Related Research Articles

A hydraulic ram, or hydram, is a cyclic water pump powered by hydropower. It takes in water at one "hydraulic head" (pressure) and flow rate, and outputs water at a higher hydraulic head and lower flow rate. The device uses the water hammer effect to develop pressure that allows a portion of the input water that powers the pump to be lifted to a point higher than where the water originally started. The hydraulic ram is sometimes used in remote areas, where there is both a source of low-head hydropower and a need for pumping water to a destination higher in elevation than the source. In this situation, the ram is often useful, since it requires no outside source of power other than the kinetic energy of flowing water.

A pump is a device that moves fluids, or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy.

A sanitary sewer is an underground pipe or tunnel system for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings to a sewage treatment plant or disposal. Sanitary sewers are a type of gravity sewer and are part of an overall system called a "sewage system" or sewerage. Sanitary sewers serving industrial areas may also carry industrial wastewater. In municipalities served by sanitary sewers, separate storm drains may convey surface runoff directly to surface waters. An advantage of sanitary sewer systems is that they avoid combined sewer overflows. Sanitary sewers are typically much smaller in diameter than combined sewers which also transport urban runoff. Backups of raw sewage can occur if excessive stormwater inflow or groundwater infiltration occurs due to leaking joints, defective pipes etc. in aging infrastructure.
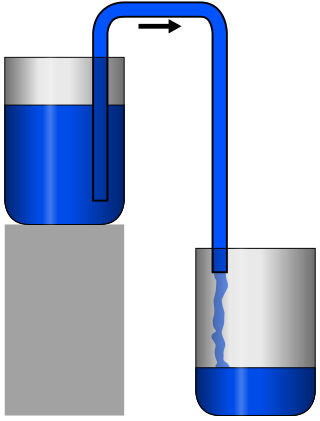
A siphon is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir from which it came.

In modern plumbing, a drain-waste-vent is a system that allows air to enter the plumbing system to maintain proper air pressure to enable the removal of sewage and greywater from a dwelling. Drain refers to water produced at fixtures such as sinks, and showers; waste refers to water from toilets. As the water runs down, proper venting is required to allow water to flow freely, and avoid a vacuum from being created. As the water runs down air must be allowed into the waste pipe either through a roof vent (external), or an internal vent.
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.

An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of:

Hydronics is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution as heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and refrigerant systems.

An airlift is device based on a pipe, used in nautical archaeology to suck small objects, sand and mud from the sea bed and to transport the resulting debris upwards and away from its source. It is sometimes called a suction dredge. A water dredge or water eductor may be used for the same purpose.

Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from which it exits.

Thermosiphon is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney.

An airlift pump is a pump that has low suction and moderate discharge of liquid and entrained solids. The pump injects compressed air at the bottom of the discharge pipe which is immersed in the liquid. The compressed air mixes with the liquid causing the air-water mixture to be less dense than the rest of the liquid around it and therefore is displaced upwards through the discharge pipe by the surrounding liquid of higher density. Solids may be entrained in the flow and if small enough to fit through the pipe, will be discharged with the rest of the flow at a shallower depth or above the surface. Airlift pumps are widely used in aquaculture to pump, circulate and aerate water in closed, recirculating systems and ponds. Other applications include dredging, underwater archaeology, salvage operations and collection of scientific specimens.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect straight sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of water, gas, or liquid waste in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes.

Flexible suction hose, not to be confused with hard suction hose in U.S., is a specific type of fire hose used in drafting operations, when a fire engine uses a vacuum to draw water from a portable water tank, pool, or other static water source. It is built to withstand vacuum, rather than pressure, abrasion, and heat. Conversely, hard suction is capable of withstanding up to 200 PSIG, as well as vacuum. In the United States, it is standard equipment according to the National Fire Protection Association standards for fire engines. It is used in both structural and wildland firefighting throughout the world, and is made in various diameters and connection types.

A central vacuum cleaner is a type of vacuum cleaner appliance, installed into a building as a semi-permanent fixture. Central vacuum systems are designed to remove dirt and debris from homes and buildings, sending dirt particles through piping installed inside the walls to a collection container in a remote utility space. The power unit is a permanent fixture, usually installed in a basement, garage, or storage room, along with the collection container. Inlets are installed in walls throughout the building that attach to power hoses and other central vacuum accessories to remove dust, particles, and small debris from interior rooms. Most power hoses usually have a power switch located on the handle.

A pulser pump is a gas lift device that uses gravity to pump water to a higher elevation. It has no moving parts.
High-density solids pumps are hydrostatically operating machines which displace the medium being pumped and thus create a flow.
The Glossary of Geothermal Heating and Cooling provides definitions of many terms used within the Geothermal heat pump industry. The terms in this glossary may be used by industry professionals, for education materials, and by the general public.

A concentric reducer is used to join pipe sections or tube sections on the same axis. The concentric reducer is cone-shaped, and is used when there is a shift in diameter between pipes. For example, when a 1" pipe transitions into a 3/4" pipe and the top or bottom of the pipe doesn't need to remain level. This pipe reducer may be used when there is a single diameter change or multiple diameter changes.
References
- 1 2 Mahaffey, Ross; van Vuuren, Stefanus Johannes (28 August 2014). "Reducer Fittings Decrease Pipe Size to Avoid Failure (First of Two Parts)". Pumps & Systems. Retrieved 19 June 2021.
- ↑ Mahaffey, R; van Vuuren, S J (October 2014). "Review of pump suction reducer selection: Eccentric or concentric reducers" (PDF). Journal of the South African Institution of Civil Engineering. 56 (3): 65–76. Retrieved 20 June 2021.
- ↑ Parisher, Roy A.; Rhea, Robert A. (2012). "3 – Pipe Fittings". Pipe Drafting and Design (Third ed.). Elsevier. pp. 13–55. Archived from the original on 19 June 2021. Retrieved 19 June 2021.
- Bloch, Heinz P. (September 2010). "HP Reliability: Eccentric reducers and straight runs of pipe at pump suction" . Hydrocarbon Processing. Retrieved 19 June 2021.