Related Research Articles
E-procurement is a collective term used to refer to a range of technologies which can be used to automate the internal and external processes associated with procurement, strategic sourcing and purchasing.
When used in foreign trade, a commercial invoice is a customs document. It is used as a customs declaration provided by the person or corporation that is exporting an item across international borders. Although there is no standard format, the document must include a few specific pieces of information such as the parties involved in the shipping transaction, the goods being transported, the country of manufacture, and the Harmonized System codes for those goods. A commercial invoice must often include a statement certifying that the invoice is true, and a signature.

A concession or concession agreement is a grant of rights, land, property, or facility by a government, local authority, corporation, individual or other legal entity.
Government procurement or public procurement is undertaken by the public authorities of the European Union (EU) and its member states in order to award contracts for public works and for the purchase of goods and services in accordance with principles derived from the Treaties of the European Union. Such procurement represents 13.6% of EU GDP as of March 2023, and has been the subject of increasing European regulation since the 1970s because of its importance to the European single market.
Government procurement or public procurement is when a governing body purchases goods, works, and services from an organization for themselves or the taxpayers. In 2019, public procurement accounted for approximately 12% of GDP in OECD countries. In 2021 the World Bank Group estimated that public procurement made up about 15% of global GDP. Therefore, government procurement accounts for a substantial part of the global economy.

Transport in the European Union is a shared competence of the Union and its member states. The European Commission includes a Commissioner for Transport, currently Adina Ioana Vălean. Since 2012, the commission also includes a Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport which develops EU policies in the transport sector and manages funding for Trans-European Networks and technological development and innovation, worth €850 million yearly for the period 2000–2006.

The Schengen Area is an area encompassing 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.
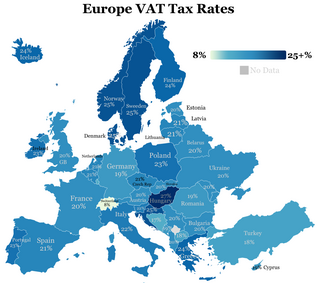
The European Union value-added tax is a value added tax on goods and services within the European Union (EU). The EU's institutions do not collect the tax, but EU member states are each required to adopt in national legislation a value added tax that complies with the EU VAT code. Different rates of VAT apply in different EU member states, ranging from 17% in Luxembourg to 27% in Hungary. The total VAT collected by member states is used as part of the calculation to determine what each state contributes to the EU's budget.
The Trade Control and Expert System (TRACES), is a web-based veterinarian certification tool used by the European Union for controlling the import and export of live animals and animal products within and without its borders. Its network falls under the responsibility of the European Commission. TRACES constitutes a key element of how the European Union facilitates trade and improves health protection for the consumer, as laid down in the First Pillar principle. Other countries use computer networks to provide veterinary certification, but TRACES is the only supranational network working at a continental scale of 28 countries and almost 500 million people.
The Single European Railway Directive 2012 is an EU Directive that regulates railway networks in European Union law. This recast the First Railway Directive" and consolidates legislation from each of the first to the fourth "Package" from 1991 to 2016, and allows open access operations on railway lines by companies other than those that own the rail infrastructure. The legislation was extended by further directives to include cross border transit of freight.

The Body of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC) is the body in which the regulators of the telecommunications markets in the European Union work together. Other participants include representatives of the European Commission, as well as telecommunication regulators from the member states of the EEA and of states that are in the process of joining the EU.
A European Investigation Order (EIO) is a mechanism established under EU law by which a judge or magistrate in one EU member state can make a binding request to the law enforcement agencies of another member state to collect evidence to assist in a criminal investigation. The order may authorise such actions as searches, wiretapping, surveillance, the subpoena of documents or records, etc. The mechanism exists throughout the EU, with the exception of Denmark and Ireland, who have opt-outs in this area of EU law. The EIO was established by Directive 2014/41/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 3 April 2014 regarding the European Investigation Order in criminal matters.

An invitation to tender is a formal, structured procedure for generating competing offers from different potential suppliers or contractors looking to obtain an award of business activity in works, supply, or service contracts, often from companies who have been previously assessed for suitability by means of a supplier questionnaire (SQ) or pre-qualification questionnaire (PQQ).
The European Single Procurement Document (ESPD) is an electronic self-declaration document to be submitted by suppliers interested in tendering for contracts for the supply of goods, works or services to public bodies located anywhere within the European Union.
The term digital single market refers to the policy objective of eliminating national or other jurisdictional barriers to online transactions, building on the common market concept designed to remove trade barriers in other commercial fields.
The Small Business Act for Europe(SBA) is a package of principles put forward by the European Commission in 2008, designed to assist small businesses within the European Union (EU). The package contains ten "guiding principles intended for adoption "at the highest political level" across the EU. It is not a legislative act as such.

European company law is the part of European Union law which concerns the formation, operation and insolvency of companies in the European Union. The EU creates minimum standards for companies throughout the EU, and has its own corporate forms. All member states continue to operate separate companies acts, which are amended from time to time to comply with EU Directives and Regulations. There is, however, also the option of businesses to incorporate as a Societas Europaea (SE), which allows a company to operate across all member states.

The Energy Efficiency Directive 2012/27/EU is a European Union directive which mandates energy efficiency improvements within the European Union. It was approved on 25 October 2012 and entered into force on 4 December 2012. The directive introduces legally binding measures to encourage efforts to use energy more efficiently in all stages and sectors of the supply chain. It establishes a common framework for the promotion of energy efficiency within the EU in order to meet its energy efficiency headline target of 20% by 2020. It also paves the way for further improvements thereafter.
References
- ↑ Welcome to e-CERTIS, accessed 21 October 2018
- ↑ "Answer to Question No E-006587/11". europarl.europa.eu. European Parliament . Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- ↑ Directive 2014/24/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 February 2014 on public procurement and repealing Directive 2004/18/EC, preamble 87 and Article 61; implementation date stated in 90, section 5
- ↑ European Commission, e-Certis, updated 9 March 2017, accessed 30 June 2018