Related Research Articles
Waldric was the eighth Lord Chancellor and Lord Keeper of England, from 1103 to 1107. He was also Bishop of Laon from 1106 to 1112. He had been a royal chaplain as early as 3 September 1101.
Richard le Gras was Lord Keeper of England and Abbot of Evesham in the 13th century.
Richard de Luci was first noted as High Sheriff of Essex, after which he was made Chief Justiciar of England.

Birinus was the first Bishop of Dorchester and was known as the "Apostle to the West Saxons" for his conversion of the Kingdom of Wessex to Christianity. He is venerated as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, and Anglican churches.

The Archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the Province of York, which covers the northern regions of England as well as the Isle of Man. The archbishop of York is an ex officio member of the House of Lords and is styled Primate of England; the archbishop of Canterbury is the Primate of All England.
Sir Robert Parning was an English lawyer and administrator.

The Bishop of Winchester is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Winchester in the Church of England. The bishop's seat (cathedra) is at Winchester Cathedral in Hampshire. The Bishop of Winchester holds ex officio the office of Prelate of the Most Noble Order of the Garter since its foundation in 1348, and Bishops of Winchester often held the positions of Lord Treasurer and Lord Chancellor ex officio. During the Middle Ages, it was one of the wealthiest English sees, and its bishops have included a number of politically prominent Englishmen, notably the 9th century Saint Swithun and medieval magnates including William of Wykeham and Henry of Blois.
Æthelric was Bishop of Durham from 1041 to 1056 when he resigned.
Ætla, who lived in the 7th century, is believed to be one of many Bishops of Dorchester during the Anglo-Saxon period. The village of Attlebridge, Norfolk is named after him, as he is credited for the construction of a bridge there.
Ælfwold was a medieval Bishop of Crediton.
Ealdbeorht may have been a medieval Bishop of Dunwich.
Aethelweald was a medieval Bishop of Elmham.
William de Beaufeu was a medieval Bishop of Thetford and a major landholder mentioned in the Domesday Book.
John Carpenter (1399–1476) was an English Bishop, Provost, and University Chancellor.
Wulfsige was a medieval Bishop of Cornwall.
Æthelred was a medieval Bishop of Cornwall.
Cuthwine was a medieval Bishop of Leicester.
Edward Synge
Joseph Deane Bourke, 3rd Earl of Mayo was an Irish peer and cleric who held several high offices in the Church of Ireland including Bishop of Ferns and Leighlin (1772–82) and archbishopric of Tuam (1782–94).
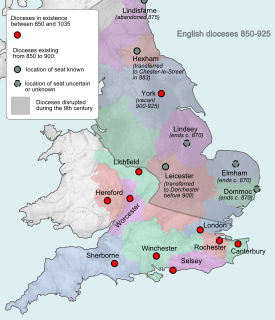
The Bishop of Dunwich is an episcopal title which was first used by an Anglo-Saxon bishop between the seventh and ninth centuries and is currently used by the suffragan bishop of the Diocese of St Edmundsbury and Ipswich. The title takes its name after Dunwich in the English county of Suffolk, which has now largely been lost to the sea.
References
- Powicke, F. Maurice; Fryde, E.B. (1961). Handbook of British Chronology (2nd ed.). London: Offices of the Royal Historical Society. p. 220.
- Fryde, E. B.; Greenway, D. E.; Porter, S.; Roy, I., eds. (1986). Handbook of British Chronology (3rd, reprinted 2003 ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-56350-X.