
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.

Dell EMC is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Hopkinton, Massachusetts, and Round Rock, Texas, United States. Dell EMC sells data storage, information security, virtualization, analytics, cloud computing and other products and services that enable organizations to store, manage, protect, and analyze data. Dell EMC's target markets include large companies and small- and medium-sized businesses across various vertical markets. The company's stock was added to the New York Stock Exchange on April 6, 1986, and was also listed on the S&P 500 index.
NetApp, Inc. is an intelligent data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.

In finance, market data is price and other related data for a financial instrument reported by a trading venue such as a stock exchange. Market data allows traders and investors to know the latest price and see historical trends for instruments such as equities, fixed-income products, derivatives, and currencies.
Gluster Inc. was a software company that provided an open source platform for scale-out public and private cloud storage. The company was privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster was funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index Ventures. Gluster was acquired by Red Hat on October 7, 2011.

Dell EMC Isilon is a scale out network-attached storage platform offered by Dell EMC for high-volume storage, backup and archiving of unstructured data. It provides a cluster-based storage array based on industry standard hardware, and is scalable to 50 petabytes in a single filesystem using its FreeBSD-derived OneFS file system.
Cloud storage is a model of computer data storage in which data, said to be on "the cloud", is stored remotely in logical pools and is accessible to users over a network, typically the Internet. The physical storage spans multiple servers, and the physical environment is typically owned and managed by a cloud computing provider. These cloud storage providers are responsible for keeping the data available and accessible, and the physical environment secured, protected, and running. People and organizations buy or lease storage capacity from the providers to store user, organization, or application data.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically uses a pay-as-you-go model, which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for users.
GlobalScape, Inc. (AMEX:GSB) is a software developer headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, United States.
In computer storage, a global file system is a distributed file system that can be accessed from multiple locations, typically across a wide-area network, and provides concurrent access to a global namespace from all locations. In order for a file system to be considered global, it must allow for files to be created, modified, and deleted from any location. This access is typically provided by a cloud storage gateway at each edge location, which provides access using the NFS or SMB network file sharing protocols.
A cloud storage gateway is a hybrid cloud storage device, implemented in hardware or software, which resides at the customer premises and translates cloud storage APIs such as SOAP or REST to block-based storage protocols such as iSCSI or Fibre Channel or file-based interfaces such as NFS or SMB.
EMC Atmos is a cloud storage services platform developed by EMC Corporation. Atmos can be deployed as either a hardware appliance or as software in a virtual environment. The Atmos technology uses an object storage architecture designed to manage petabytes of information and billions of objects across multiple geographic locations as a single system.
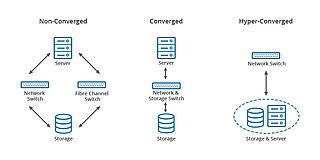
Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.
Panzura is a privately owned American software company based in San Jose, California, that provides hybrid-cloud data management software and services for the enterprise software market. Its software helps users access, manage, analyze, and store unstructured data using techniques in distributed data consolidation, artificial intelligence, and network load balancing.
Object storage is a computer data storage approach that manages data as "blobs" or "objects", as opposed to other storage architectures like file systems which manages data as a file hierarchy, and block storage which manages data as blocks within sectors and tracks. Each object is typically associated with a variable amount of metadata, and a globally unique identifier. Object storage can be implemented at multiple levels, including the device level, the system level, and the interface level. In each case, object storage seeks to enable capabilities not addressed by other storage architectures, like interfaces that are directly programmable by the application, a namespace that can span multiple instances of physical hardware, and data-management functions like data replication and data distribution at object-level granularity.
ViPR Controller is a software-defined storage offering from EMC Corporation announced on May 6, 2013, at EMC World. ViPR abstracts storage from disparate arrays into a single pool of storage capacity that "makes it easier to manage and automate its own data-storage devices and those made by competitors." ViPR became generally available September 27, 2013.
Scality is a global technology provider of software-defined storage (SDS) solutions, specializing in distributed file and object storage with cloud data management. Scality maintains offices in Paris (France), London (UK), San Francisco and Washington DC (USA), and Tokyo (Japan) and has employees in 14 countries.
An elastic cloud is a cloud computing offering that provides variable service levels based on changing needs.
Dell EMC Data Domain was Dell EMC’s data deduplication storage system. Development began with the founding of Data Domain, and continued since that company’s acquisition by EMC Corporation.

Datera was a global enterprise software company headquartered in Santa Clara, California that developed an enterprise software-defined storage platform. Datera was acquired by VMware in April 2021.






