
Treece is a ghost town in Cherokee County, Kansas, United States, and part of the historic Tri-State Mining District. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 138. As of May 2012 the city was abandoned and most buildings and other facilities demolished due to pervasive problems with lead pollution resulting from past mining. Two people who had refused an Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) buyout remained in 2012, then one died in 2016.

ASARCO is a mining, smelting, and refining company based in Tucson, Arizona, which mines and processes primarily copper. The company has been a subsidiary of Grupo México since 1999.

Gilman is an abandoned mining town in southeastern Eagle County, Colorado, United States. The Gilman post office operated from November 3, 1886, until April 22, 1986. The U.S. Post Office at Minturn now serves Gilman postal addresses.

Naylors Run is a 4.6-mile-long (7.4 km) tributary of Cobbs Creek in Haverford and Upper Darby Township, Pennsylvania, United States.

Burke Canyon is the canyon of the Burke-Canyon Creek, which runs through the northernmost part of Shoshone County, Idaho, U.S., within the northeastern Silver Valley. A hotbed for mining in the late-nineteenth and twentieth centuries, Burke Canyon now contains several ghost towns and remnants of former communities along Idaho State Highway 4, which runs northeast through the narrow canyon to the Montana border.
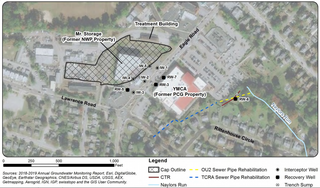
Havertown Superfund is a 13-acre polluted groundwater site in Havertown, Pennsylvania contaminated by the dumping of industrial waste by National Wood Preservers from 1947 to 1991. The state first became aware of the pollution in 1962 and initiated legal action against the owners in 1973 to force them to cleanup the site. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) ranked the site the eighth worst cleanup project in the United States. The site was added to the National Priorities List in 1983 and designated as a Superfund cleanup site in the early 1990s. Remediation and monitoring efforts are ongoing and the EPA transferred control of the site to the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection in 2013.

The Midnite Mine is an inactive uranium mine in the Selkirk Mountains of the state of Washington that operated from 1955 to 1965 and again from 1968 to 1981. Located within the reservation of the Spokane Tribe of Indians, it is approximately 8 miles (13 km) from Wellpinit, Stevens County. The mine was listed as a Superfund site under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA) on May 11, 2000. In addition to elevated levels of radioactivity, heavy metals mobilized in uranium acid mine drainage pose a potential threat to human health and the environment.

The Leadville mining district, located in the Colorado Mineral Belt, was the most productive silver-mining district in the state of Colorado and hosts one of the largest lead-zinc-silver deposits in the world. Oro City, an early Colorado gold placer mining town located about a mile east of Leadville in California Gulch, was the location to one of the richest placer gold strikes in Colorado, with estimated gold production of 120,000–150,000 ozt, worth $2.5 to $3 million at the then-price of $20.67 per troy ounce.

Tar Creek Superfund site is a United States Superfund site, declared in 1983, located in the cities of Picher, Douthat and Cardin, Ottawa County, in northeastern Oklahoma. From 1900 to the 1960s lead mining and zinc mining companies left behind huge open chat piles that were heavily contaminated by these metals, cadmium, and others. Metals from the mining waste leached into the soil, and seeped into groundwater, ponds, and lakes. Because of the contamination, Picher children have suffered elevated lead, zinc and manganese levels, resulting in learning disabilities and a variety of other health problems. The EPA declared Picher to be one of the most toxic areas in the United States.

The Church Rock uranium mill spill occurred in the U.S. state of New Mexico on July 16, 1979, when United Nuclear Corporation's tailings disposal pond at its uranium mill in Church Rock breached its dam. The accident remains the largest release of radioactive material in U.S. history, having released more radioactivity than the Three Mile Island accident four months earlier.

The relationship between Uranium mining and the Navajo people began in 1944 in northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southeastern Utah.

