Beechcraft is an American brand of civil aviation and military aircraft owned by Textron Aviation since 2014, headquartered in Wichita, Kansas. Originally, it was a brand of Beech Aircraft Corporation, an American manufacturer of general aviation, commercial, and military aircraft, ranging from light single-engined aircraft to twin-engined turboprop transports, business jets, and military trainers. Beech later became a division of Raytheon and then Hawker Beechcraft before a bankruptcy sale turned its assets over to Textron. It remains a brand of Textron Aviation.

Cessna is an American brand of general aviation aircraft owned by Textron Aviation since 2014, headquartered in Wichita, Kansas. Originally, it was a brand of the Cessna Aircraft Company, an American general aviation aircraft manufacturing corporation also headquartered in Wichita. The company produced small, piston-powered aircraft, as well as business jets. For much of the mid-to-late 20th century, Cessna was one of the highest-volume and most diverse producers of general aviation aircraft in the world. It was founded in 1927 by Clyde Cessna and Victor Roos and was purchased by General Dynamics in 1985, then by Textron, Inc. in 1992. In March 2014, when Textron purchased the Beechcraft and Hawker Aircraft corporations, Cessna ceased operations as a subsidiary company, and joined the others as one of the three distinct brands produced by Textron Aviation.

A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of taking off and landing (alighting) on water. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their technological characteristics: floatplanes and flying boats; the latter are generally far larger and can carry far more. Seaplanes that can also take off and land on airfields are in a subclass called amphibious aircraft, or amphibians. Seaplanes were sometimes called hydroplanes, but currently this term applies instead to motor-powered watercraft that use the technique of hydrodynamic lift to skim the surface of water when running at speed.
The United Aircraft and Transport Corporation was formed in 1929, when William Boeing of Boeing Airplane & Transport Corporation teamed up with Frederick Rentschler of Pratt & Whitney to form a large, vertically integrated, amalgamated firm, uniting business interests in all aspects of aviation—a combination of airframe and aircraft engine manufacturing and airline business, to serve all aviation markets, both civil aviation and military aviation.

The de Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter is a single-engined, high-wing, propeller-driven, short take-off and landing (STOL) aircraft developed by de Havilland Canada. It was conceived to be capable of performing the same roles as the earlier and highly successful Beaver, including as a bush plane, but is overall a larger aircraft.
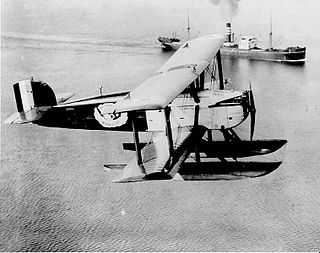
The Douglas World Cruiser (DWC) was developed to meet a requirement from the United States Army Air Service for an aircraft suitable for an attempt at the first flight around the world. The Douglas Aircraft Company responded with a modified variant of their DT torpedo bomber, the DWC.

The Blackburn B-20 was an experimental aircraft, first flying in 1940, that attempted to drastically increase the performance of flying boat designs. Blackburn Aircraft undertook an independent design study based on a patent filed by their chief designer, John Douglas Rennie for a retractable pontoon float that formed the planing hull.
Monocoupe Aircraft was a manufacturer of light airplanes originally produced in the late 1920s and 30s. They introduced relatively inexpensive, compact, and sporty aircraft in an era of large, maintenance intensive, open-cockpit biplanes, and the Monocoupe series was one of the first economical, closed-cabin, two-seat, light aircraft in the United States. As a result, the Monocoupe soon became a successful brand.

The Edo OSE was a 1940s American single-seat multi-role floatplane designed and manufactured by the Edo Aircraft Corporation.

The Keystone K-55 Pronto was a mail plane developed in the United States in the late 1920s.
Taquan Air is the operating name for Venture Travel, LLC, an American regional airline headquartered in Ketchikan, a city in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska. It operates domestic scheduled passenger and charter services. Its base is Ketchikan Harbor Seaplane Base, which shares the same harbor and airspace as Ketchikan International Airport. As per the United States Department of Transportation in a report dated August 2, 2010, Taquan Air is a "U.S. Certificated Air Carrier", and is 1 of 125 such carriers in the US.

The Swallow Airplane Company was an early manufacturer of airplanes.

The Verville Sport Trainer AT was a two-seat tandem biplane designed by Alfred V. Verville as a civilian version of the YPT-10 primary trainer, intended to appeal to the wealthy private owner.

The Waco Standard Cabin series is a range of American single-engine 4–5 seat fabric covered cabin biplanes produced by the Waco Aircraft Company beginning in 1931 with the QDC and continuing until 1942 when production ended for the VKS-7F. They were used as light passenger and utility transports, navigational trainers, bushplanes and briefly as maritime reconnaissance aircraft during World War 2.

The Waco 9 is an American-built three-seat biplane design that first flew in 1925.

The Vought XSO2U was an American observation floatplane developed by Vought-Sikorsky for the United States Navy during the late 1930s. Intended to replace the Curtiss SOC Seagull in service as a scout aboard cruisers, it proved superior to the Curtiss SO3C in evaluation, but failed to win a production contract due to Vought's lack of manufacturing capacity.

The Curtiss Model 41 Lark was a commercial biplane manufactured by Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company that was used by pioneering airmail, airline and bush pilots in the 1920s.
Wipaire is a third-generation family-owned American aircraft manufacturing and repair company, best known for its aircraft floats.
Dwane Leon Wallace was an American aviation businessman and aircraft designer. He served as the president and/or chairman of the board of the Cessna Aircraft Company from 1935 until the 1970s, continuing then on the board as a director and consultant into the 1980s. Later known as the "Quiet Giant of Aviation", Wallace oversaw the company during a period of rapid and expansive growth within the general aviation industry, including development of the most-produced aircraft in history, the Cessna 172, as well as the popular Cessna Citation I business jet. He was posthumously inducted into the National Aviation Hall of Fame in 2012, and was included in Flying Magazine's list of the "51 Heroes of Aviation" in 2013, placing at number 11.

Aircraft Radio Corporation (ARC) – not to be confused with Aeronautical Radio, Inc. (ARINC) – was a principal pioneer and major manufacturer of avionics for military and commercial aircraft, and later general aviation (light) aircraft, from the 1920s to the 1950s—subsequently acquired and rebranded by a succession of other companies, each of whom changed the official name, of the enterprise, while initially continuing ARC's primary function, staffing, facilities and product focus.

















