Related Research Articles

In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences, such as calculating the distance cost between strings in a natural language or in financial data.
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins through the design and production of unnatural polypeptides, often by altering amino acid sequences found in nature. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It has been used to improve the function of many enzymes for industrial catalysis. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017.

Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its secondary and tertiary structure from primary structure. Structure prediction is different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by computational biology; and it is important in medicine and biotechnology.

Structural alignment attempts to establish homology between two or more polymer structures based on their shape and three-dimensional conformation. This process is usually applied to protein tertiary structures but can also be used for large RNA molecules. In contrast to simple structural superposition, where at least some equivalent residues of the two structures are known, structural alignment requires no a priori knowledge of equivalent positions. Structural alignment is a valuable tool for the comparison of proteins with low sequence similarity, where evolutionary relationships between proteins cannot be easily detected by standard sequence alignment techniques. Structural alignment can therefore be used to imply evolutionary relationships between proteins that share very little common sequence. However, caution should be used in using the results as evidence for shared evolutionary ancestry because of the possible confounding effects of convergent evolution by which multiple unrelated amino acid sequences converge on a common tertiary structure.
In molecular biology, protein threading, also known as fold recognition, is a method of protein modeling which is used to model those proteins which have the same fold as proteins of known structures, but do not have homologous proteins with known structure. It differs from the homology modeling method of structure prediction as it is used for proteins which do not have their homologous protein structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), whereas homology modeling is used for those proteins which do. Threading works by using statistical knowledge of the relationship between the structures deposited in the PDB and the sequence of the protein which one wishes to model.
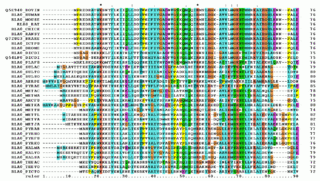
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a linkage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino acids or nucleotides.
Nucleic acid structure prediction is a computational method to determine secondary and tertiary nucleic acid structure from its sequence. Secondary structure can be predicted from one or several nucleic acid sequences. Tertiary structure can be predicted from the sequence, or by comparative modeling.

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein. Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.
Modeller, often stylized as MODELLER, is a computer program used for homology modeling to produce models of protein tertiary structures and quaternary structures (rarer). It implements a method inspired by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins, termed satisfaction of spatial restraints, by which a set of geometrical criteria are used to create a probability density function for the location of each atom in the protein. The method relies on an input sequence alignment between the target amino acid sequence to be modeled and a template protein which structure has been solved.
Loop modeling is a problem in protein structure prediction requiring the prediction of the conformations of loop regions in proteins with or without the use of a structural template. Computer programs that solve these problems have been used to research a broad range of scientific topics from ADP to breast cancer. Because protein function is determined by its shape and the physiochemical properties of its exposed surface, it is important to create an accurate model for protein/ligand interaction studies. The problem arises often in homology modeling, where the tertiary structure of an amino acid sequence is predicted based on a sequence alignment to a template, or a second sequence whose structure is known. Because loops have highly variable sequences even within a given structural motif or protein fold, they often correspond to unaligned regions in sequence alignments; they also tend to be located at the solvent-exposed surface of globular proteins and thus are more conformationally flexible. Consequently, they often cannot be modeled using standard homology modeling techniques. More constrained versions of loop modeling are also used in the data fitting stages of solving a protein structure by X-ray crystallography, because loops can correspond to regions of low electron density and are therefore difficult to resolve.
BLAT is a pairwise sequence alignment algorithm that was developed by Jim Kent at the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) in the early 2000s to assist in the assembly and annotation of the human genome. It was designed primarily to decrease the time needed to align millions of mouse genomic reads and expressed sequence tags against the human genome sequence. The alignment tools of the time were not capable of performing these operations in a manner that would allow a regular update of the human genome assembly. Compared to pre-existing tools, BLAT was ~500 times faster with performing mRNA/DNA alignments and ~50 times faster with protein/protein alignments.

