Related Research Articles
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphics represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of square pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.

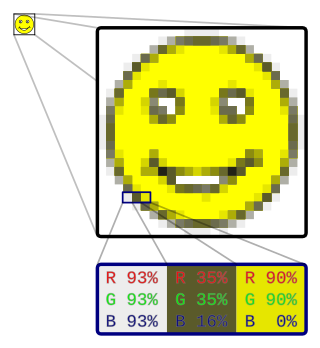
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue.

The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation CMYK refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black).
In digital imaging systems, color management is the controlled conversion between the color representations of various devices, such as image scanners, digital cameras, monitors, TV screens, film printers, computer printers, offset presses, and corresponding media.
Web colors are colors used in displaying web pages on the World Wide Web ; they can be described by way of three methods: a color may be specified as an RGB triplet, in hexadecimal format or according to its common English name in some cases. A color tool or other graphics software is often used to generate color values. In some uses, hexadecimal color codes are specified with notation using a leading number sign (#). A color is specified according to the intensity of its red, green and blue components, each represented by eight bits. Thus, there are 24 bits used to specify a web color within the sRGB gamut, and 16,777,216 colors that may be so specified.
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an amount of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest.
The rg chromaticity space, two dimensions of the normalized RGB, or rgb, space, is a chromaticity space, a two-dimensional color space in which there is no intensity information.

sRGB is a standard RGB color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile.
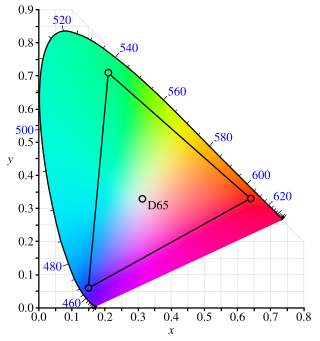
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 50% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.

In photography and image processing, color balance is the global adjustment of the intensities of the colors. An important goal of this adjustment is to render specific colors – particularly neutral colors like white or grey – correctly. Hence, the general method is sometimes called gray balance, neutral balance, or white balance. Color balance changes the overall mixture of colors in an image and is used for color correction. Generalized versions of color balance are used to correct colors other than neutrals or to deliberately change them for effect. White balance is one of the most common kinds of balancing, and is when colors are adjusted to make a white object appear white and not a shade of any other colour.

The ProPhoto RGB color space, also known as ROMM RGB, is an output referred RGB color space developed by Kodak. It offers an especially large gamut designed for use with photographic output in mind. The ProPhoto RGB color space encompasses over 90% of possible surface colors in the CIE L*a*b* color space, and 100% of likely occurring real-world surface colors documented by Michael Pointer in 1980, making ProPhoto even larger than the Wide-gamut RGB color space. The ProPhoto RGB primaries were also chosen in order to minimize hue rotations associated with non-linear tone scale operations. One of the downsides to this color space is that approximately 13% of the representable colors are imaginary colors that do not exist and are not visible colors.
The aim of color calibration is to measure and/or adjust the color response of a device to a known state. In International Color Consortium (ICC) terms, this is the basis for an additional color characterization of the device and later profiling. In non-ICC workflows, calibration refers sometimes to establishing a known relationship to a standard color space in one go. The device that is to be calibrated is sometimes known as a calibration source; the color space that serves as a standard is sometimes known as a calibration target. Color calibration is a requirement for all devices taking an active part of a color-managed workflow, and is used by many industries, such as television production, gaming, photography, engineering, chemistry, medicine and more.
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the device source or target color space and a profile connection space (PCS). This PCS is either CIELAB (L*a*b*) or CIEXYZ. Mappings may be specified using tables, to which interpolation is applied, or through a series of parameters for transformations.

A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of color – whether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names, or structured with mathematical rigor. A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised.

DCI-P3 is an RGB color space first defined in 2005 as part of the Digital Cinema Initiative, to be used for digital theatrical motion picture distribution (DCDM). Display P3 is a variant developed by Apple Inc. for wide-gamut displays.
Media Standard Print is a publication of the Bundesverband Druck und Medien, available on its website. The publication contains instructions on how to produce data and proofs that are to be sent to a printer. It is based on ProcessStandard Offset and therefore on the ISO standards 12647 and 15930. As such, it serves as the foundation for smooth cooperation between customer, prepress service provider and printer during media production, covering data formats, colour spaces, printing conditions, workflows, means of proofing, standards, black composition and much more.
The European Color Initiative (ECI) is an expert group that is concerned with media-neutral reproduction of color data in digital publication systems. It was formed in June 1996 by German publishers Bauer, Burda, Gruner + Jahr and Springer in Hamburg.
References
- ↑ "eciRGB_v2 - the update of eciRGB 1.0 - Background information". European Color Initiative.
- ↑ Homann, Jan-Peter (25 Sep 2008). Digital Color Management: Principles and Strategies for the Standardized Print Production. Germany: Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 123–129. ISBN 978-3-540-67119-0.
- ↑ "Downloads". European Color Initiative.