Leviathan Mine is a United States superfund site at an abandoned open-pit sulfur mine located in Alpine County, California. The mine is located on the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada at about 7,000-foot (2,100 m) elevation, 6 miles (9.7 km) east of Markleeville and 24 miles (39 km) southeast of Lake Tahoe. The mine site comprises approximately 250 acres (100 ha) of land surrounded by the Toiyabe National Forest, which is only accessible a few months a year. The approximately 22 million tons of sulfur ore-containing crushed rock at the mine are responsible for contaminating the Leviathan and Aspen Creek, which join with Mountaineer Creek to form Bryant Creek which ultimately empties into the East Fork of the Carson River. These water bodies are listed as 303(d) impaired. The site location is seismically active.

The Tri-State district was a historic lead-zinc mining district located in present-day southwest Missouri, southeast Kansas and northeast Oklahoma. The district produced lead and zinc for over 100 years. Production began in the 1850s and 1860s in the Joplin - Granby area of Jasper and Newton counties of southwest Missouri. Production was particularly high during the World War I era and continued after World War II, but with declining activity. As jobs left the area, the communities declined in population.

The Bunker Hill Mine and Smelting Complex was a large smelter located in Kellogg, Idaho, in the Coeur d'Alene Basin. When built, it was the largest smelting facility in the world. It is located in what became known as the Silver Valley of the Coeur d'Alene Basin, an area for a century that was a center of extensive silver and other metal mining and processing. This resulted in extensive contamination of water, land and air, endangering residents including the Coeur d'Alene Tribe, which had traditionally depended on fish from the waterways as part of its subsistence.
Rimini, is a ghost town in Lewis and Clark County, Montana, United States. It is one of the oldest mining districts in the state. It was established when silver lodes were discovered in 1864. Other names for the district were Lewis and Clark, Tenmile, Vaughn, Colorado, and Bear Gulch. It was the site of Camp Rimini.

Silver Bow Creek is a 26-mile-long (42 km) headwater stream of the Clark Fork (river) originating within the city limits of Butte, Montana, from the confluence of Little Basin and Blacktail Creeks. A former northern tributary, Yankee Doodle Creek, no longer flows directly into Silver Bow Creek as it is now captured by the Berkeley Pit. Silver Bow Creek flows northwest and north through a high mountain valley, passing east of Anaconda, Montana, where it becomes the Clark Fork at the confluence with Warm Springs Creek.

The California Gulch site consists of approximately 18 square miles in Lake County, Colorado. The area includes the city of Leadville, parts of the Leadville Historic Mining District and a section of the Arkansas River from the confluence of California Gulch downstream to the confluence of Two-Bit Gulch. The site was listed as a Superfund site in 1983.
According to a survey completed by the Colorado Geological Survey between 1991 and 1999, the number of abandoned mines in Colorado is 18,382. The Arkansas Headwaters, Las Animas River, Rio Grande Headwaters, Alamosa, and Uncompahgre were the priority watersheds studied in this survey. In the survey, analysis was completed with Environmental Degradation Measures ranging from none to extreme. Results showed 26 abandoned mines with extreme degradation and mineral hazards, 219 with significant degradation, and 672 potentially significant hazards.
The Dewey Loeffel Landfill is an EPA superfund site located in Rensselaer County, New York. In the 1950s and 1960s, several companies including General Electric, Bendix Corporation and Schenectady Chemicals used the site as a disposal facility for more than 46,000 tons of industrial hazardous wastes, including solvents, waste oils, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), scrap materials, sludges and solids. Some hazardous substances, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and PCBs, have migrated from the facility to underlying aquifers and downstream surface water bodies, resulting in contamination of groundwater, surface water, sediments and several species of fish. There is currently a ban on fish consumption in Nassau Lake and the impacted tributaries. Following prior assessments and attempts at mitigating drainage from the site, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has placed the site on its National Priority List. As of 2024, the EPA reports ongoing site investigations.
The Lava Cap Mine is an abandoned gold mine in Nevada County, California. The mine is located 5 miles (8.0 km) southeast of Nevada City. The site is undergoing cleanup by the United States Environmental Protection Agency for arsenic contamination.
