HMMER is a free and commonly used software package for sequence analysis written by Sean Eddy. Its general usage is to identify homologous protein or nucleotide sequences, and to perform sequence alignments. It detects homology by comparing a profile-HMM to either a single sequence or a database of sequences. Sequences that score significantly better to the profile-HMM compared to a null model are considered to be homologous to the sequences that were used to construct the profile-HMM. Profile-HMMs are constructed from a multiple sequence alignment in the HMMER package using the hmmbuild program. The profile-HMM implementation used in the HMMER software was based on the work of Krogh and colleagues. HMMER is a console utility ported to every major operating system, including different versions of Linux, Windows, and Mac OS.

RAPTOR is protein threading software used for protein structure prediction. It has been replaced by RaptorX, which is much more accurate than RAPTOR.
CS-BLAST (Context-Specific BLAST) is a tool that searches a protein sequence that extends BLAST, using context-specific mutation probabilities. More specifically, CS-BLAST derives context-specific amino-acid similarities on each query sequence from short windows on the query sequences [4]. Using CS-BLAST doubles sensitivity and significantly improves alignment quality without a loss of speed in comparison to BLAST. CSI-BLAST is the context-specific analog of PSI-BLAST, which computes the mutation profile with substitution probabilities and mixes it with the query profile [2]. CSI-BLAST is the context specific analog of PSI-BLAST. Both of these programs are available as web-server and are available for free download.
Protein function prediction methods are techniques that bioinformatics researchers use to assign biological or biochemical roles to proteins. These proteins are usually ones that are poorly studied or predicted based on genomic sequence data. These predictions are often driven by data-intensive computational procedures. Information may come from nucleic acid sequence homology, gene expression profiles, protein domain structures, text mining of publications, phylogenetic profiles, phenotypic profiles, and protein-protein interaction. Protein function is a broad term: the roles of proteins range from catalysis of biochemical reactions to transport to signal transduction, and a single protein may play a role in multiple processes or cellular pathways.
Phyre and Phyre2 are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques, it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
RaptorX is a software and web server for protein structure and function prediction that is free for non-commercial use. RaptorX is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction. Like other remote homology recognition/protein threading techniques, RaptorX is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when the widely used PSI-BLAST cannot. However, RaptorX is also significantly different from those profile-based methods in that RaptorX excels at modeling of protein sequences without a large number of sequence homologs by exploiting structure information. RaptorX Server has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods.
SWISS-MODEL is a structural bioinformatics web-server dedicated to homology modeling of 3D protein structures. Homology modeling is currently the most accurate method to generate reliable three-dimensional protein structure models and is routinely used in many practical applications. Homology modelling methods make use of experimental protein structures ("templates") to build models for evolutionary related proteins ("targets").
The HH-suite is an open-source software package for sensitive protein sequence searching. It contains programs that can search for similar protein sequences in protein sequence databases. Sequence searches are a standard tool in modern biology with which the function of unknown proteins can be inferred from the functions of proteins with similar sequences. HHsearch and HHblits are two main programs in the package and the entry point to its search function, the latter being a faster iteration. HHpred is an online server for protein structure prediction that uses homology information from HH-suite.

I-TASSER is a bioinformatics method for predicting three-dimensional structure model of protein molecules from amino acid sequences. It detects structure templates from the Protein Data Bank by a technique called fold recognition. The full-length structure models are constructed by reassembling structural fragments from threading templates using replica exchange Monte Carlo simulations. I-TASSER is one of the most successful protein structure prediction methods in the community-wide CASP experiments.
References
- ↑ Lambert, C.; Leonard, N.; De Bolle, X.; Depiereux, E. (1 August 2002). "ESyPred3D: Prediction of proteins 3D structures". Bioinformatics. 18 (9): 1250–1256. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.9.1250 .
- ↑ Lee, Minho; Jeong, Chan-seok; Kim, Dongsup (December 2007). "Predicting and improving the protein sequence alignment quality by support vector regression". BMC Bioinformatics. 8 (1): 471. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-471 .