
The Susitna River is a 313-mile (504 km) long river in the Southcentral Alaska. It is the 15th largest river in the United States, ranked by average discharge volume at its mouth. The river stretches from the Susitna Glacier to Cook Inlet's Knik Arm.

Eklutna is a native village within the Municipality of Anchorage in the U.S. state of Alaska. The Tribal Council estimates the population at 70; many tribal members live in the surrounding communities.

The Kenai Peninsula is a large peninsula jutting from the coast of Southcentral Alaska. The name Kenai is derived from the word "Kenaitze" or "Kenaitze Indian Tribe", the name of the Native Athabascan Alaskan tribe, the Kahtnuht’ana Dena’ina, that historically inhabited the area. They called the Kenai Peninsula Yaghanen.

Knik Arm is a waterway into the northwestern part of the Gulf of Alaska. It is one of two narrow branches of Cook Inlet, the other being Turnagain Arm. Knik Glacier empties into the Knik Arm. The Port of Anchorage is located on the arm.

The Chilkat River is a river in British Columbia and southeastern Alaska that flows southward from the Coast Range to the Chilkat Inlet and ultimately Lynn Canal. It is about 80 kilometres (50 mi) long. It begins at Chilkat Glacier, in Alaska, flows west and south in British Columbia for 27 kilometres (17 mi), enters Alaska and continues southwest for another 60 kilometres (37 mi). It reaches the ocean at the abandoned area of Wells, Alaska and deposits into a long delta area.

The Knik River is a 25-mile-long (40 km) river in the U.S. state of Alaska. Its source is at Knik Glacier, from which it flows northwest and west and empties into the head of Cook Inlet's Knik Arm, near the mouth of the Matanuska River. It is bridged twice where the Old Glenn Highway crosses it near the Butte, and also bridged on the Hayflats.

Mount Susitna is a 4,396-foot (1,340 m) mountain in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the west bank of the lower Susitna River, about 33 miles (53 km) northwest of Anchorage, Alaska. The mountain is a prominent landmark in the Anchorage area and can be seen across the Knik Arm of the Cook Inlet from most of the city, especially at higher elevations.

Ship Creek is an Alaskan river that flows from the Chugach Mountains into Cook Inlet. The Port of Anchorage at the mouth of Ship Creek gave its name to the city of Anchorage that grew up nearby. The river lies entirely within the limits of the Municipality of Anchorage, Alaska. Most of its upper length traverses Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson.

Anchorage is a unified home rule municipality in the U.S. state of Alaska. With an estimated 298,192 residents in 2016, it is Alaska's most populous city and contains more than 40 percent of the state's total population; among the 50 states, only New York has a higher percentage of residents who live in its most populous city. All together, the Anchorage metropolitan area, which combines Anchorage with the neighboring Matanuska-Susitna Borough, had a population of 401,635 in 2016, which accounts for more than half of the state's population. At 1,706 square miles of land area, the city is the fourth largest city by land in the United States and larger than the smallest state, Rhode Island, at 1,212 square miles.
Cape Ugat is a rocky point on the northwestern side of Kodiak Island, Alaska. It is the tip of the Spiridon Peninsula and protrudes into the Shelikof Strait. It is the closest point on Kodiak Island to mainland Alaska. In World War II Cape Ugat was occupied by US forces as a lookout station, the rationale being that it was the best vantage point to detect potential Japanese naval forces that could head up the Shelikof Strait towards the Cook Inlet and Anchorage, the logistical center of Alaska.
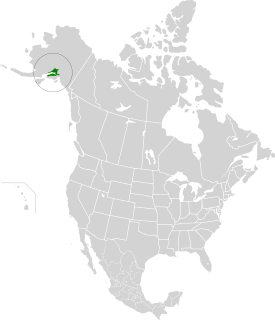
The Cook Inlet taiga ecoregion, in the Taiga and Boreal forests Biome, is located in Alaska.
Bradfield Canal is an inlet in Southeast Alaska, United States. It extends 30 kilometres (19 mi) west from the mouth of the Bradfield River to Ernest Sound at Point Warde. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791–95 expedition. Vancouver later named it "Bradfield Channel".

The Eagle River is a stream, 5 miles (8 km) long, in the borough of Juneau in the U.S. state of Alaska. Heading at Eagle Glacier in the Coast Mountains, it flows southwest into Favorite Channel, 20 miles (32 km) northeast of the city of Juneau. Alaska Route 7 links the city to the river, a state recreation area, a church camp, and a boy scout camp near the river mouth.

The Eagle River is a stream, 8 miles (13 km) long, in the borough of Wrangell in the U.S. state of Alaska. Heading at Eagle Lake in the Coast Mountains, it flows northwest through part of the Tongass National Forest into Eagle Bay on the Bradfield Canal. Near the midpoint of its course, the river passes through Little Eagle Lake. On the shore opposite Eagle Bay and the Eagle River mouth, the Harding River enters Bradfield Canal.

Campbell Creek is one of several streams that flow through the city of Anchorage, Alaska. It runs for 21 miles from the Chugach Mountains to the Turnagain Arm of Cook Inlet.
The Chulitna River is a 110 km long right tributary of the Susitna River in southern part of interior Alaska. Three forks converge to form the river, which itself flows into the Susitna River near Talkeetna.













