
The economy of Equatorial Guinea has traditionally been dependent on commodities such as cocoa and coffee but is now heavily dependent on petroleum due to the discovery and exploitation of significant oil reserves in the 1980s. In 2017, it graduated from "Least Developed Country" status, the only Sub-Saharan African nation that managed to do so alongside Botswana.

Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume of natural gas in the gaseous state (at standard conditions for temperature and pressure).

The Sakhalin-2 project is an oil and gas development in Sakhalin Island, Russia. It includes development of the Piltun-Astokhskoye oil field and the Lunskoye natural gas field offshore Sakhalin Island in the Okhotsk Sea, and associated infrastructure onshore. The project is managed and operated by Sakhalin Energy Investment Company Ltd..

Sonagas is the Equatorial Guinean national natural gas company. It was formed in 2005. It operates in conjunction with GEPetrol, the nation's principal petroleum company, and EG LNG, the nation's liquid natural gas company, to manage the nation's fossil fuel resources.

SEGESA is the national electricity company of Equatorial Guinea, with its head offices in Malabo, Equatorial Guinea. It is the sole operator of the electricity sector of Equatorial Guinea. The company was created in November 2001 by a merger of the national rural electrification company SONER and the national electricity corporation ENERGE. In 2013 the company was reorganized into three units: SEGESA Comercial for distribution and sales, SEGESA Generación for generation activities and SEGESA Transmisión for transmission. The three units are overseen by SEGESA Holding.
Angola LNG is a liquid natural gas (LNG) facility in Soyo, Angola.
RasGas Company Limited was a liquefied natural gas (LNG) producing company in Qatar. It was the second-biggest LNG producer in Qatar after Qatargas. RasGas operated seven LNG trains located in Ras Laffan Industrial City. It was merged with Qatargas on 1 January 2018.
Liquid Niugini LNG is a natural gas liquefaction project in Papua New Guinea. It is developed by Liquid Niugini Gas Ltd, and owned by PNG LNG Inc., a Bahamas-based parent holding company.

Yemen LNG is the first natural gas liquefaction (LNG) project in Yemen. The LNG plant is located in Balhaf.

Oman LNG is a LNG plant in Qalhat near Sur, Oman. The company was established by the Royal decree of Sultan Qaboos of Oman in 1994. The construction was launched in November 1996, and the plant was commissioned in September 2000. Oman LNG operates three LNG trains with a total capacity of 10.4 million tonnes per year. The company's production facilities are located on the coast at Qalhat near Sur in the South Sharqiyah Governorate, Oman.

Sakhalin Energy Investment Company Ltd. is a consortium for developing the Sakhalin-2 oil and gas project with corporate head office in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. Andrei Galaev has been the chief executive officer since 2009.
Malaysia LNG (MLNG) is a liquefied natural gas manufacturer in Malaysia. In 2007, it was the largest LNG manufacturing complex.
SEGAS LNG is a liquefied natural gas complex in Damietta, Egypt. It is located 60 kilometres (37 mi) west of Port Said. The name SEGAS comes from the Spanish Egyptian Gas Company.
Iran LNG, also known as NIOC LNG, is a LNG plant under development at Tombak Port, approximately 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of Assaluyeh Port and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) southeast of Kangan, Iran.
Energy in Equatorial Guinea is an industry with plenty of potential, especially in the fields of oil and natural gas.
Peru LNG is a natural gas liquefaction plant in Pampa Melchorita, Peru, at the 170-kilometre (110 mi) of the South Pan American Highway in San Vicente de Cañete. It is the first natural gas liquefaction plant in South America.

The EG LNG Pipeline Suspension Bridge is a suspension bridge in Bioko, Equatorial Guinea. It is the first in the world to carry a Liquefied Natural Gas pipeline.
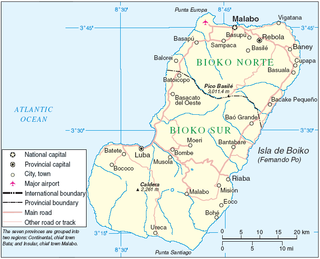
Bioko is an island 32 km (20 mi) off the west coast of Africa and the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea. Its population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of 2,017 km2 (779 sq mi). The island is located off the Ambazonian segment of Cameroon, in the Bight of Bonny portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at 3,012 m (9,882 ft).
LNG Canada is a large industrial energy project that will build and operate a terminal for the liquefaction, storage, and loading of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in the port of Kitimat, British Columbia, Canada. It will export LNG produced by the project's partners in the Montney Formation gas fields near Dawson Creek, B.C.











