright when at rest, or under acceleration and deceleration
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.






