A constellation is a group of stars that forms an imaginary outline or pattern on the celestial sphere, typically representing an animal, mythological person or creature, a god, or an inanimate object.

Cambridge is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, and part of the Boston metropolitan area.

Cambridgeshire is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the west. The city of Cambridge is the county town. Modern Cambridgeshire was formed in 1974 as an amalgamation of the counties of Cambridgeshire and Isle of Ely and Huntingdon and Peterborough, the former covering the historic county of Cambridgeshire and the latter covering the historic county of Huntingdonshire and the Soke of Peterborough, historically part of Northamptonshire. It contains most of the region known as Silicon Fen.

Gorillas are ground-dwelling, predominantly herbivorous apes that inhabit the forests of central Sub-Saharan Africa. The genus Gorilla is divided into two species: the eastern gorillas and the western gorillas, and either four or five subspecies. They are the largest living primates. The DNA of gorillas is highly similar to that of humans, from 95 to 99% depending on what is included, and they are the next closest living relatives to humans after the chimpanzees and bonobos.

The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark, often shortened to Hamlet, is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1602. Set in Denmark, the play depicts Prince Hamlet and his revenge against his uncle, Claudius, who has murdered Hamlet's father in order to seize his throne and marry Hamlet's mother.

Macbeth is a tragedy by William Shakespeare; it is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those who seek power for its own sake. Of all the plays that Shakespeare wrote during the reign of James I, who was patron of Shakespeare's acting company, Macbeth most clearly reflects the playwright's relationship with his sovereign. It was first published in the Folio of 1623, possibly from a prompt book, and is Shakespeare's shortest tragedy.

William Shakespeare was an English poet, playwright and actor, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's greatest dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon". His extant works, including collaborations, consist of approximately 39 plays, 154 sonnets, two long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright.

Cambridge is a university city and the county town of Cambridgeshire, England, on the River Cam approximately 50 miles (80 km) north of London. At the United Kingdom Census 2011, its population was 123,867 including 24,506 students. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951.
Cambridge University Press (CUP) is the publishing business of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the world's oldest publishing house and the second-largest university press in the world. It also holds letters patent as the Queen's Printer.
The terms alien abduction or abduction phenomenon describe "subjectively real memories of being taken secretly unwillingly by apparently unhuman figures (aliens) and subjected to complex physical and psychological procedures". People claiming to have been abducted are usually called "abductees" or "experiencers". Typical claims involve being subjected to forced medical examinations that emphasize abductee reproductive systems. Abductees sometimes claim to have been warned against environmental abuse and the dangers of nuclear weapons.
The Cambridge Apostles is an intellectual society at the University of Cambridge founded in 1820 by George Tomlinson, a Cambridge student who went on to become the first Bishop of Gibraltar.

The Buyid dynasty or the Buyids, also known as Buwaihids, Bowayhids, Buyahids, or Buyyids, was a Shia Iranian dynasty of Daylamite origin. Coupled with the rise of other Iranian dynasties in the region, the approximate century of Buyid rule represents the period in Iranian history sometimes called the 'Iranian Intermezzo' since, after the Muslim conquest of Persia, it was an interlude between the rule of the Abbasid Caliphate and the Seljuk Empire.

English is a West Germanic language that was first spoken in early medieval England and eventually became a global lingua franca. It is named after the Angles, one of the Germanic tribes that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, as England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula in the Baltic Sea. The language is closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, and its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Norse, and to a greater extent by Latin and French.
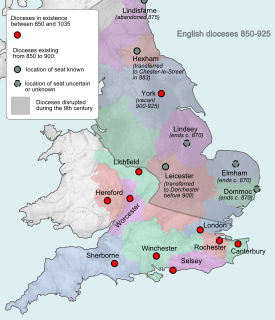
Aldberht was a medieval Bishop of Hereford.
Ealdbeorht was a medieval Bishop of Dunwich.
The Wolfson Brain Imaging Centre (WBIC) is a leading UK Biomedical Imaging Centre, located at Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, England, on the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus at the southwestern end of Hills Road. It is a division of the Department of Clinical Neurosciences of the University of Cambridge.

Ely is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, England, about 14 miles (23 km) north-northeast of Cambridge and about 80 miles (129 km) by road from London. Æthelthryth founded an abbey at Ely in 673; the abbey was destroyed in 870 by Danish invaders and was rebuilt by Æthelwold, Bishop of Winchester, in 970. Construction of the cathedral was started in 1083 by a Norman abbot, Simeon. Alan of Walsingham's octagon, built over Ely's nave crossing between 1322 and 1328, is the "greatest individual achievement of architectural genius at Ely Cathedral", according to architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner. Building continued until the dissolution of the abbey in 1539 during the Reformation. The cathedral was sympathetically restored between 1845 and 1870 by the architect George Gilbert Scott. As the seat of a diocese, Ely has long been considered a city; in 1974, city status was granted by royal charter.

The University of Cambridge is a collegiate public research university in Cambridge, United Kingdom. Founded in 1209 and granted a Royal Charter by King Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the second-oldest university in the English-speaking world and the world's fourth-oldest surviving university. The university grew out of an association of scholars who left the University of Oxford after a dispute with the townspeople. The two 'ancient universities' share many common features and are often referred to jointly as 'Oxbridge'. The history and influence of the University of Cambridge has made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world.