
Hemet is a city in the San Jacinto Valley in Riverside County, California. It covers a total area of 29.3 square miles (76 km2), about half of the valley, which it shares with the neighboring city of San Jacinto. The population was 89,833 at the 2020 census. It borders San Jacinto to the north, East Hemet to the east, Polly Butte and Diamond Valley Lake to the south, and Green Acres and Juniper Springs to the west.

Water reclamation is the process of converting municipal wastewater or sewage and industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a variety of purposes. It is also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling. There are many types of reuse. It is possible to reuse water in this way in cities or for irrigation in agriculture. Other types of reuse are environmental reuse, industrial reuse, and reuse for drinking water, whether planned or not. Reuse may include irrigation of gardens and agricultural fields or replenishing surface water and groundwater. This latter is also known as groundwater recharge. Reused water also serve various needs in residences such as toilet flushing, businesses, and industry. It is possible to treat wastewater to reach drinking water standards. Injecting reclaimed water into the water supply distribution system is known as direct potable reuse. Drinking reclaimed water is not typical. Reusing treated municipal wastewater for irrigation is a long-established practice. This is especially so in arid countries. Reusing wastewater as part of sustainable water management allows water to remain an alternative water source for human activities. This can reduce scarcity. It also eases pressures on groundwater and other natural water bodies.

Lake Hemet is a water storage reservoir located in the San Jacinto Mountains in Mountain Center, Riverside County, California, with a capacity of 14,000 acre-feet (17,000,000 m3) of water. It was created in 1895 with the construction of Lake Hemet Dam. Originally built by a private company, today it is owned and operated by the Lake Hemet Municipal Water District (LHMWD).

The Metropolitan Water District of Southern California is a regional wholesaler and the largest supplier of treated water in the United States. The name is usually shortened to "Met," "Metropolitan," or "MWD." It is a cooperative of fourteen cities, eleven municipal water districts, and one county water authority, that provides water to 19 million people in a 5,200-square-mile (13,000 km2) service area. It was created by an act of the California State Legislature in 1928, primarily to build and operate the Colorado River Aqueduct. Metropolitan became the first contractor to the State Water Project in 1960.

The Perris Union High School District is a school district serving Menifee and Perris, California. It is the only high school-only district in Riverside County.
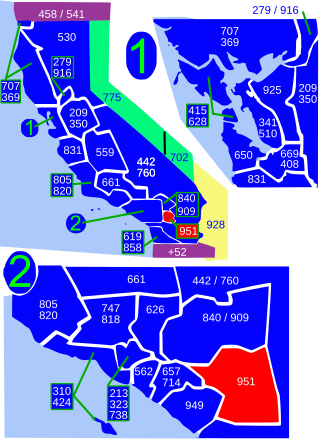
Area code 951 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan for western Riverside County in the southern part of the U.S. state of California. It was assigned in 2004 to a new numbering plan area that was created by an area code split of area code 909.

The San Jacinto River is a 42-mile-long (68 km) river in Riverside County, California. The river's headwaters are in Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument. The lower portion of the 765-square-mile (1,980 km2) watershed is urban and agricultural land. As a partially endorheic watershed that is contiguous with other Great Basin watersheds, the western side of the San Jacinto Basin is a portion of the Great Basin Divide.

Menifee is a city in Riverside County, California, United States, and is part of the Inland Empire. Named after a local miner, Luther Menifee Wilson, it was settled in the 19th century, and incorporated as a city in 2008. Since then, Menifee has become one of the fastest growing cities in California and the United States.
Water supply and sanitation in the United States involves a number of issues including water scarcity, pollution, a backlog of investment, concerns about the affordability of water for the poorest, and a rapidly retiring workforce. Increased variability and intensity of rainfall as a result of climate change is expected to produce both more severe droughts and flooding, with potentially serious consequences for water supply and for pollution from combined sewer overflows. Droughts are likely to particularly affect the 66 percent of Americans whose communities depend on surface water. As for drinking water quality, there are concerns about disinfection by-products, lead, perchlorates, PFAS and pharmaceutical substances, but generally drinking water quality in the U.S. is good.

The Riverside Transit Agency (RTA) is the main transit agency for western Riverside County, California, United States. RTA provides both local and regional services throughout the region with 32 fixed-routes ,3 CommuterLink routes, Micro Transit in the Hemet San Jacinto area, and Dial-A-Ride services using a fleet of 339 vehicles. In the cities of Corona, Beaumont and Banning, RTA coordinates regional services with municipal transit systems. In Riverside, RTA coordinates with the city's Riverside Special Services, which provides ADA complementary service to RTA's fixed-route services.
The Riverside County Office of Education (RCOE) serves as an intermediary between the California Department of Education and local school districts. It provides a wide range of educational and administrative services to the 23 school districts and more than 423,000 students in Riverside County.

The San Jacinto Valley is a valley located in Riverside County, in Southern California, in the Inland Empire. The valley is located at the base of the San Jacinto Mountains in the east and Santa Rosa Hills to the south with the San Gorgonio Pass to the north. The average elevation is 1,500 feet (460 m), with the highest points in the foothills south of Hemet and the western slopes of the San Jacinto Mountains. It is home to two cities, Hemet and San Jacinto, and several unincorporated communities. According to the 2020 census, the valley has a combined population of over 190,000 residents, including more than 143,000 residents within the city limits of Hemet and San Jacinto. The valley is also where the story and play "Ramona" was set; the story was written after author Helen Hunt Jackson visited the valley in the 1880s. The valley is also known for being an area of agriculture, which has given way to more urbanized development.
Mt. San Jacinto College (MSJC) is a public community college in Riverside County, California. It is part of the California Community College system and consists of four locations: San Jacinto, Menifee, Banning and Temecula. Classes are also held at numerous satellite locations such as local high schools and online.

Riverside County is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most populous county in California and the 10th-most populous in the United States. The name was derived from the city of Riverside, which is the county seat.
Irvine Ranch Water District (IRWD) is a California Special District formed in 1961 and incorporated under the California water code. The IRWD headquarters is located in Irvine, California.
The Coachella Valley Water District is an independent special district formed in 1918, specifically to protect and conserve local water sources in the Coachella Valley. Since then, the district has grown into a multi-faceted agency that delivers irrigation and domestic (drinking) water, collects and recycles wastewater, provides regional storm water protection, replenishes the groundwater basin and promotes water conservation.
The Perris Block is the central block of three major fault-bounded blocks of the northern part of the Peninsular Ranges. The Perris Block lies between the Santa Ana Block to the west and the San Jacinto Block to the east. The Perris Block, was named by Walter A. English in 1925 for the city of Perris, located near the center of the block.
Temecula Basin is a sedimentary basin, which, along with the Aguanga Basin, is part of the Elsinore Fault Zone, in southwestern Riverside County, California. The Temecula Basin is a basin of down faulted Mesozoic basement rock, overlain by late Cenozoic continental sediments.

Water reuse in California is the use of reclaimed water for beneficial use. As a heavily populated state in the drought-prone arid west, water reuse is developing as an integral part of water in California enabling both the economy and population to grow.
The San Jacinto tunnel is considered the key link in Colorado River Aqueduct system. The 13 mi (21 km) long, 16 ft diameter tunnel runs beneath the San Jacinto Mountains between Cabazon, California and Gilman Hot Springs in Riverside County, California.












